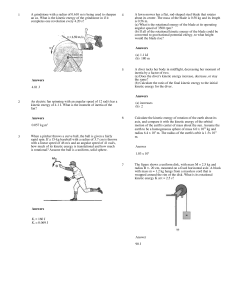
FP-1st Sem Final Review-11
... position vs time graph look like? What is the significance of the slope of this graph? What is the equation for the graph for this experiment? Could you make a velocity time graph using the data from the position vs. time graph? Uniform motion of a glider on a level air track (video analysis)-What d ...
... position vs time graph look like? What is the significance of the slope of this graph? What is the equation for the graph for this experiment? Could you make a velocity time graph using the data from the position vs. time graph? Uniform motion of a glider on a level air track (video analysis)-What d ...
Chapter 7 (Universal Gravitation)
... acts directly between Earth and the Moon. How does Einstein’s view of the attractive force between the two bodies differ from Newton’s view? (7.2) Einstein’s view is that gravity is an effect of the curvature of space as a result of the presence of mass, whereas Newton’s view of gravity is that it i ...
... acts directly between Earth and the Moon. How does Einstein’s view of the attractive force between the two bodies differ from Newton’s view? (7.2) Einstein’s view is that gravity is an effect of the curvature of space as a result of the presence of mass, whereas Newton’s view of gravity is that it i ...
I L - IBPhysicsLund
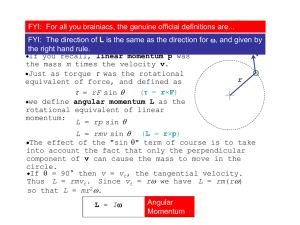
... ext t From Newton's 3rd, for every force there is an equal and opposite reaction. Thus all the internal forces sum to zero: In an analogous way, all the internal torques also sum to zero: ...Thus L = ext t Then if all of the external torques sum to zero, we have L = 0 t which implies that ...
... ext t From Newton's 3rd, for every force there is an equal and opposite reaction. Thus all the internal forces sum to zero: In an analogous way, all the internal torques also sum to zero: ...Thus L = ext t Then if all of the external torques sum to zero, we have L = 0 t which implies that ...
Chap.4 Conceptual Modules Fishbane
... After the cart is released, there is no longer a force in the x-direction. This does not mean that the cart stops moving!! It simply means that the cart will continue moving with the same velocity it had at the moment of release. The initial push got the cart moving, but that force is not needed to ...
... After the cart is released, there is no longer a force in the x-direction. This does not mean that the cart stops moving!! It simply means that the cart will continue moving with the same velocity it had at the moment of release. The initial push got the cart moving, but that force is not needed to ...
Ch. 7 PP - Lemon Bay High School
... • Orbiting objects are in free fall. • To see how this idea is true, we can use a thought experiment that Newton developed. Consider a cannon sitting on a high mountaintop. Each successive cannonball has a greater initial speed, so the horizontal distance that the ball travels increases. If the init ...
... • Orbiting objects are in free fall. • To see how this idea is true, we can use a thought experiment that Newton developed. Consider a cannon sitting on a high mountaintop. Each successive cannonball has a greater initial speed, so the horizontal distance that the ball travels increases. If the init ...
Chapter 10
... coordinate system rotating with the ball; e.g., the earth. Now, the ball appears stationary (if it is rotating at the same rate as the earth, but the centripetal force is still acting on the ball, namely the pull of the string. In order to apply Newton’s second law to describe the motion relative to ...
... coordinate system rotating with the ball; e.g., the earth. Now, the ball appears stationary (if it is rotating at the same rate as the earth, but the centripetal force is still acting on the ball, namely the pull of the string. In order to apply Newton’s second law to describe the motion relative to ...
PHYS101
... velocity is zero, but the acceleration is negative because there is a net downward force. 2. The mass is now moving downward, so the velocity is negative. As the mass nears equilibrium, the restoring force— and thus the magnitude of the acceleration—decreases. 3. At this time the mass is moving ...
... velocity is zero, but the acceleration is negative because there is a net downward force. 2. The mass is now moving downward, so the velocity is negative. As the mass nears equilibrium, the restoring force— and thus the magnitude of the acceleration—decreases. 3. At this time the mass is moving ...
Conservation of Linear Momentum
... Linear Momentum and Newton's Laws of Motion The concept of conservation of linear momentum applied to a rigid body, together with the realization that forces exchange momentum between the surroundings and the body, is actually a statement of Newton's three laws of motion. Newton's first law of mot ...
... Linear Momentum and Newton's Laws of Motion The concept of conservation of linear momentum applied to a rigid body, together with the realization that forces exchange momentum between the surroundings and the body, is actually a statement of Newton's three laws of motion. Newton's first law of mot ...
Problem set 11
... constant k = 4 and external force FE = 10 cos (3t). Determine the position of the mass at any time. 4. A body of mass 4 kg will stretch a spring 80 centimeters. This same body is attached to such a spring with an accompanying dashpot. Suppose the damping constant is 49 N. At t = 0, the mass is given ...
... constant k = 4 and external force FE = 10 cos (3t). Determine the position of the mass at any time. 4. A body of mass 4 kg will stretch a spring 80 centimeters. This same body is attached to such a spring with an accompanying dashpot. Suppose the damping constant is 49 N. At t = 0, the mass is given ...