PowerPoint Presentation - Physics 121. Lecture 16.
... • Look at the end of chapter problems. There is only a limited number of types of question one can ask. • But ……. Since the questions are grouped by section, you know already what approach to use based on the section to which the problems are assigned. • Some students benefit from copying the questi ...
... • Look at the end of chapter problems. There is only a limited number of types of question one can ask. • But ……. Since the questions are grouped by section, you know already what approach to use based on the section to which the problems are assigned. • Some students benefit from copying the questi ...
9.hamilton11e_ppt_11
... – gain speed towards the ground. – at height of release object will have the same velocity it was given at release. © 2008 McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All Rights Reserved. ...
... – gain speed towards the ground. – at height of release object will have the same velocity it was given at release. © 2008 McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All Rights Reserved. ...
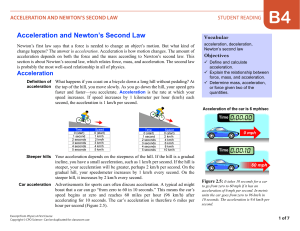
determination of the acceleration of an elevator.
... DETERMINATION OF THE ACCELERATION OF AN ELEVATOR. INTRODUCTION: In order for an object to accelerate, there must be a net force acting on it. We know that the direction of the acceleration will be in the same direction as the direction of the net force. The equation for Newton’s 2nd law is F = ma o ...
... DETERMINATION OF THE ACCELERATION OF AN ELEVATOR. INTRODUCTION: In order for an object to accelerate, there must be a net force acting on it. We know that the direction of the acceleration will be in the same direction as the direction of the net force. The equation for Newton’s 2nd law is F = ma o ...
Chapter 7
... A roller coaster goes upside down performing a circular loop of radius 15 m. What speed does the roller coaster need at the top of the loop so that it does not need to be held onto the track? ...
... A roller coaster goes upside down performing a circular loop of radius 15 m. What speed does the roller coaster need at the top of the loop so that it does not need to be held onto the track? ...
Ch. 6 Newton`s Second law of Motion Force and Acceleration
... Both liquids and gases are called fluids because they flow. • Fluid friction occurs as an object pushes aside the fluid it is moving through. • The friction of liquids is appreciable, even at low speeds. • Air resistance is the friction acting on something moving through air. ...
... Both liquids and gases are called fluids because they flow. • Fluid friction occurs as an object pushes aside the fluid it is moving through. • The friction of liquids is appreciable, even at low speeds. • Air resistance is the friction acting on something moving through air. ...
6 Newton`s Second Law of Motion–Force and Acceleration
... Both liquids and gases are called fluids because they flow. • Fluid friction occurs as an object pushes aside the fluid it is moving through. • The friction of liquids is appreciable, even at low speeds. • Air resistance is the friction acting on something moving through air. ...
... Both liquids and gases are called fluids because they flow. • Fluid friction occurs as an object pushes aside the fluid it is moving through. • The friction of liquids is appreciable, even at low speeds. • Air resistance is the friction acting on something moving through air. ...
Chap04-2014
... Galileo did many experiments, and he concluded that in the ideal case of zero resistance, horizontal motion would never stop. Galileo was the first to recognize that the general principles of motion could be found by extrapolating experimental results to the ideal case, in which there is no resistan ...
... Galileo did many experiments, and he concluded that in the ideal case of zero resistance, horizontal motion would never stop. Galileo was the first to recognize that the general principles of motion could be found by extrapolating experimental results to the ideal case, in which there is no resistan ...
5 th - Soran University
... plays an important role in changing the form of the body and thus moment of inertia him during the movement circular .oatanm player that exploits the ability to change the moment of inertia in many athletic movements during rotation, so that it can increase the speed of rotation or decreased it . An ...
... plays an important role in changing the form of the body and thus moment of inertia him during the movement circular .oatanm player that exploits the ability to change the moment of inertia in many athletic movements during rotation, so that it can increase the speed of rotation or decreased it . An ...
Lecture 2d - Momentum, Impulse & Collisions
... suspended like a pendulum. As a result of the collision, the pendulum and projectile together swing up to a maximum height h. Determine the relationship between the initial horizontal speed of the projectile, v, and the 26 maximum height h. ...
... suspended like a pendulum. As a result of the collision, the pendulum and projectile together swing up to a maximum height h. Determine the relationship between the initial horizontal speed of the projectile, v, and the 26 maximum height h. ...
Physical Science Bell Ringers
... make work easier in two ways, one way is by changing the direction of the applied force, what is the other way? ...
... make work easier in two ways, one way is by changing the direction of the applied force, what is the other way? ...