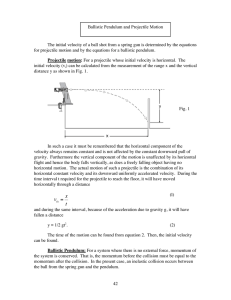
Fundamental of Physics
... so that Eq. 7-7 leads to W F x 5.8 104 J. The fact that this agrees with the result of part (c) provides insight into the concept of work. 14. The forces are all constant, so the total work done by them is given by W Fnet x , where Fnet is the magnitude of the net force and x is the ma ...
... so that Eq. 7-7 leads to W F x 5.8 104 J. The fact that this agrees with the result of part (c) provides insight into the concept of work. 14. The forces are all constant, so the total work done by them is given by W Fnet x , where Fnet is the magnitude of the net force and x is the ma ...
The Science Behind Safe Driving:
... On this screen, the skateboard is replaced by the car and the cake is replaced by the driver. When the car hits the fire hydrant and comes to an immediate stop, the unrestrained driver continue ...
... On this screen, the skateboard is replaced by the car and the cake is replaced by the driver. When the car hits the fire hydrant and comes to an immediate stop, the unrestrained driver continue ...
Powerpoint
... A. If you park on a hill with a 10 degree slope with the car held by the parking brake, what is the magnitude of the frictional force that holds your car in place? B. The coefficient of static friction between your car's wheels and the road when wet is 0.30. What is the largest angle slope on which ...
... A. If you park on a hill with a 10 degree slope with the car held by the parking brake, what is the magnitude of the frictional force that holds your car in place? B. The coefficient of static friction between your car's wheels and the road when wet is 0.30. What is the largest angle slope on which ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Physics 121. Lecture 21.
... • The interesting solutions are solutions where A ≠ 0 and ≠ 0. In this case, our general solution can only satisfy the equation of motion if ...
... • The interesting solutions are solutions where A ≠ 0 and ≠ 0. In this case, our general solution can only satisfy the equation of motion if ...
How is friction useful?
... object across a floor at constant velocity? Assume the coefficient of kinetic friction is ...
... object across a floor at constant velocity? Assume the coefficient of kinetic friction is ...
2-d motion - U of M Physics
... The problems in this laboratory will help you investigate objects moving in uniform circular motion. This is the same motion that describes satellites in orbit around the earth, or objects whirled around on a rope. Circular motion can be explained with the same concepts as those used in explaining p ...
... The problems in this laboratory will help you investigate objects moving in uniform circular motion. This is the same motion that describes satellites in orbit around the earth, or objects whirled around on a rope. Circular motion can be explained with the same concepts as those used in explaining p ...
Homework 4 solutions
... will fracture when the compressive stress on it exceeds about σb = 1.60 · 108 N/m . If you land on both legs, the maximum force Fmax that your ankles can safely exert on the rest of your body is then about Fmax = 2Fb = 2σb A = 5.12 · 104 N ...
... will fracture when the compressive stress on it exceeds about σb = 1.60 · 108 N/m . If you land on both legs, the maximum force Fmax that your ankles can safely exert on the rest of your body is then about Fmax = 2Fb = 2σb A = 5.12 · 104 N ...
pdf file
... and modelling of other phenomena in Nature. Within Cognitive Science realism is one of the problems identified for the symbolic/computational approach, i.e., how do internal states described by symbols relate to the real world in a natural manner. As DST is proposed as an alternative to the symbolic ...
... and modelling of other phenomena in Nature. Within Cognitive Science realism is one of the problems identified for the symbolic/computational approach, i.e., how do internal states described by symbols relate to the real world in a natural manner. As DST is proposed as an alternative to the symbolic ...
Phy CH 07 circular motion
... along an imaginary line drawn tangent to the car’s circular path. This definition can be applied to any object moving in circular motion. When the tangential speed is constant, the motion is described as uniform circular motion. The tangential speed depends on the distance from the object to the cen ...
... along an imaginary line drawn tangent to the car’s circular path. This definition can be applied to any object moving in circular motion. When the tangential speed is constant, the motion is described as uniform circular motion. The tangential speed depends on the distance from the object to the cen ...
California Physics Standard 2a Send comments to: layton@physics
... It is useful to introduce the idea of energy through the concept of work. Once work is understood, it can be shown that energy is transferred through work. Introducing the concept of work. Students need to know that force and work are different. Several different examples of applying forces, some wh ...
... It is useful to introduce the idea of energy through the concept of work. Once work is understood, it can be shown that energy is transferred through work. Introducing the concept of work. Students need to know that force and work are different. Several different examples of applying forces, some wh ...