L4 Prokaryotes eukaryotes and onion cheek preps
... • To understand the similarities and differences between Eukaryotes and Prokaryotes. • To be able to prepare, describe and draw a cheek cell slide preparation, onion cell slide preparation and plant material slides ...
... • To understand the similarities and differences between Eukaryotes and Prokaryotes. • To be able to prepare, describe and draw a cheek cell slide preparation, onion cell slide preparation and plant material slides ...
cell test review 15-16 - Mercer Island School District
... B. Understand the differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. C. Understand the hierarchy of multicellular organisms (what makes up what) atomsmolecules organellescells tissues organs organ systems multicellular organism D. Review your labs and understand the concepts that were ...
... B. Understand the differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. C. Understand the hierarchy of multicellular organisms (what makes up what) atomsmolecules organellescells tissues organs organ systems multicellular organism D. Review your labs and understand the concepts that were ...
Cell Membrane - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... outside of the cell and dispose of the wastes that build up inside of the cell. These processes occur through the cell membrane. Regulating what enters and exits the cell is the main function of the cell membrane. The cell membrane is made of two layers of lipids and a variety of protein molecules a ...
... outside of the cell and dispose of the wastes that build up inside of the cell. These processes occur through the cell membrane. Regulating what enters and exits the cell is the main function of the cell membrane. The cell membrane is made of two layers of lipids and a variety of protein molecules a ...
Presentazione di PowerPoint
... ionotropic glutamate receptors (NMDA receptors (NMDARs) and AMPA receptors (AMPARs)) and metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluR1 to mGluR8) on the membranes of both postsynaptic and presynaptic neurons and glial cells. Upon binding, the receptors initiate various responses, including membrane depol ...
... ionotropic glutamate receptors (NMDA receptors (NMDARs) and AMPA receptors (AMPARs)) and metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluR1 to mGluR8) on the membranes of both postsynaptic and presynaptic neurons and glial cells. Upon binding, the receptors initiate various responses, including membrane depol ...
Types of Signal Transmission
... 3. Release of the neurotransmitter into the synaptic cleft. 4. Binding and recognition of the neurotransmitter by target receptors. 4b. Binding of neurotransmitter to autoreceptors that regulate transmitter release, synthesis, or firing rate. Binding of ACh to autoreceptors on the presynaptic membra ...
... 3. Release of the neurotransmitter into the synaptic cleft. 4. Binding and recognition of the neurotransmitter by target receptors. 4b. Binding of neurotransmitter to autoreceptors that regulate transmitter release, synthesis, or firing rate. Binding of ACh to autoreceptors on the presynaptic membra ...
Molecular Cell Biology course 1BL320 Spring
... b) The cellular response to Erk activation depends on whether the activation is transient or sustained. Describe why a sustained Erk activation is necessary to promote cell cycle progression and why a transient burst of Erk activation fails to do so. (2p) c) Signaling pathways often lead to changes ...
... b) The cellular response to Erk activation depends on whether the activation is transient or sustained. Describe why a sustained Erk activation is necessary to promote cell cycle progression and why a transient burst of Erk activation fails to do so. (2p) c) Signaling pathways often lead to changes ...
The Cell Study Guide Vocabulary: Cell theory Cytoplasm Organelle
... Summarize the functions of organelles in plant and animal cells. Know how organelles can work together as a system. For example, ribosomes are made in the nucleolus, they exit through the pores in the nucleus and are found in the RER. Ribosomes are the site of protein synthesis, where amino acids ar ...
... Summarize the functions of organelles in plant and animal cells. Know how organelles can work together as a system. For example, ribosomes are made in the nucleolus, they exit through the pores in the nucleus and are found in the RER. Ribosomes are the site of protein synthesis, where amino acids ar ...
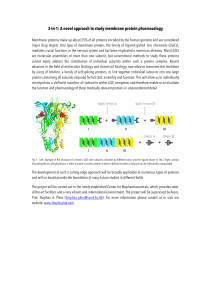
3-in-1: A novel approach to study membrane protein pharmacology
... 3-in-1: A novel approach to study membrane protein pharmacology Membrane proteins make up about 25% of all proteins encoded by the human genome and are considered major drug targets. One type of membrane protein, the family of ligand-gated ion channels (LGICs), mediates crucial functions in the nerv ...
... 3-in-1: A novel approach to study membrane protein pharmacology Membrane proteins make up about 25% of all proteins encoded by the human genome and are considered major drug targets. One type of membrane protein, the family of ligand-gated ion channels (LGICs), mediates crucial functions in the nerv ...
Now for the rest of the cell. - Saint Demetrios Astoria School
... • Isolates cell from outside environment • Regulates movement of molecules in and out of cell. • Permeable to small molecules and non-polar molecules; impermeable to polar molecules and ...
