P-GAP-43 Is Enriched in Horizontal Cell
... 2005). These experiments further support the notion that asymmetric inheritance of fate determinants located in the apical membrane patch may be crucial to determine the unequal fate of daughter cells in the developing cortex. However, it is not clear how the orientation of cell division is regulate ...
... 2005). These experiments further support the notion that asymmetric inheritance of fate determinants located in the apical membrane patch may be crucial to determine the unequal fate of daughter cells in the developing cortex. However, it is not clear how the orientation of cell division is regulate ...
Abstract Panax ginseng Meyer, belonging to the genus Panax of the
... to antibodies or enzymes, and are able to detect or bind complex carbohydrate structures specifically through the carbohydrate-recognition domain (CRD) [46] and [47]. Each animal lectin possess its own CRD which has an identical sequence motif of 115 to 130 amino acid residues and four cysteines tha ...
... to antibodies or enzymes, and are able to detect or bind complex carbohydrate structures specifically through the carbohydrate-recognition domain (CRD) [46] and [47]. Each animal lectin possess its own CRD which has an identical sequence motif of 115 to 130 amino acid residues and four cysteines tha ...
isolation, characterization, and expression of mouse icam
... cells in and tissues. presence of a second ligand for LFA- 1 wasimplicated by Furthermore, COS cells transfectedwithmouse the observation that antibodies to ICAM-1 only partially ICAM-2 complementary and genomic DNA bind to purified human LFA-1, demonstrating the conser- inhibited adhesion of leukoc ...
... cells in and tissues. presence of a second ligand for LFA- 1 wasimplicated by Furthermore, COS cells transfectedwithmouse the observation that antibodies to ICAM-1 only partially ICAM-2 complementary and genomic DNA bind to purified human LFA-1, demonstrating the conser- inhibited adhesion of leukoc ...
Cell Death Suppressor, Arabidopsis BI
... mitochondrion may be required to induce cell death by some apoptotic signals; alteration of calcium level in ER could signal apoptotic cell death (Scorrano et al, 2003). On the other hand, over-expression of Bcl-2 reduces ER calcium level (Foyouzi-Youssefi et al., 2000), suggesting that the effect o ...
... mitochondrion may be required to induce cell death by some apoptotic signals; alteration of calcium level in ER could signal apoptotic cell death (Scorrano et al, 2003). On the other hand, over-expression of Bcl-2 reduces ER calcium level (Foyouzi-Youssefi et al., 2000), suggesting that the effect o ...
Proteins and Albumin
... (from the Greek oligos, meaning “few”). Proteins are typically defined as polypeptides with a molecular weight of greater than 5000 Daltons (ie, > 5 kDa). Proteins adopt stable conformations based on chemical interactions between neighboring amino acids within the sequence, between remote domains, a ...
... (from the Greek oligos, meaning “few”). Proteins are typically defined as polypeptides with a molecular weight of greater than 5000 Daltons (ie, > 5 kDa). Proteins adopt stable conformations based on chemical interactions between neighboring amino acids within the sequence, between remote domains, a ...
Chapter 12
... At the Resting Potential—the activation gates of the voltage-gated sodium channels are closed. At the Refractory Period—the membrane does not respond to additional depolarizing stimuli from the time an action potential begins until the normal resting membrane potential has stabilized. At the Absolu ...
... At the Resting Potential—the activation gates of the voltage-gated sodium channels are closed. At the Refractory Period—the membrane does not respond to additional depolarizing stimuli from the time an action potential begins until the normal resting membrane potential has stabilized. At the Absolu ...
Subcellular Localization and Activity of Multidrug
... could easily ascertain the phenotypes conferred by the protein of interest, because nonexpressing cells were present alongside cells expressing the protein and exposed to identical culture conditions. The ECFP tag on each protein permitted easy identification of those cells that expressed a drug tra ...
... could easily ascertain the phenotypes conferred by the protein of interest, because nonexpressing cells were present alongside cells expressing the protein and exposed to identical culture conditions. The ECFP tag on each protein permitted easy identification of those cells that expressed a drug tra ...
to the full text - David Moore`s World of Fungi: where
... Chapter 3: Metabolism and biochemistry of hyphal systems In this chapter I present an account of the ways in which fungal hyphal systems obtain, absorb, metabolise, reprocess and redistribute nutrients. The description is relatively brief and more details can be found in texts on fungal physiology, ...
