3.4 Congruence in Hyperbolic Space
... Note: In the hyperbolic plane, you cannot have similarity without congruence. Theorem: Saccheri quadrilaterals with congruent summits and summit angles are congruent. Theorem: Two omega triangles are congruent if the sides of finite length are congruent and if a pair of corresponding angles not loca ...
... Note: In the hyperbolic plane, you cannot have similarity without congruence. Theorem: Saccheri quadrilaterals with congruent summits and summit angles are congruent. Theorem: Two omega triangles are congruent if the sides of finite length are congruent and if a pair of corresponding angles not loca ...
Non-Euclidean Geometry
... • The sides of an ideal triangle get closer as they approach the edge of the disk ...
... • The sides of an ideal triangle get closer as they approach the edge of the disk ...
1. To introduce the topic show students a clip from
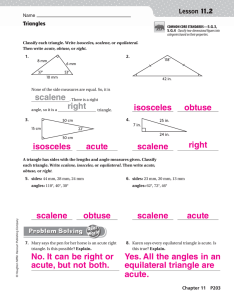
... area of one of the triangles. For example, if each side has length 5 cm then we can take one of the equilateral triangles and we know each side of it has a length of 5 cm. To find the area of the triangle we can draw a perpendicular to form two right triangles. The hypotenuse is still 5 cm and the ...
... area of one of the triangles. For example, if each side has length 5 cm then we can take one of the equilateral triangles and we know each side of it has a length of 5 cm. To find the area of the triangle we can draw a perpendicular to form two right triangles. The hypotenuse is still 5 cm and the ...
Solutions 13-14 - Durham University
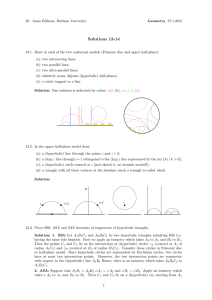
... 14.10 (*) We have proved that an isometry fixing 3 points of the absolute is identity map. How many isometries fix two points of the absolute? Solution: We will work in the upper half-plane model. Let f be an isometry fixing two points of the absolute. First, we can conjugate f by an isometry h whic ...
... 14.10 (*) We have proved that an isometry fixing 3 points of the absolute is identity map. How many isometries fix two points of the absolute? Solution: We will work in the upper half-plane model. Let f be an isometry fixing two points of the absolute. First, we can conjugate f by an isometry h whic ...
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston
... then enlarged the circles repeatedly. 3. Sample answer: Move one triangle onto a coordinate plane in a convenient position like the first quadrant. Apply the dilation with center (0, 0) and scale factor 2. (x, y) (2x, 2y). The image should then be congruent to the image created with the graphics p ...
... then enlarged the circles repeatedly. 3. Sample answer: Move one triangle onto a coordinate plane in a convenient position like the first quadrant. Apply the dilation with center (0, 0) and scale factor 2. (x, y) (2x, 2y). The image should then be congruent to the image created with the graphics p ...
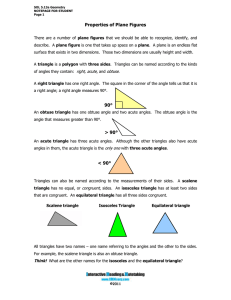
THE MEASURE OF ONE ANGLE IS 38 LESS THAN THE MEASURE
... SEGMENTS CALLED SIDES. 2) EACH SIDE INTERSECTS EXACTLY TWO SIDE, ONE AT EACH ENDPOINT, SO THAT NO TWO SIDES WITH A COMMON ENDPOINT ARE COLLINEAR EACH ENDPOINT OF A SIDE IS A VERTEX OF THE POLYGON. ...
... SEGMENTS CALLED SIDES. 2) EACH SIDE INTERSECTS EXACTLY TWO SIDE, ONE AT EACH ENDPOINT, SO THAT NO TWO SIDES WITH A COMMON ENDPOINT ARE COLLINEAR EACH ENDPOINT OF A SIDE IS A VERTEX OF THE POLYGON. ...
Slide 1
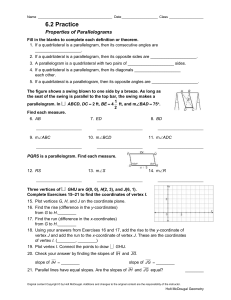
... Tuesday, May 23, 2017 Quadrilateral QRST and quadrilateral WXYZ, shown at right, both have integer coordinates. ...
... Tuesday, May 23, 2017 Quadrilateral QRST and quadrilateral WXYZ, shown at right, both have integer coordinates. ...
similar polygons
... 7-1 Ratios in Similar Polygons A similarity ratio is the ratio of the lengths of the corresponding sides of two similar polygons. The similarity ratio of ∆ABC to ∆DEF is ...
... 7-1 Ratios in Similar Polygons A similarity ratio is the ratio of the lengths of the corresponding sides of two similar polygons. The similarity ratio of ∆ABC to ∆DEF is ...
Tessellation

A tessellation of a flat surface is the tiling of a plane using one or more geometric shapes, called tiles, with no overlaps and no gaps. In mathematics, tessellations can be generalized to higher dimensions and a variety of geometries.A periodic tiling has a repeating pattern. Some special kinds include regular tilings with regular polygonal tiles all of the same shape, and semi-regular tilings with regular tiles of more than one shape and with every corner identically arranged. The patterns formed by periodic tilings can be categorized into 17 wallpaper groups. A tiling that lacks a repeating pattern is called ""non-periodic"". An aperiodic tiling uses a small set of tile shapes that cannot form a repeating pattern. In the geometry of higher dimensions, a space-filling or honeycomb is also called a tessellation of space.A real physical tessellation is a tiling made of materials such as cemented ceramic squares or hexagons. Such tilings may be decorative patterns, or may have functions such as providing durable and water-resistant pavement, floor or wall coverings. Historically, tessellations were used in Ancient Rome and in Islamic art such as in the decorative tiling of the Alhambra palace. In the twentieth century, the work of M. C. Escher often made use of tessellations, both in ordinary Euclidean geometry and in hyperbolic geometry, for artistic effect. Tessellations are sometimes employed for decorative effect in quilting. Tessellations form a class of patterns in nature, for example in the arrays of hexagonal cells found in honeycombs.