PSCh5GR - TeacherPage.com
... Where is energy lost in a machine and in what form does it come out? ...
... Where is energy lost in a machine and in what form does it come out? ...
Chapter 14 - Work and Power – Physical Science Study Guide What
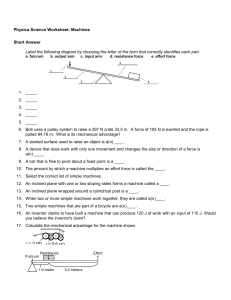
... 9. A machine is a device that can multiply __________. 10. When a machine does work it can not increase a force and _______________________. 11. How can a machine make work easier for you? 12. How can you make the work output of a machine greater than the work input? 13. The actual mechanical advant ...
... 9. A machine is a device that can multiply __________. 10. When a machine does work it can not increase a force and _______________________. 11. How can a machine make work easier for you? 12. How can you make the work output of a machine greater than the work input? 13. The actual mechanical advant ...
ENERGY- Is the ability to do work
... WORK - Is performed when a force is applied through a distance You can tell something has moved when it has changed _POSITION_. To calculate speed, you must know _TIME_ and _DISTANCE_. FRICTION_ -A force between objects that slows an object down. ACCELERATION_ -A change in speed or direction. INERTI ...
... WORK - Is performed when a force is applied through a distance You can tell something has moved when it has changed _POSITION_. To calculate speed, you must know _TIME_ and _DISTANCE_. FRICTION_ -A force between objects that slows an object down. ACCELERATION_ -A change in speed or direction. INERTI ...
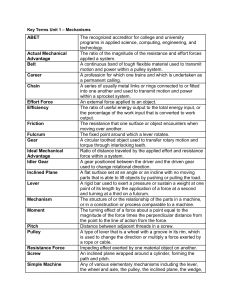
Lesson 1.1 Key Terms ABET The recognized accreditor for college
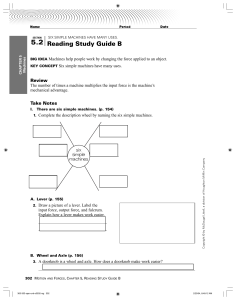
... force within a system. A gear positioned between the driver and the driven gear used to change rotational direction. A flat surface set at an angle or an incline with no moving parts that is able to lift objects by pushing or pulling the load. A rigid bar used to exert a pressure or sustain a weight ...
... force within a system. A gear positioned between the driver and the driven gear used to change rotational direction. A flat surface set at an angle or an incline with no moving parts that is able to lift objects by pushing or pulling the load. A rigid bar used to exert a pressure or sustain a weight ...
Machine (mechanical)

Machines employ power to achieve desired forces and movement (motion). A machine has a power source and actuators that generate forces and movement, and a system of mechanisms that shape the actuator input to achieve a specific application of output forces and movement. Modern machines often include computers and sensors that monitor performance and plan movement, and are called mechanical systems.The meaning of the word ""machine"" is traced by the Oxford English Dictionary to an independently functioning structure and by Merriam-Webster Dictionary to something that has been constructed. This includes human design into the meaning of machine.The adjective ""mechanical"" refers to skill in the practical application of an art or science, as well as relating to or caused by movement, physical forces, properties or agents such as is dealt with by mechanics. Similarly Merriam-Webster Dictionary defines ""mechanical"" as relating to machinery or tools.Power flow through a machine provides a way to understand the performance of devices ranging from levers and gear trains to automobiles and robotic systems. The German mechanician Franz Reuleaux wrote ""a machine is a combination of resistant bodies so arranged that by their means the mechanical forces of nature can be compelled to do work accompanied by certain determinate motion."" Notice that forces and motion combine to define power.More recently, Uicker et al. stated that a machine is ""a device for applying power or changing its direction."" And McCarthy and Soh describe a machine as a system that ""generally consists of a power source and a mechanism for the controlled use of this power.""