... Chapter 3: Metabolism and biochemistry of hyphal systems In this chapter I present an account of the ways in which fungal hyphal systems obtain, absorb, metabolise, reprocess and redistribute nutrients. The description is relatively brief and more details can be found in texts on fungal physiology, ...
HUMAN BIOCHEMISTRY
... Proteins have many different functions in the body, from providing structure, to enzymes, to energy sources. We will consider several of them here. (1) Enzymes: All enzymes are globular proteins which catalyze biochemical reactions Amylase is an enzyme which catalyzes the breakup of starch into ...
... Proteins have many different functions in the body, from providing structure, to enzymes, to energy sources. We will consider several of them here. (1) Enzymes: All enzymes are globular proteins which catalyze biochemical reactions Amylase is an enzyme which catalyzes the breakup of starch into ...
programmed cell death in plant
... extracellular bacteria to fungi that are both intra- and extracellular. The notable features of several cloned R genes are that they have leucine-rich repeats that are suggestive of a domain that interacts with other proteins and a sequence that may encode a nucleotide-binding domain (82). Other pla ...
... extracellular bacteria to fungi that are both intra- and extracellular. The notable features of several cloned R genes are that they have leucine-rich repeats that are suggestive of a domain that interacts with other proteins and a sequence that may encode a nucleotide-binding domain (82). Other pla ...
The unique proline-rich domain of parotid proline
... 33 of PRP are deleted in the PRP∆T portion of the construct (Castle et al., 1992). PROPTH-PRP, encodes the same PTH segment attached to the N terminus (residue 17) of full-length PRP. Full-length PRP containing its native signal sequence and transition domain was included in some of the studies (Cas ...
... 33 of PRP are deleted in the PRP∆T portion of the construct (Castle et al., 1992). PROPTH-PRP, encodes the same PTH segment attached to the N terminus (residue 17) of full-length PRP. Full-length PRP containing its native signal sequence and transition domain was included in some of the studies (Cas ...
Discussion
... result does not correlate with the mRNA expression levels for the transfected clones, since clone 4-2 was shown to express more serglycin mRNA than clone 1-7 (figures 4-11.B and 4-12.A). The reason for this is not investigated in detail. However, it is important to note that the MDCK II cell line co ...
... result does not correlate with the mRNA expression levels for the transfected clones, since clone 4-2 was shown to express more serglycin mRNA than clone 1-7 (figures 4-11.B and 4-12.A). The reason for this is not investigated in detail. However, it is important to note that the MDCK II cell line co ...
tr-kit promotes the formation of a multimolecular complex composed
... the SH3 domain of Fyn is necessary for Fyn-dependent tyrosine phosphorylation of Sam68 (Shen et al., 1999). Once phosphorylated in the carboxyterminal region, Sam68 recruits the SH2 domains of PLCg1, Grb2 and Src-kinases themselves (Richard et al., 1995). Since these signaling proteins already inter ...
... the SH3 domain of Fyn is necessary for Fyn-dependent tyrosine phosphorylation of Sam68 (Shen et al., 1999). Once phosphorylated in the carboxyterminal region, Sam68 recruits the SH2 domains of PLCg1, Grb2 and Src-kinases themselves (Richard et al., 1995). Since these signaling proteins already inter ...
3.Cellular Sensing of Viral DNA and Viral Evasion Mechanisms.
... DAI-dependent antiviral cytokine expression as DAI−/− cells and mice responded normally to immunostimulatory DNA (28). Interestingly, DAI appears to have an effect on HSV infection independent of its putative DNA-sensing activity. DAI depletion resulted in enhanced HSV-1 replication due to increased ...
... DAI-dependent antiviral cytokine expression as DAI−/− cells and mice responded normally to immunostimulatory DNA (28). Interestingly, DAI appears to have an effect on HSV infection independent of its putative DNA-sensing activity. DAI depletion resulted in enhanced HSV-1 replication due to increased ...
Embryonic stem cell differentiation and the analysis of mammalian
... mented with MEDII (Fig. 1A; Rathjen et al., 2002). The formation ectoderm, EPL cells represent an important obligate intermediate of EPL cells occurs in the presence or absence of exogenous LIF, cell population in the differentiation of ES cells in culture. Establishbut as would be predicted from in ...
... mented with MEDII (Fig. 1A; Rathjen et al., 2002). The formation ectoderm, EPL cells represent an important obligate intermediate of EPL cells occurs in the presence or absence of exogenous LIF, cell population in the differentiation of ES cells in culture. Establishbut as would be predicted from in ...
