1st quiz, NTU KIN02
... 1. Elbow extension is accomplished by extension of the ulna relative to the humerus associated with _____ glide of the _____ on the humerus. a. anterior, radius b. anterior, ulna c. posterior, radius d. posterior, ulna 2. Which of the following statements about arthrokinematic movement is NOT TRUE ? ...
... 1. Elbow extension is accomplished by extension of the ulna relative to the humerus associated with _____ glide of the _____ on the humerus. a. anterior, radius b. anterior, ulna c. posterior, radius d. posterior, ulna 2. Which of the following statements about arthrokinematic movement is NOT TRUE ? ...
PowerPoint プレゼンテーション
... important because it relates to all factors included in the ‘Health’ defined by WHO. The notion of ‘QOM’ is proposed by Dr. Kando Kobayashi (Honorary Prof. of The University of Tokyo) from a view point of human movement, and is considered to construct the basis for QOL. QOM means ‘the quality of mot ...
... important because it relates to all factors included in the ‘Health’ defined by WHO. The notion of ‘QOM’ is proposed by Dr. Kando Kobayashi (Honorary Prof. of The University of Tokyo) from a view point of human movement, and is considered to construct the basis for QOL. QOM means ‘the quality of mot ...
Glossary
... Efficiency: In physics, mechanical efficiency is the effectiveness of a machine. To show the effectiveness of a machine one must compare its work input to its work output. Efficiency is often indicated by a percentage, the efficiency of an ideal machine is 100%. Due to the fact that energy cannot em ...
... Efficiency: In physics, mechanical efficiency is the effectiveness of a machine. To show the effectiveness of a machine one must compare its work input to its work output. Efficiency is often indicated by a percentage, the efficiency of an ideal machine is 100%. Due to the fact that energy cannot em ...
Presentazione1
... autonoumus vehicle connected with a rubber material and a spring. Each vehicle is equipped with two driven wheeled arms and a dc motor. Each arm is pressed to the inner surface of the pipe by a linear spring, and can adapt to diameters changing by folding itself. ...
... autonoumus vehicle connected with a rubber material and a spring. Each vehicle is equipped with two driven wheeled arms and a dc motor. Each arm is pressed to the inner surface of the pipe by a linear spring, and can adapt to diameters changing by folding itself. ...
Power is the rate of doing work (or transferring energy), or the ratio
... Power is the rate of doing work (or transferring energy), or the ratio of work done to the time interval required to do the work. You can also calculate power using the product of the prime mover and a rate. The equations for calculating power in mechanical, fluid, and electrical systems are listed ...
... Power is the rate of doing work (or transferring energy), or the ratio of work done to the time interval required to do the work. You can also calculate power using the product of the prime mover and a rate. The equations for calculating power in mechanical, fluid, and electrical systems are listed ...
Section 2 What Is a Machine?
... • The unit used to express power is joules per second (J/s), also called the watt. One watt (W) is equal to 1 J/s. ...
... • The unit used to express power is joules per second (J/s), also called the watt. One watt (W) is equal to 1 J/s. ...
mechanisms_and_movement
... past, then locks the wheel in place when it is stationary. The Geneva stop mechanism is used commonly in film projectors to move the film on one frame at a time. ...
... past, then locks the wheel in place when it is stationary. The Geneva stop mechanism is used commonly in film projectors to move the film on one frame at a time. ...
simple machines.
... • A machine is any device that transmits or modifies force, usually by changing the force applied to an object. • All machines are combinations or modifications of six fundamental types of machines, called simple machines. • These six simple machines are the lever, pulley, inclined plane, wheel and ...
... • A machine is any device that transmits or modifies force, usually by changing the force applied to an object. • All machines are combinations or modifications of six fundamental types of machines, called simple machines. • These six simple machines are the lever, pulley, inclined plane, wheel and ...
Principles of Technology
... ◦ Describe in your own words, what force is. ◦ Give examples of complex technological devices where force must be controlled, measured, or applied ◦ Describe what force, pressure, voltage and temperature difference have in common ◦ Describe or predict what happens to an object when forces on it are ...
... ◦ Describe in your own words, what force is. ◦ Give examples of complex technological devices where force must be controlled, measured, or applied ◦ Describe what force, pressure, voltage and temperature difference have in common ◦ Describe or predict what happens to an object when forces on it are ...
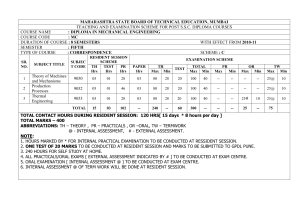
Teaching Scheme - Government Polytechnic Distance Learning Pune
... Mechanical engineers have to work with various power producing & power absorbing devices like boilers, turbines, compressors, pumps etc. In order to understand the principles, construction & working of these devices, it is essential to understand the concept of energy, work, heat & conversion betwee ...
... Mechanical engineers have to work with various power producing & power absorbing devices like boilers, turbines, compressors, pumps etc. In order to understand the principles, construction & working of these devices, it is essential to understand the concept of energy, work, heat & conversion betwee ...
Grade 8 Science
... different axis, the gears are not attached, they use teeth that mesh together. The teeth on gears are very specifically designed. Their shape is one that allows them to be in contact with each other for as long as possible, but yet they do not cause an obstacle for rotation. Compare the followi ...
... different axis, the gears are not attached, they use teeth that mesh together. The teeth on gears are very specifically designed. Their shape is one that allows them to be in contact with each other for as long as possible, but yet they do not cause an obstacle for rotation. Compare the followi ...
Basic Biomechanics
... 3. Curvilinear – combined rotary AND translatory motion. Gait is also an excellent example b/c rotary movement at the major LE joints results in translatory movement of the whole body. ...
... 3. Curvilinear – combined rotary AND translatory motion. Gait is also an excellent example b/c rotary movement at the major LE joints results in translatory movement of the whole body. ...
Machine (mechanical)

Machines employ power to achieve desired forces and movement (motion). A machine has a power source and actuators that generate forces and movement, and a system of mechanisms that shape the actuator input to achieve a specific application of output forces and movement. Modern machines often include computers and sensors that monitor performance and plan movement, and are called mechanical systems.The meaning of the word ""machine"" is traced by the Oxford English Dictionary to an independently functioning structure and by Merriam-Webster Dictionary to something that has been constructed. This includes human design into the meaning of machine.The adjective ""mechanical"" refers to skill in the practical application of an art or science, as well as relating to or caused by movement, physical forces, properties or agents such as is dealt with by mechanics. Similarly Merriam-Webster Dictionary defines ""mechanical"" as relating to machinery or tools.Power flow through a machine provides a way to understand the performance of devices ranging from levers and gear trains to automobiles and robotic systems. The German mechanician Franz Reuleaux wrote ""a machine is a combination of resistant bodies so arranged that by their means the mechanical forces of nature can be compelled to do work accompanied by certain determinate motion."" Notice that forces and motion combine to define power.More recently, Uicker et al. stated that a machine is ""a device for applying power or changing its direction."" And McCarthy and Soh describe a machine as a system that ""generally consists of a power source and a mechanism for the controlled use of this power.""