12. Molecular Recognition: The Thermodynamics of
... In Chapter 11 we introduced the concept of the equilibrium constant, K, which governs the concentrations of reactants and products in a reaction that has reached equilibrium. In this chapter and the next one we focus on the analysis of equilibrium constants for a particularly important subset of mol ...
... In Chapter 11 we introduced the concept of the equilibrium constant, K, which governs the concentrations of reactants and products in a reaction that has reached equilibrium. In this chapter and the next one we focus on the analysis of equilibrium constants for a particularly important subset of mol ...
Downstream Regulatory Element Antagonist Modulator Regulates
... DREAM downregulates transcription of the NCX3 promoter To understand the regulatory mechanisms controlling NCX3 expression in vivo, we inspected the proximal regulatory region of the NCX3 gene and found several DRE elements (GTCA) that could be targeted by the transcriptional repressor DREAM and med ...
... DREAM downregulates transcription of the NCX3 promoter To understand the regulatory mechanisms controlling NCX3 expression in vivo, we inspected the proximal regulatory region of the NCX3 gene and found several DRE elements (GTCA) that could be targeted by the transcriptional repressor DREAM and med ...
The Structure and Function of Large Biological Molecules
... cellular work, but their carbon skeletons also serve as raw material for the synthesis of other types of small organic molecules, such as amino acids and fatty acids. Sugar molecules that are not immediately used in these ways are generally incorporated as monomers into disaccharides or polysacchari ...
... cellular work, but their carbon skeletons also serve as raw material for the synthesis of other types of small organic molecules, such as amino acids and fatty acids. Sugar molecules that are not immediately used in these ways are generally incorporated as monomers into disaccharides or polysacchari ...
Nuclear Localization and Interaction with COP1 Are Required for
... under monochromatic light (Supplemental Fig. S1B). To investigate the biological relevance of the nuclear localization of BBX24, we generated transgenic homozygous bbx24-1 lines constitutively expressing EGFPBBX24 or EGFP-bbx24NLS. The subcellular localization of EGFP-BBX24 and EGFP-bbx24NLS in 5-d- ...
... under monochromatic light (Supplemental Fig. S1B). To investigate the biological relevance of the nuclear localization of BBX24, we generated transgenic homozygous bbx24-1 lines constitutively expressing EGFPBBX24 or EGFP-bbx24NLS. The subcellular localization of EGFP-BBX24 and EGFP-bbx24NLS in 5-d- ...
Signaling Mechanisms That Regulate Smooth Muscle Cell
... MRTF-A that traps endogenous MRTFs in the cytoplasm.12 Because this intervention does not affect myocardin activity or MRTF expression, these data provided direct evidence for MRTF nuclear translocation as an important signaling mechanism in the control of SMC-specific gene expression. The mechanism ...
... MRTF-A that traps endogenous MRTFs in the cytoplasm.12 Because this intervention does not affect myocardin activity or MRTF expression, these data provided direct evidence for MRTF nuclear translocation as an important signaling mechanism in the control of SMC-specific gene expression. The mechanism ...
ch.6
... charges, size and solubility of molecules Electrophoresis – effects separation in an electric field on the basis of differences in charges carried by amino acids and proteins under specific condition Ultracentrifugation – effects separation on the basis of molecular weight when large gravitational f ...
... charges, size and solubility of molecules Electrophoresis – effects separation in an electric field on the basis of differences in charges carried by amino acids and proteins under specific condition Ultracentrifugation – effects separation on the basis of molecular weight when large gravitational f ...
Roles of Chromatin insulators in gene regulation and diseases
... several other loci. So, CTCF binding regulation through DNA methylation is a common mechanism to regulate the function of insulators. The second mechanism controls the insulators function is shared by mammals and invertebrates such as drosophila. In this mechanism, competitor proteins compete with C ...
... several other loci. So, CTCF binding regulation through DNA methylation is a common mechanism to regulate the function of insulators. The second mechanism controls the insulators function is shared by mammals and invertebrates such as drosophila. In this mechanism, competitor proteins compete with C ...
9/18/08 Transcript I
... Each of these their own sets of promoters and genes that they transcribe. All 3 are big, multimeric proteins (500-700 kD). All have 2 large subunits which are very similar to prokaryotic. RNA polymerase subunits and ' which we talked about yesterday. And the catalytic site may be conserve ...
... Each of these their own sets of promoters and genes that they transcribe. All 3 are big, multimeric proteins (500-700 kD). All have 2 large subunits which are very similar to prokaryotic. RNA polymerase subunits and ' which we talked about yesterday. And the catalytic site may be conserve ...