... • Isolates cell from outside environment • Regulates movement of molecules in and out of cell. • Permeable to small molecules and non-polar molecules; impermeable to polar molecules and ...
Cell Membrane Structure & Function
... Membranes are “fluid mosaics” with proteins embedded in or attached to the membrane ...
... Membranes are “fluid mosaics” with proteins embedded in or attached to the membrane ...
Protein Folding and Membrane Structure
... Fluid Mosaic Model of Biological Membranes • Singer and Nicolson (1972) synthesized a variety of results that implied the unit membrane is a fluid and contains proteins as integral components • Today we recognize fluidity restrictions and local membrane domains (Domain Mosaic Model) ...
... Fluid Mosaic Model of Biological Membranes • Singer and Nicolson (1972) synthesized a variety of results that implied the unit membrane is a fluid and contains proteins as integral components • Today we recognize fluidity restrictions and local membrane domains (Domain Mosaic Model) ...
Slide 1
... of the membrane and orient themselves AWAY from water •phospholipids form a bilayer; • cholesterol also found among fatty acid tails ...
... of the membrane and orient themselves AWAY from water •phospholipids form a bilayer; • cholesterol also found among fatty acid tails ...
Cell Organelle Notes worksheet
... 3-1 The Cell Theory A cell is defined as ______________________________________________________________ ________________________. Cells contain structures called ___________________________. This terms means tiny _________________________. Cells were first described by the English scientist ________ ...
... 3-1 The Cell Theory A cell is defined as ______________________________________________________________ ________________________. Cells contain structures called ___________________________. This terms means tiny _________________________. Cells were first described by the English scientist ________ ...
Anatomy of Cells
... • Penetrate into the hydrophobic regions of the plasma membrane • Transport mechanism • Transport proteins are often specific for certain molecules • “Gates” can open or close ...
... • Penetrate into the hydrophobic regions of the plasma membrane • Transport mechanism • Transport proteins are often specific for certain molecules • “Gates” can open or close ...
Chapter 2 - Regulation of protein activities
... cyclase, phosphodiesterase, phospholipases, ion channels and other proteins. Thus, the same hormone may elicit different responses in different cells by interacting with different downstream effectors. G-proteins are capable of eliciting a huge range of intracellular responses. A number of serious h ...
... cyclase, phosphodiesterase, phospholipases, ion channels and other proteins. Thus, the same hormone may elicit different responses in different cells by interacting with different downstream effectors. G-proteins are capable of eliciting a huge range of intracellular responses. A number of serious h ...
CELL MEMBRANE: Structure and Function
... Osmosis- the movement of water from an area of higher to lower concentration… or the movement of water from an area of low solute concentration to an area of high solute concentration. ...
... Osmosis- the movement of water from an area of higher to lower concentration… or the movement of water from an area of low solute concentration to an area of high solute concentration. ...
Lysosomes: Nickname: Job: Contains made by the ribosomes and
... 3. Smooth ER pinches off and the digestive enzymes is contained in the _____________________________. ...
... 3. Smooth ER pinches off and the digestive enzymes is contained in the _____________________________. ...
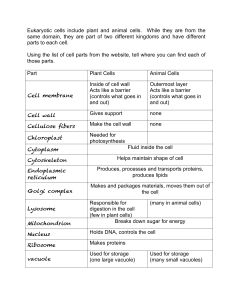
Cell membrane Cell wall Cellulose fibers Chloroplast Cytoplasm
... Eukaryotic cells include plant and animal cells. While they are from the same domain, they are part of two different kingdoms and have different parts to each cell. Using the list of cell parts from the website, tell where you can find each of those parts. Part ...
... Eukaryotic cells include plant and animal cells. While they are from the same domain, they are part of two different kingdoms and have different parts to each cell. Using the list of cell parts from the website, tell where you can find each of those parts. Part ...
cell organization
... called organelles. Cells (and organisms) depend on each organelle performing its specified task correctly within the cell. ...
... called organelles. Cells (and organisms) depend on each organelle performing its specified task correctly within the cell. ...
WKS 8.1 - Blair Community Schools
... 11. Why do proteins stay within the lipid bilayer of the cell membrane? _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ ____________________________________ ...
... 11. Why do proteins stay within the lipid bilayer of the cell membrane? _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ ____________________________________ ...
Signal transduction
Signal transduction occurs when an extracellular signaling molecule activates a specific receptor located on the cell surface or inside the cell. In turn, this receptor triggers a biochemical chain of events inside the cell, creating a response. Depending on the cell, the response alters the cell's metabolism, shape, gene expression, or ability to divide. The signal can be amplified at any step. Thus, one signaling molecule can cause many responses.