Triangles and Squares
... How many different choices are there? Equivalently, how many independent sets of 120-cell vertices up to 120-cell symmetries? ...
... How many different choices are there? Equivalently, how many independent sets of 120-cell vertices up to 120-cell symmetries? ...
Study Guide Quiz #5
... 32. Find the number of sides of a regular polygon with each interior angle equal to 144. 33. The measure of each interior angle of a regular polygon is 120°. How many sides does the polygon have? ...
... 32. Find the number of sides of a regular polygon with each interior angle equal to 144. 33. The measure of each interior angle of a regular polygon is 120°. How many sides does the polygon have? ...
2.02 Geometry Vocab Quiz
... two lines that do not intersect, but are in the same plane a polygon having all sides equal in length and angles of equal ...
... two lines that do not intersect, but are in the same plane a polygon having all sides equal in length and angles of equal ...
P6 - CEMC
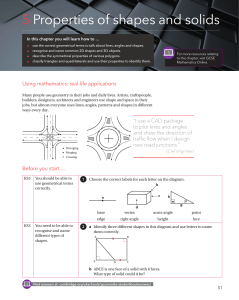
... 1. Suppose the polygons in a) to e) above were not regular, i.e., they could have unequal sides. Which of your two columns of the results would remain unchanged? Experiment with the three non-regular polygons below. ...
... 1. Suppose the polygons in a) to e) above were not regular, i.e., they could have unequal sides. Which of your two columns of the results would remain unchanged? Experiment with the three non-regular polygons below. ...
File - F.O.M. Math 11
... d) Use the function S(n) = 180(n-2) to determine the sum of the interior angles of a regular octagon. Compare your answer with the sum you determined in part c) ...
... d) Use the function S(n) = 180(n-2) to determine the sum of the interior angles of a regular octagon. Compare your answer with the sum you determined in part c) ...
Acute Angle - An angle that measures less than 90
... Square – a rectangle with all sides of equal length; all angles in a square are right angles; all squares are also rectangles, but not all rectangles are squares ...
... Square – a rectangle with all sides of equal length; all angles in a square are right angles; all squares are also rectangles, but not all rectangles are squares ...
Teach Geometry for Understanding
... Triangles are sorted by numbers of equal sides (scalene, isosceles, equilateral) relating also to symmetry. Quadrilaterals will have one or two pairs of opposite sides parallel and one or more pairs of opposite or adjacent sides equal. At this stage it is best to make the differences between quadril ...
... Triangles are sorted by numbers of equal sides (scalene, isosceles, equilateral) relating also to symmetry. Quadrilaterals will have one or two pairs of opposite sides parallel and one or more pairs of opposite or adjacent sides equal. At this stage it is best to make the differences between quadril ...
Tessellation

A tessellation of a flat surface is the tiling of a plane using one or more geometric shapes, called tiles, with no overlaps and no gaps. In mathematics, tessellations can be generalized to higher dimensions and a variety of geometries.A periodic tiling has a repeating pattern. Some special kinds include regular tilings with regular polygonal tiles all of the same shape, and semi-regular tilings with regular tiles of more than one shape and with every corner identically arranged. The patterns formed by periodic tilings can be categorized into 17 wallpaper groups. A tiling that lacks a repeating pattern is called ""non-periodic"". An aperiodic tiling uses a small set of tile shapes that cannot form a repeating pattern. In the geometry of higher dimensions, a space-filling or honeycomb is also called a tessellation of space.A real physical tessellation is a tiling made of materials such as cemented ceramic squares or hexagons. Such tilings may be decorative patterns, or may have functions such as providing durable and water-resistant pavement, floor or wall coverings. Historically, tessellations were used in Ancient Rome and in Islamic art such as in the decorative tiling of the Alhambra palace. In the twentieth century, the work of M. C. Escher often made use of tessellations, both in ordinary Euclidean geometry and in hyperbolic geometry, for artistic effect. Tessellations are sometimes employed for decorative effect in quilting. Tessellations form a class of patterns in nature, for example in the arrays of hexagonal cells found in honeycombs.