Storage globulins pass through the Golgi apparatus and
... storage vacuoles (PSVs). Multiple mechanisms have been proposed to be responsible for transporting storage proteins to PSVs in developing seeds. In this study, a specific antibody was raised against the mung bean (Vigna radiata) seed storage protein 8S globulin and its deposition was followed via im ...
... storage vacuoles (PSVs). Multiple mechanisms have been proposed to be responsible for transporting storage proteins to PSVs in developing seeds. In this study, a specific antibody was raised against the mung bean (Vigna radiata) seed storage protein 8S globulin and its deposition was followed via im ...
Purine nucleosides: endogenous neuroprotectants in hypoxic brain
... ATP, which results in profound deficiencies in cellular function. Following ischemia, dying, injured, and hypoxic cells release soluble purine-nucleotide and -nucleoside pools. Growing evidence suggests that purine nucleosides might act as trophic factors in the CNS and PNS. In addition to equilibra ...
... ATP, which results in profound deficiencies in cellular function. Following ischemia, dying, injured, and hypoxic cells release soluble purine-nucleotide and -nucleoside pools. Growing evidence suggests that purine nucleosides might act as trophic factors in the CNS and PNS. In addition to equilibra ...
Isolation of Spherosomes with Lysosome Characteristics from
... particle suspensions was omitted and the tonicity of the medium was m aintained during incubation (20% sucrose), very low activities were measured as com pared with activities of sonicated controls. Moreover freezing and thawing of the suspensions prior to the enzyme assay increased the activities ...
... particle suspensions was omitted and the tonicity of the medium was m aintained during incubation (20% sucrose), very low activities were measured as com pared with activities of sonicated controls. Moreover freezing and thawing of the suspensions prior to the enzyme assay increased the activities ...
Isolation of Spherosomes with Lysosome
... particle suspensions was omitted and the tonicity of the medium was m aintained during incubation (20% sucrose), very low activities were measured as com pared with activities of sonicated controls. Moreover freezing and thawing of the suspensions prior to the enzyme assay increased the activities ...
... particle suspensions was omitted and the tonicity of the medium was m aintained during incubation (20% sucrose), very low activities were measured as com pared with activities of sonicated controls. Moreover freezing and thawing of the suspensions prior to the enzyme assay increased the activities ...
The Structure and Function of Large Biological Molecules
... • Enzymes that digest starch by hydrolyzing linkages can’t hydrolyze linkages in cellulose • Cellulose in human food passes through the digestive tract as insoluble fiber • Some microbes use enzymes to digest cellulose • Many herbivores, from cows to termites, have symbiotic relationships with ...
... • Enzymes that digest starch by hydrolyzing linkages can’t hydrolyze linkages in cellulose • Cellulose in human food passes through the digestive tract as insoluble fiber • Some microbes use enzymes to digest cellulose • Many herbivores, from cows to termites, have symbiotic relationships with ...
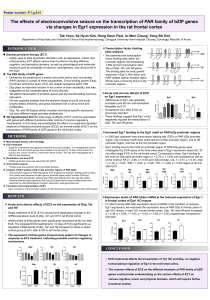
The effects of electroconvulsive seizure on the transcription
... functions such as excitability of neurons, neurogenesis, and cell survival in the brain The PAR family of bZIP genes • Defined by the presence of a proline and acidic amino acid–rich protein (PAR) domain is consist of three polypeptides, D-box binding protein (Dbp), thyrotroph embryonic factor (Te ...
... functions such as excitability of neurons, neurogenesis, and cell survival in the brain The PAR family of bZIP genes • Defined by the presence of a proline and acidic amino acid–rich protein (PAR) domain is consist of three polypeptides, D-box binding protein (Dbp), thyrotroph embryonic factor (Te ...
Interleukin 1 Receptor Antagonist (IL-1Ra) Is an Acute-Phase
... biochemical changes that accompany infection, trauma, or immunologically mediated inflammation. The acute-phase proteins (APP),1 considered to be the hallmark of the acute-phase response, include a variety of secreted proteins the levels of which are modified during inflammatory conditions (1). Thes ...
... biochemical changes that accompany infection, trauma, or immunologically mediated inflammation. The acute-phase proteins (APP),1 considered to be the hallmark of the acute-phase response, include a variety of secreted proteins the levels of which are modified during inflammatory conditions (1). Thes ...
Glycan-independent Role of Calnexin in the Intracellular
... with CNX in sciatic nerves and that this interaction is prolonged in the case of mutant Gas3/PMP22 (18). This result suggested that sequestration by CNX may be relevant for CMT1A-related neuropathies. In this study, we have demonstrated that Gas3/PMP22 interacts with CNX in a glycan-dependent manner ...
