Physical Science Name_____________________ Simple
... This is the number of times that a machine increases your input force. 4. What is Ideal Mechanical Advantage? This is the number of times that a machine increases your input force, if there is no friction in the system. 5. What is efficiency? Efficiency is the percentage of work output compared to w ...
... This is the number of times that a machine increases your input force. 4. What is Ideal Mechanical Advantage? This is the number of times that a machine increases your input force, if there is no friction in the system. 5. What is efficiency? Efficiency is the percentage of work output compared to w ...
Kinesthetic Displays for Remote and Virtual Environments
... • Sense force, impose controlled movement ...
... • Sense force, impose controlled movement ...
Bio-physical principles
... 1. Anything can be balanced if its centre of gravity is directly over its base of support 2. The wider the base of support the more balanced or stable the object or body is. 3. The lower the centre of gravity the more balanced or stable the object is. ...
... 1. Anything can be balanced if its centre of gravity is directly over its base of support 2. The wider the base of support the more balanced or stable the object or body is. 3. The lower the centre of gravity the more balanced or stable the object is. ...
Holt Physics--Chapter 8 Rotational Equilibrium and Dynasmics
... 3. The center of mass moves as the object's "point mass" (see fig 8-7) 4. For most situations the center of mass and the "center of gravity" are the same B. Moment of Inertia 1. An object can rotate around many axes 2. The resistance of an object to changes in its rotation is measured by a quantity ...
... 3. The center of mass moves as the object's "point mass" (see fig 8-7) 4. For most situations the center of mass and the "center of gravity" are the same B. Moment of Inertia 1. An object can rotate around many axes 2. The resistance of an object to changes in its rotation is measured by a quantity ...
WORK AND ENERGY
... 4. Power is equal to work divided by time and the label is … 1. Watts 2. Joules 3. Newtons ...
... 4. Power is equal to work divided by time and the label is … 1. Watts 2. Joules 3. Newtons ...
MECHANISMS I: SIMPLE MACHINES INDEX 1) PRELIMINARIES a
... In many applications, both fixed and moveable pulleys are used in combination to form a device known as a block and tackle. A block and tackle is capable of both changing the direction of a force and creating a mechanical advantage. ...
... In many applications, both fixed and moveable pulleys are used in combination to form a device known as a block and tackle. A block and tackle is capable of both changing the direction of a force and creating a mechanical advantage. ...
WYSIWYG - DiMaggio
... Levers are classified based on the location of the fulcrum, input, and output. (MA is >, =, or < 1 depending on arrangement) o To increase the MA, move the output closer to the fulcrum, and/or the input farther away from the fulcrum Pulleys are classified based on if they move with the object or not ...
... Levers are classified based on the location of the fulcrum, input, and output. (MA is >, =, or < 1 depending on arrangement) o To increase the MA, move the output closer to the fulcrum, and/or the input farther away from the fulcrum Pulleys are classified based on if they move with the object or not ...
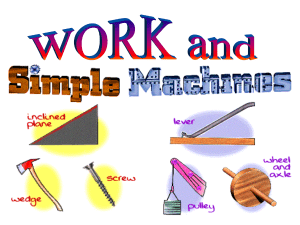
Key Words: inclined plane, simple machine, screw
... a simple machine used for over four thousand years to decrease the effort required to move heavy objects sloped surface (ramp) can move a heavy load using less force over a greater distance ex. 150 kg fridge (1500N) 1m off the ground ...
... a simple machine used for over four thousand years to decrease the effort required to move heavy objects sloped surface (ramp) can move a heavy load using less force over a greater distance ex. 150 kg fridge (1500N) 1m off the ground ...
Machine (mechanical)

Machines employ power to achieve desired forces and movement (motion). A machine has a power source and actuators that generate forces and movement, and a system of mechanisms that shape the actuator input to achieve a specific application of output forces and movement. Modern machines often include computers and sensors that monitor performance and plan movement, and are called mechanical systems.The meaning of the word ""machine"" is traced by the Oxford English Dictionary to an independently functioning structure and by Merriam-Webster Dictionary to something that has been constructed. This includes human design into the meaning of machine.The adjective ""mechanical"" refers to skill in the practical application of an art or science, as well as relating to or caused by movement, physical forces, properties or agents such as is dealt with by mechanics. Similarly Merriam-Webster Dictionary defines ""mechanical"" as relating to machinery or tools.Power flow through a machine provides a way to understand the performance of devices ranging from levers and gear trains to automobiles and robotic systems. The German mechanician Franz Reuleaux wrote ""a machine is a combination of resistant bodies so arranged that by their means the mechanical forces of nature can be compelled to do work accompanied by certain determinate motion."" Notice that forces and motion combine to define power.More recently, Uicker et al. stated that a machine is ""a device for applying power or changing its direction."" And McCarthy and Soh describe a machine as a system that ""generally consists of a power source and a mechanism for the controlled use of this power.""