Week 18 - Crossroads Academy
... Some general concepts we will be covering: • Prokaryotic cells lack true nuclei and other bodies bound by membranes. • Eukaryotic cells contain membrane bound nuclei such as a nucleus. • The cytoplasm is a souplike fluid containing water, dissolved substances and many small organelles • The Endoplas ...
... Some general concepts we will be covering: • Prokaryotic cells lack true nuclei and other bodies bound by membranes. • Eukaryotic cells contain membrane bound nuclei such as a nucleus. • The cytoplasm is a souplike fluid containing water, dissolved substances and many small organelles • The Endoplas ...
cells jeopardy3
... A form of transport where the cell must expend energy to move a solute against a concentration ...
... A form of transport where the cell must expend energy to move a solute against a concentration ...
Organelles - Fcusd.org
... are made up on one or more cells. • 2. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in organisms. • 3. All cells arise from existing cells. ...
... are made up on one or more cells. • 2. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in organisms. • 3. All cells arise from existing cells. ...
Chapter 3 review
... What are cell recognition proteins? glycoproteins that help the body recognize self vs others and can help recognize invaders like bacteria ...
... What are cell recognition proteins? glycoproteins that help the body recognize self vs others and can help recognize invaders like bacteria ...
Chapter 5 - Dr. Jennifer Capers
... Toll in fruit flies ○ Mutation caused susceptibility to infection of ...
... Toll in fruit flies ○ Mutation caused susceptibility to infection of ...
Talks
... 2004, Mol. Biol. Cell 15:1374-1386). We hypothesize that this may involve altered localization of mitotic regulatory proteins to the spindle pole body (SPB). In collaboration with the laboratories of Dr. Michael Hynes and Dr. Stephen Osmani, we have developed a rapid and efficient gene targeting pro ...
... 2004, Mol. Biol. Cell 15:1374-1386). We hypothesize that this may involve altered localization of mitotic regulatory proteins to the spindle pole body (SPB). In collaboration with the laboratories of Dr. Michael Hynes and Dr. Stephen Osmani, we have developed a rapid and efficient gene targeting pro ...
Chapter 3 - Dr. Jennifer Capers
... Toll in fruit flies ○ Mutation caused susceptibility to infection of ...
... Toll in fruit flies ○ Mutation caused susceptibility to infection of ...
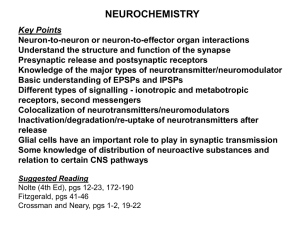
ionotropic and metabotropic receptors, second messengers
... Knowledge of the major types of neurotransmitter/neuromodulator Basic understanding of EPSPs and IPSPs Different types of signalling - ionotropic and metabotropic receptors, second messengers Colocalization of neurotransmitters/neuromodulators Inactivation/degradation/re-uptake of neurotransmitters ...
... Knowledge of the major types of neurotransmitter/neuromodulator Basic understanding of EPSPs and IPSPs Different types of signalling - ionotropic and metabotropic receptors, second messengers Colocalization of neurotransmitters/neuromodulators Inactivation/degradation/re-uptake of neurotransmitters ...
Receptor Protein
... nucleus of a cell. After receiving proteins from the endoplasmic reticulum, the main function of the golgi apparatus is to sort and process proteins. What this means is that “the golgi” modifies the proteins it receives so they can be sorted into the right vesicle. A vesicle is a small membrane boun ...
... nucleus of a cell. After receiving proteins from the endoplasmic reticulum, the main function of the golgi apparatus is to sort and process proteins. What this means is that “the golgi” modifies the proteins it receives so they can be sorted into the right vesicle. A vesicle is a small membrane boun ...
Proteins
... and the proteins are different because the shape and function of the cell are different! BUT, BUT, BUT! ALL proteins are made up of the same 20 Amino Acids! Just like our alphabet... 26 letters make up thousands of words! ...
... and the proteins are different because the shape and function of the cell are different! BUT, BUT, BUT! ALL proteins are made up of the same 20 Amino Acids! Just like our alphabet... 26 letters make up thousands of words! ...
The Endocrine System
... 2) The G protein is then activated 3) Activated G protein activates the effector enzyme adenylate cyclase 4) Adenylate cyclase generates cAMP from ATP 5) cAMP activates protein kinases (chemical reactions) ...
... 2) The G protein is then activated 3) Activated G protein activates the effector enzyme adenylate cyclase 4) Adenylate cyclase generates cAMP from ATP 5) cAMP activates protein kinases (chemical reactions) ...
bch221 tutorial kit - Covenant University
... Sugar Phosphates - monosaccharides found in several metabolic pathways that are often phosphorylated (i.e. converted to phosphate esters. E.g triose phosphate, dihydroxyacetone-phosphate and D-glyceraldehyde-phosphate, found in the Calvin cycle and glycolytic pathway. 8. Discuss the following: a. Mi ...