... with CNX in sciatic nerves and that this interaction is prolonged in the case of mutant Gas3/PMP22 (18). This result suggested that sequestration by CNX may be relevant for CMT1A-related neuropathies. In this study, we have demonstrated that Gas3/PMP22 interacts with CNX in a glycan-dependent manner ...
Roles of ion channels and transporters in guard cell signal
... outwardly-rectifying, or weakly rectifying (Fig. 2). The inward K+ channels KAT1, KAT2, AKT1, the outward K+ channel GORK, the K+ channel AKT2/3, whose rectification properties are dependent on its phosphorylation status [30], and the subunit AtKC1, which forms a heteromeric channel with KAT1 or AKT1 ...
... outwardly-rectifying, or weakly rectifying (Fig. 2). The inward K+ channels KAT1, KAT2, AKT1, the outward K+ channel GORK, the K+ channel AKT2/3, whose rectification properties are dependent on its phosphorylation status [30], and the subunit AtKC1, which forms a heteromeric channel with KAT1 or AKT1 ...
Vacuolar Sorting Receptor-Mediated Trafficking of Soluble Vacuolar
... these atvsr mutants have smaller PSVs than the wild type, which may be due to the reduced levels of PSV proteins in the PSVs resulting from defects in PSV trafficking. However, single and double mutants of atvrs1, atvsr3, and atvsr4 do not show any obvious defective phenotype in their vegetative tis ...
... these atvsr mutants have smaller PSVs than the wild type, which may be due to the reduced levels of PSV proteins in the PSVs resulting from defects in PSV trafficking. However, single and double mutants of atvrs1, atvsr3, and atvsr4 do not show any obvious defective phenotype in their vegetative tis ...
CHAPTER FOUR Pseudomonas aeruginosa INFLUENCED PLANKTONIC AND BIOFILM POPULATIONS BASED UPON
... sessile multicellular communities known as biofilms (Costerton et al., 1987; 1995). The transition to surface-attached (biofilm) growth is known to result in diverse changes in gene expression, which causes the attaching cells to become phenotypically and metabolically distinct from their planktonic ...
... sessile multicellular communities known as biofilms (Costerton et al., 1987; 1995). The transition to surface-attached (biofilm) growth is known to result in diverse changes in gene expression, which causes the attaching cells to become phenotypically and metabolically distinct from their planktonic ...
University of Pennsylvania Chemical and
... Endocytosis is a highly orchestrated process involving a variety of proteins. ...
... Endocytosis is a highly orchestrated process involving a variety of proteins. ...
Isolation by Calcium-Dependent Translocation to
... the defense against microbes. Phagocytosing neutrophils kill and degrade bacteria through the action of toxic oxygen metabolites and proteolytic enzymes.’.2Recognition of the microbes as well as phagolysosome formation, a prerequisite for killing, is dependent on secretion or degranulation of granul ...
... the defense against microbes. Phagocytosing neutrophils kill and degrade bacteria through the action of toxic oxygen metabolites and proteolytic enzymes.’.2Recognition of the microbes as well as phagolysosome formation, a prerequisite for killing, is dependent on secretion or degranulation of granul ...
Vitamins as Hormones
... Retinoid receptors are members of the nuclear receptor superfamily and are classified in two families; the retinoic acid receptors (RARs) and the retinoid X receptors (RXRs) [10]. They act as ligand-dependent transcription factors. RARs can bind both atRA and 9cRA with high affinity, while RXRs select ...
... Retinoid receptors are members of the nuclear receptor superfamily and are classified in two families; the retinoic acid receptors (RARs) and the retinoid X receptors (RXRs) [10]. They act as ligand-dependent transcription factors. RARs can bind both atRA and 9cRA with high affinity, while RXRs select ...
The monocarboxylate transporter family
... Molecular Mechanism of MCT1. The molecular mechanism by which MCT1 transports monocarboxylates has been extensively studied by analysis of transport kinetics, the use of inhibitors and more recently through site-directed mutagenesis. Detailed kinetic analysis of monocarboxylate transport in erythroc ...
... Molecular Mechanism of MCT1. The molecular mechanism by which MCT1 transports monocarboxylates has been extensively studied by analysis of transport kinetics, the use of inhibitors and more recently through site-directed mutagenesis. Detailed kinetic analysis of monocarboxylate transport in erythroc ...
Signal transduction
Signal transduction occurs when an extracellular signaling molecule activates a specific receptor located on the cell surface or inside the cell. In turn, this receptor triggers a biochemical chain of events inside the cell, creating a response. Depending on the cell, the response alters the cell's metabolism, shape, gene expression, or ability to divide. The signal can be amplified at any step. Thus, one signaling molecule can cause many responses.