Slide 1
... Small-diameter structures would have to rotate at high speeds to provide a simulated gravitational acceleration of 1 g. Sensitive and delicate organs in our inner ears sense rotation. Although there appears to be no difficulty at 1 RPM, many people have difficulty adjusting to rotational rates great ...
... Small-diameter structures would have to rotate at high speeds to provide a simulated gravitational acceleration of 1 g. Sensitive and delicate organs in our inner ears sense rotation. Although there appears to be no difficulty at 1 RPM, many people have difficulty adjusting to rotational rates great ...
eBook AQA GCSE Physics Unit P2 Part 1
... acceleration in more detail later, but you can think of acceleration as a change in speed or a change in direction. If you double the resultant force acting on an object, its acceleration will double (as long as you keep the mass of the object the same). Applying a resultant force of 12 N might make ...
... acceleration in more detail later, but you can think of acceleration as a change in speed or a change in direction. If you double the resultant force acting on an object, its acceleration will double (as long as you keep the mass of the object the same). Applying a resultant force of 12 N might make ...
Document
... a tree, and bets that Tarzan can’t hit him. Tarzan aims at George, and is sorry that he didn’t pay more attention in physics class. Why ? (neglect air resistance) A) The stone will go over the gorilla’s head B) The stone will go below the gorilla C) The earth’s rotation must be taken into account ...
... a tree, and bets that Tarzan can’t hit him. Tarzan aims at George, and is sorry that he didn’t pay more attention in physics class. Why ? (neglect air resistance) A) The stone will go over the gorilla’s head B) The stone will go below the gorilla C) The earth’s rotation must be taken into account ...
Work and Energy
... where h is the distance the mass was raised. Record your values in the data table. Does the work done on the mass correspond to the change in gravitational potential energy? Should it? 2. In Part II you did work to stretch the spring. The graph of force vs. distance depends on the particular spring ...
... where h is the distance the mass was raised. Record your values in the data table. Does the work done on the mass correspond to the change in gravitational potential energy? Should it? 2. In Part II you did work to stretch the spring. The graph of force vs. distance depends on the particular spring ...
Final Momentum NRG Review
... this gravitational force that allows the ball to be lowered rather than accelerate to earth. Since there is no acceleration, the net force =0. Therefore, the force exerted by the girl is equal but opposite to the force of gravity and in the opposite direction to motion. Since the force and motion ar ...
... this gravitational force that allows the ball to be lowered rather than accelerate to earth. Since there is no acceleration, the net force =0. Therefore, the force exerted by the girl is equal but opposite to the force of gravity and in the opposite direction to motion. Since the force and motion ar ...
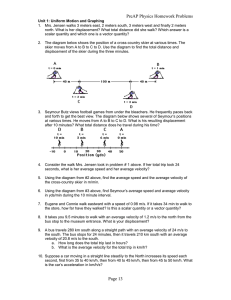
SPH4U Sample Test – Dynamics 1of14
... 17. Newton’s third law talks about forces always acting in pairs with the two forces of any pair being equal in strength and opposite in direction. Does this imply a “balanced” force situation and, if so, how is it possible to ever accelerate anything? 18. Describe how “artificial” gravity can be pr ...
... 17. Newton’s third law talks about forces always acting in pairs with the two forces of any pair being equal in strength and opposite in direction. Does this imply a “balanced” force situation and, if so, how is it possible to ever accelerate anything? 18. Describe how “artificial” gravity can be pr ...
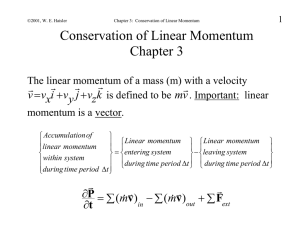
Chapter 3
... also be equal and opposite. The normal on FB 1also points in the opposite direction to FB 2. The traction on the surface with unit normal n is denoted as t(-n ) and we have that t(-n ) t(n ) Now lets consider a differential volume system in the fluid (or solid). Just as for the pipe example, t ...
... also be equal and opposite. The normal on FB 1also points in the opposite direction to FB 2. The traction on the surface with unit normal n is denoted as t(-n ) and we have that t(-n ) t(n ) Now lets consider a differential volume system in the fluid (or solid). Just as for the pipe example, t ...
Powerpoint
... You like to drive home fast, slam on your brakes at the start of the driveway, and screech to a stop “laying rubber” all the way. It’s particularly fun when your mother is in the car with you. You practice this trick driving at 20 mph and with some groceries in your car with the same mass as your mo ...
... You like to drive home fast, slam on your brakes at the start of the driveway, and screech to a stop “laying rubber” all the way. It’s particularly fun when your mother is in the car with you. You practice this trick driving at 20 mph and with some groceries in your car with the same mass as your mo ...
Ch_5
... with a 2 kg, 3 kg and 4 kg block. The acceleration is inversely proportional to the mass. © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... with a 2 kg, 3 kg and 4 kg block. The acceleration is inversely proportional to the mass. © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
Solutions #5
... wall of the tube, so that there can be a centripetal force to move the objects in a circle. See the free-body diagram for an object on the inside of the outer wall, and a portion of the tube. The normal force of contact between the object and the wall must be maintaining the circular motion. Write N ...
... wall of the tube, so that there can be a centripetal force to move the objects in a circle. See the free-body diagram for an object on the inside of the outer wall, and a portion of the tube. The normal force of contact between the object and the wall must be maintaining the circular motion. Write N ...
Stacey Carpenter
... (Keep in mind that we will learn more about the concepts of velocity, acceleration, and force later on)! Examples of NON-vectors are: distance, time, speed Vectors can be added together to get a resultant (sum) vector. For example, if two people push in the same direction on a stalled car, their f ...
... (Keep in mind that we will learn more about the concepts of velocity, acceleration, and force later on)! Examples of NON-vectors are: distance, time, speed Vectors can be added together to get a resultant (sum) vector. For example, if two people push in the same direction on a stalled car, their f ...