elementary montessori geometry album
... Presentation of the theorem: “The amplitude of the angle does not depend on the length of its arms Presentation of the measurement of angles Presentation of the addition applied to the amplitude of angles Presentation of the subtraction applied to the amplitude of angles Presentation of the relatio ...
... Presentation of the theorem: “The amplitude of the angle does not depend on the length of its arms Presentation of the measurement of angles Presentation of the addition applied to the amplitude of angles Presentation of the subtraction applied to the amplitude of angles Presentation of the relatio ...
Chapter 6 Notes Section 6.1 Polygons Definitions
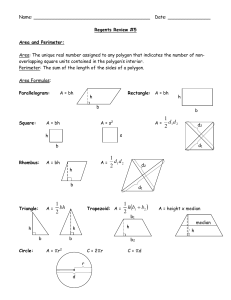
... Polygon Is formed by three or more segments called sides, such that no two sides with a common endpoints are collinear. Each side intersects exactly two other sides, one at each endpoint. ...
... Polygon Is formed by three or more segments called sides, such that no two sides with a common endpoints are collinear. Each side intersects exactly two other sides, one at each endpoint. ...
Chapter 7 Similar Polygons
... The reason this is a postulate is that we cannot prove it, but as we examine more and more cases, this seems to hold up. Since it does, we accept it as true without proof. Any postulate or theorem that has a name must be important, so make sure you know what this one says and means. Like ll theorems ...
... The reason this is a postulate is that we cannot prove it, but as we examine more and more cases, this seems to hold up. Since it does, we accept it as true without proof. Any postulate or theorem that has a name must be important, so make sure you know what this one says and means. Like ll theorems ...
Polygons Around the World
... • About Our Trip……Polygons are all around us in our everyday lives. They are on buildings, road signs, playgrounds, and even in the classroom! We are going to travel the world looking for polygons in real life situations. • A polygon is a two dimensional shape that is closed and made with straight ...
... • About Our Trip……Polygons are all around us in our everyday lives. They are on buildings, road signs, playgrounds, and even in the classroom! We are going to travel the world looking for polygons in real life situations. • A polygon is a two dimensional shape that is closed and made with straight ...
6.1 Polygons - Teacher Notes
... • Polygon—a plane figure that meets the following conditions: – It is formed by 3 or more segments called sides, such that no two sides with a common endpoint are collinear. – Each side intersects exactly two other sides, one at each endpoint. ...
... • Polygon—a plane figure that meets the following conditions: – It is formed by 3 or more segments called sides, such that no two sides with a common endpoint are collinear. – Each side intersects exactly two other sides, one at each endpoint. ...
6-12 Comp 3 trainer notes - Math6-12TestPrep
... 3 Knowledge of geometry from a synthetic perspective 1. Determine the change in the area or volume of a figure when its dimensions are altered. 2. Estimate measurements of familiar objects using metric or standard units. 3. Determine the relationships between points, lines, and planes, including the ...
... 3 Knowledge of geometry from a synthetic perspective 1. Determine the change in the area or volume of a figure when its dimensions are altered. 2. Estimate measurements of familiar objects using metric or standard units. 3. Determine the relationships between points, lines, and planes, including the ...
Geometry Curriculum Map
... showing that triangles are congruent. - To use the properties of congruent triangles. - To identify the relationships formed by the various segments of triangles. - To understand the Triangle ...
... showing that triangles are congruent. - To use the properties of congruent triangles. - To identify the relationships formed by the various segments of triangles. - To understand the Triangle ...
Tessellation

A tessellation of a flat surface is the tiling of a plane using one or more geometric shapes, called tiles, with no overlaps and no gaps. In mathematics, tessellations can be generalized to higher dimensions and a variety of geometries.A periodic tiling has a repeating pattern. Some special kinds include regular tilings with regular polygonal tiles all of the same shape, and semi-regular tilings with regular tiles of more than one shape and with every corner identically arranged. The patterns formed by periodic tilings can be categorized into 17 wallpaper groups. A tiling that lacks a repeating pattern is called ""non-periodic"". An aperiodic tiling uses a small set of tile shapes that cannot form a repeating pattern. In the geometry of higher dimensions, a space-filling or honeycomb is also called a tessellation of space.A real physical tessellation is a tiling made of materials such as cemented ceramic squares or hexagons. Such tilings may be decorative patterns, or may have functions such as providing durable and water-resistant pavement, floor or wall coverings. Historically, tessellations were used in Ancient Rome and in Islamic art such as in the decorative tiling of the Alhambra palace. In the twentieth century, the work of M. C. Escher often made use of tessellations, both in ordinary Euclidean geometry and in hyperbolic geometry, for artistic effect. Tessellations are sometimes employed for decorative effect in quilting. Tessellations form a class of patterns in nature, for example in the arrays of hexagonal cells found in honeycombs.