... Sugar Phosphates - monosaccharides found in several metabolic pathways that are often phosphorylated (i.e. converted to phosphate esters. E.g triose phosphate, dihydroxyacetone-phosphate and D-glyceraldehyde-phosphate, found in the Calvin cycle and glycolytic pathway. 8. Discuss the following: a. Mi ...
USA College of Medicine Cell Signaling Translational Research
... smooth muscle contraction, MAP kinase regulation of inflammation and cell motility, Actin binding proteins in smooth muscle contraction and regulation of cell motility, Small heat shock proteins and stress response, Nanoparticle drug delivery in therapy of pulmonary hypertension and asthma, ...
... smooth muscle contraction, MAP kinase regulation of inflammation and cell motility, Actin binding proteins in smooth muscle contraction and regulation of cell motility, Small heat shock proteins and stress response, Nanoparticle drug delivery in therapy of pulmonary hypertension and asthma, ...
In This Issue - The Journal of Cell Biology
... protein helps the defensive cells set their traps. During an infection or inflammation, dying neutrophils spill their DNA to form pathogentrapping NETs (neutrophil extracellular traps). This gooey material is one of the ingredients of pus. Unlike the chromatin in cells, the extracellular chromatin c ...
... protein helps the defensive cells set their traps. During an infection or inflammation, dying neutrophils spill their DNA to form pathogentrapping NETs (neutrophil extracellular traps). This gooey material is one of the ingredients of pus. Unlike the chromatin in cells, the extracellular chromatin c ...
MODELING THE CELL RECOGNITION PROCESS
... The recognition process is used by the cell to learn about its environment and is necessary for the viability and motility of singe cells but also tissues. The process is onset by the formation of ligand‐receptor bonds that form adhesion clusters. In the later stages, controlled by active regu ...
... The recognition process is used by the cell to learn about its environment and is necessary for the viability and motility of singe cells but also tissues. The process is onset by the formation of ligand‐receptor bonds that form adhesion clusters. In the later stages, controlled by active regu ...
Endocytosis and Exocytosis
... B9 - Describe the structure and function of the cell membrane: Describe and compare endocytosis and exocytosis in terms of: Method of transport (use of vesicles) Use of energy (active vs. passive) Type / size of molecule transported ...
... B9 - Describe the structure and function of the cell membrane: Describe and compare endocytosis and exocytosis in terms of: Method of transport (use of vesicles) Use of energy (active vs. passive) Type / size of molecule transported ...
Cell Organelle Card Sort
... The power producers of the cell. They take glucose and turn it into energy for the cell to use. ...
... The power producers of the cell. They take glucose and turn it into energy for the cell to use. ...
Chapter 7 A tour of the Cell - Foothill Technology High School
... micrometers in size •With membraneorganelles (endomembrane system) •Cell wall only in plants •Ex. Plants and animal cells ...
... micrometers in size •With membraneorganelles (endomembrane system) •Cell wall only in plants •Ex. Plants and animal cells ...
The main points that you should learn from the problems in øvelse 2
... rest of the protein is synthesized into the lumen of the ER (unless a transfer stop signal is present) (page 510). Proteins with a nuclear import signal are recognized by a receptor in the cytosol (page 505) and enter the nucleus through the nuclear pores. Proteins that shuttle between the nucleus a ...
... rest of the protein is synthesized into the lumen of the ER (unless a transfer stop signal is present) (page 510). Proteins with a nuclear import signal are recognized by a receptor in the cytosol (page 505) and enter the nucleus through the nuclear pores. Proteins that shuttle between the nucleus a ...
1. Cells PPT
... Cell Membrane Structures The cell membrane contains: 1. Two layers of phospholipids (isolate the cell from extracellular fluid) 2. Proteins (may attach cell membrane to other structures, recognize invaders, speed up chemical reactions, bind & transport certain substances) 3. Cholesterol (↑ stabilit ...
... Cell Membrane Structures The cell membrane contains: 1. Two layers of phospholipids (isolate the cell from extracellular fluid) 2. Proteins (may attach cell membrane to other structures, recognize invaders, speed up chemical reactions, bind & transport certain substances) 3. Cholesterol (↑ stabilit ...
Signal transduction
Signal transduction occurs when an extracellular signaling molecule activates a specific receptor located on the cell surface or inside the cell. In turn, this receptor triggers a biochemical chain of events inside the cell, creating a response. Depending on the cell, the response alters the cell's metabolism, shape, gene expression, or ability to divide. The signal can be amplified at any step. Thus, one signaling molecule can cause many responses.