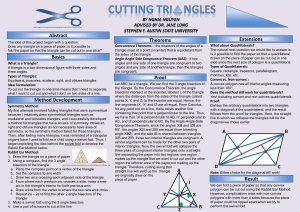
Angles of a Polygon
... Angles of a Polygon Interior Angle Sum Theorem • The sum of the measures of the interior angles of a convex polygon with n sides is (n - 2)180. Since the angles in a regular polygon are congruent, you can find the measure of one interior angle of a regular polygon by dividing (n - 2)180 by the nu ...
... Angles of a Polygon Interior Angle Sum Theorem • The sum of the measures of the interior angles of a convex polygon with n sides is (n - 2)180. Since the angles in a regular polygon are congruent, you can find the measure of one interior angle of a regular polygon by dividing (n - 2)180 by the nu ...
Regular Polygons
... business affairs. "Even if you remove 30 percent of the webs, the tire will still work." And for those of you wondering why all tires aren't simply made out of solid rubber, some construction vehicles use them on sites with debris that can easily shred a pneumatic tire, but solid tires give an incre ...
... business affairs. "Even if you remove 30 percent of the webs, the tire will still work." And for those of you wondering why all tires aren't simply made out of solid rubber, some construction vehicles use them on sites with debris that can easily shred a pneumatic tire, but solid tires give an incre ...
NYS Mathematics Glossary* – Geometry
... absolute value The distance from 0 to a number n on a number line. The absolute value of a number n is indicated by n . Example: −3 = 3 , +3 = 3 , and 0 = 0 . acute angle An angle whose measure is greater than 0° and less than 90°. acute triangle A triangle that contains three acute angles. additive ...
... absolute value The distance from 0 to a number n on a number line. The absolute value of a number n is indicated by n . Example: −3 = 3 , +3 = 3 , and 0 = 0 . acute angle An angle whose measure is greater than 0° and less than 90°. acute triangle A triangle that contains three acute angles. additive ...
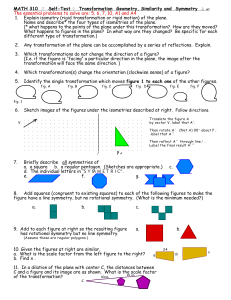
Angle Inequalities, Triangle Congruence, Points of Concurrency
... Draw triangle XYZ and label the sides accordingly. XY = 22, YZ = 42, XZ = 31. List the angles in order from least to greatest. ...
... Draw triangle XYZ and label the sides accordingly. XY = 22, YZ = 42, XZ = 31. List the angles in order from least to greatest. ...
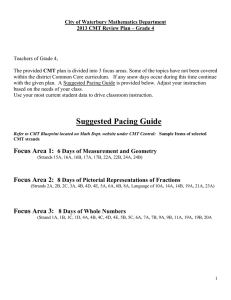
City of Waterbury Mathematics Department 2013 CMT Review Plan
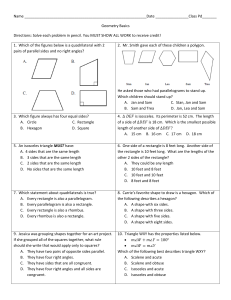
... Strategy to use when drawing polygons: place as many points as the figure has sides and connect the points to create polygon. Geometric Information Guide for Teachers: polygons - All closed figures with sides and angles AND no curved lines. triangles: all polygons with 3 angles and 3 sides. ...
... Strategy to use when drawing polygons: place as many points as the figure has sides and connect the points to create polygon. Geometric Information Guide for Teachers: polygons - All closed figures with sides and angles AND no curved lines. triangles: all polygons with 3 angles and 3 sides. ...
Year: 5 Theme: 5.4 SHAPE Week 3: 12.1.15 Prior Learning Pupils
... Ask children to write down the name of a shape that could have at least one circle as a face. Share responses. Work with a partner to write down as many shapes as you can that could have a square as one or more of its faces. Repeat for other shape faces. Hold up the cube and the cuboid. What is the ...
... Ask children to write down the name of a shape that could have at least one circle as a face. Share responses. Work with a partner to write down as many shapes as you can that could have a square as one or more of its faces. Repeat for other shape faces. Hold up the cube and the cuboid. What is the ...
Tessellation

A tessellation of a flat surface is the tiling of a plane using one or more geometric shapes, called tiles, with no overlaps and no gaps. In mathematics, tessellations can be generalized to higher dimensions and a variety of geometries.A periodic tiling has a repeating pattern. Some special kinds include regular tilings with regular polygonal tiles all of the same shape, and semi-regular tilings with regular tiles of more than one shape and with every corner identically arranged. The patterns formed by periodic tilings can be categorized into 17 wallpaper groups. A tiling that lacks a repeating pattern is called ""non-periodic"". An aperiodic tiling uses a small set of tile shapes that cannot form a repeating pattern. In the geometry of higher dimensions, a space-filling or honeycomb is also called a tessellation of space.A real physical tessellation is a tiling made of materials such as cemented ceramic squares or hexagons. Such tilings may be decorative patterns, or may have functions such as providing durable and water-resistant pavement, floor or wall coverings. Historically, tessellations were used in Ancient Rome and in Islamic art such as in the decorative tiling of the Alhambra palace. In the twentieth century, the work of M. C. Escher often made use of tessellations, both in ordinary Euclidean geometry and in hyperbolic geometry, for artistic effect. Tessellations are sometimes employed for decorative effect in quilting. Tessellations form a class of patterns in nature, for example in the arrays of hexagonal cells found in honeycombs.