Cyanidioschyzon merolae Genome. A Tool for
... 10D as the first complete algal genome. BLASTs and annotation results showed that C. merolae has a mixed gene repertoire of plants and animals, also implying a relationship with prokaryotes, although its photosynthetic components were comparable to other phototrophs. The unicellular green alga Chlam ...
... 10D as the first complete algal genome. BLASTs and annotation results showed that C. merolae has a mixed gene repertoire of plants and animals, also implying a relationship with prokaryotes, although its photosynthetic components were comparable to other phototrophs. The unicellular green alga Chlam ...
Protein Functional Annotation - Institute for Genome Sciences
... located 5-11 bp upstream of the start codon! - Similarity to match proteins, in BER and multiple alignments! (Remember to note, that the DNA sequence reads down in columns for each codon.)! -In the example below (showing just the beginning of one BER alignment), homology starts exactly at the first ...
... located 5-11 bp upstream of the start codon! - Similarity to match proteins, in BER and multiple alignments! (Remember to note, that the DNA sequence reads down in columns for each codon.)! -In the example below (showing just the beginning of one BER alignment), homology starts exactly at the first ...
The protein acetylome and the regulation of metabolism - Serval
... (Ard1) subunits, the N-Acetyl Transferase B complex (NatB) contains the subunits N-Acetyl Transferase 3 (Nat3) and Mitochondrial Distribution and Morphology 20 (Mdm20), while the N-Acetyl Transferase C complex (NatC) contains the Maintenance of Killer proteins Mak3, Mak10 and Mak31. Homologs to all ...
... (Ard1) subunits, the N-Acetyl Transferase B complex (NatB) contains the subunits N-Acetyl Transferase 3 (Nat3) and Mitochondrial Distribution and Morphology 20 (Mdm20), while the N-Acetyl Transferase C complex (NatC) contains the Maintenance of Killer proteins Mak3, Mak10 and Mak31. Homologs to all ...
The Plasma Membrane of the Cyanobacterium
... G. violaceus resembles an organism prior to the evolutionary development of the thylakoid membrane as an intracellular membrane compartment. Therefore, analyzing the cellular structure of G. violaceus may be valuable to define new concepts for the emergence of specialized membrane compartments and p ...
... G. violaceus resembles an organism prior to the evolutionary development of the thylakoid membrane as an intracellular membrane compartment. Therefore, analyzing the cellular structure of G. violaceus may be valuable to define new concepts for the emergence of specialized membrane compartments and p ...
The Plasma Membrane of the Cyanobacterium
... G. violaceus resembles an organism prior to the evolutionary development of the thylakoid membrane as an intracellular membrane compartment. Therefore, analyzing the cellular structure of G. violaceus may be valuable to define new concepts for the emergence of specialized membrane compartments and p ...
... G. violaceus resembles an organism prior to the evolutionary development of the thylakoid membrane as an intracellular membrane compartment. Therefore, analyzing the cellular structure of G. violaceus may be valuable to define new concepts for the emergence of specialized membrane compartments and p ...
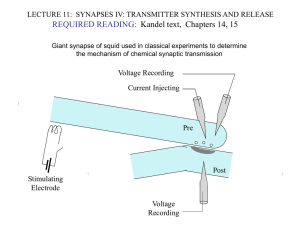
LECTURE11.SynapsesIV
... Synapsins restrain vesicles in a reserve pool. Synapsin phosphorylation by calcium/CAM-dependent protein kinase releases synapsin from vesicles. Synaptotagmin can bind to t-SNARE proteins SNAP25 and syntaxin, and also binds phospholipids in a calcium-dependent manner. ...
... Synapsins restrain vesicles in a reserve pool. Synapsin phosphorylation by calcium/CAM-dependent protein kinase releases synapsin from vesicles. Synaptotagmin can bind to t-SNARE proteins SNAP25 and syntaxin, and also binds phospholipids in a calcium-dependent manner. ...
Signal transduction
Signal transduction occurs when an extracellular signaling molecule activates a specific receptor located on the cell surface or inside the cell. In turn, this receptor triggers a biochemical chain of events inside the cell, creating a response. Depending on the cell, the response alters the cell's metabolism, shape, gene expression, or ability to divide. The signal can be amplified at any step. Thus, one signaling molecule can cause many responses.