Cell Communication
... When ligands (small molecules that bind specifically to a larger molecule) attach to the receptor protein, the receptor typically undergoes a change in shape • this may activate the receptor so that it can interact with other molecules ...
... When ligands (small molecules that bind specifically to a larger molecule) attach to the receptor protein, the receptor typically undergoes a change in shape • this may activate the receptor so that it can interact with other molecules ...
RECEPTORS STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION Chapter 4
... Neurotransmitters: Chemicals released from nerve endings which travel across a nerve synapse to bind with receptors on target cells, such as muscle cells or another nerve. Usually short lived and responsible for messages between individual cells Hormones: Chemicals released from cells or glands and ...
... Neurotransmitters: Chemicals released from nerve endings which travel across a nerve synapse to bind with receptors on target cells, such as muscle cells or another nerve. Usually short lived and responsible for messages between individual cells Hormones: Chemicals released from cells or glands and ...
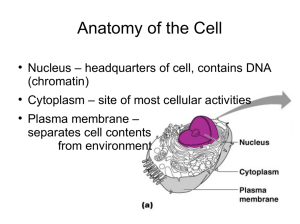
Cell Part Cell Structure and Function Mitochondria Nucleus
... Visible as pale area above nucleus. Has stacks of cisternae, is flat in the center, and is distended at the ends. Function is to provide concentration and packaging of secretory material, synthesis of substances rich in carbos, and production of lysosomes. ...
... Visible as pale area above nucleus. Has stacks of cisternae, is flat in the center, and is distended at the ends. Function is to provide concentration and packaging of secretory material, synthesis of substances rich in carbos, and production of lysosomes. ...
Fig. 4.3 - glenbrook s hs
... allows some substances to pass through, but blocks the passgae of other substances • Membranes enclose and maintain the specific chemical environment • Every membrane carries out its specific functions ...
... allows some substances to pass through, but blocks the passgae of other substances • Membranes enclose and maintain the specific chemical environment • Every membrane carries out its specific functions ...
Lecture 11: Cell proliferation, differentiation, and death
... Programmed cell death It is a normal physiological form of cell death with a distinct process known as apoptosis. It plays a key role both in the maintenance of adult tissues and in embryonic development. Renewal of 5 × 1011 blood cells a day elimination of nerve cells with faulty connection Elimin ...
... Programmed cell death It is a normal physiological form of cell death with a distinct process known as apoptosis. It plays a key role both in the maintenance of adult tissues and in embryonic development. Renewal of 5 × 1011 blood cells a day elimination of nerve cells with faulty connection Elimin ...
I Have, Who Has_Photosynthesis_CellResp
... structures that propel some cells through their environment? I have cytoskeleton. Who has an extensive system of internal membranes that move proteins? I have vesicle. ...
... structures that propel some cells through their environment? I have cytoskeleton. Who has an extensive system of internal membranes that move proteins? I have vesicle. ...
organelles
... reticulum (ER) is a complex, extensive network that transports materials throughout the inside of a cell. • Rough ER has ribosomes ...
... reticulum (ER) is a complex, extensive network that transports materials throughout the inside of a cell. • Rough ER has ribosomes ...
Gene7-26
... principle that the form bound to GDP is inactive, but the form bound to GTP is active. Receptor is a transmembrane protein, located in the plasma membrane, that binds a ligand in a domain on the extracellular side, and as a result has a change in activity of the cytoplasmic domain. (The same term is ...
... principle that the form bound to GDP is inactive, but the form bound to GTP is active. Receptor is a transmembrane protein, located in the plasma membrane, that binds a ligand in a domain on the extracellular side, and as a result has a change in activity of the cytoplasmic domain. (The same term is ...
Transduction Kit for Peptides and Proteins
... of the transduction cocktail contain a nuclear localization sequence and are therefore able to transport a cargo into the nucleus. The Kit further contains compounds for increasing rate and efficiency of transduction. DMSO enhances the permeability of cell membranes. BSA protects to some degree the ...
... of the transduction cocktail contain a nuclear localization sequence and are therefore able to transport a cargo into the nucleus. The Kit further contains compounds for increasing rate and efficiency of transduction. DMSO enhances the permeability of cell membranes. BSA protects to some degree the ...
Coordination and Regulation Check 4 (Solutions)
... more permeable to sodium ions which move into the cell. At this point, the inside of the membrane will have a positive charge compared to the outside. Once the impulse has passed, the ions involved are returned to their original position so the nerve is ready for another impulse. These changes are e ...
... more permeable to sodium ions which move into the cell. At this point, the inside of the membrane will have a positive charge compared to the outside. Once the impulse has passed, the ions involved are returned to their original position so the nerve is ready for another impulse. These changes are e ...
Slide ()
... Touch is mediated by four types of mechano receptors in the human hand. The terminals of myelinated sensory nerves innervating the hand are surrounded by specialized structures that detect contact on the skin. The receptors differ in morphology, innervation patterns, location in the skin, receptive ...
... Touch is mediated by four types of mechano receptors in the human hand. The terminals of myelinated sensory nerves innervating the hand are surrounded by specialized structures that detect contact on the skin. The receptors differ in morphology, innervation patterns, location in the skin, receptive ...
Document
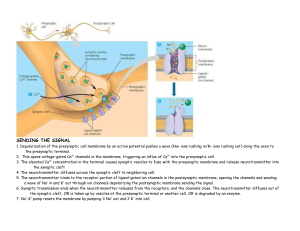
... 2. This opens voltage–gated Ca2+ channels in the membrane, triggering an influx of Ca2+ into the presynaptic cell. 3. The elevated Ca2+ concentration in the terminal causes synaptic vesicles to fuse with the presynaptic membrane and release neurotransmitter into the synaptic cleft 4. The neurotransm ...
... 2. This opens voltage–gated Ca2+ channels in the membrane, triggering an influx of Ca2+ into the presynaptic cell. 3. The elevated Ca2+ concentration in the terminal causes synaptic vesicles to fuse with the presynaptic membrane and release neurotransmitter into the synaptic cleft 4. The neurotransm ...
Chapter 11: Cell Communication - Biology E
... Intracellular receptors are found in either the cytoplasm or nucleus of target cells, where they bond to chemical messengers that are either hydrophobic enough (steroids, thyroid hormones) or small enough (nitric acid) to cross the hydrophobic interior of the membrane. [1] The steroid hormone testos ...
... Intracellular receptors are found in either the cytoplasm or nucleus of target cells, where they bond to chemical messengers that are either hydrophobic enough (steroids, thyroid hormones) or small enough (nitric acid) to cross the hydrophobic interior of the membrane. [1] The steroid hormone testos ...
Biology for Engineers: Cellular and Systems Neurophysiology
... • Metabotropic PSPs typically require multiple stimuli at high frequencies – 10 stimuli at 66 Hz (15 ms intervals) in these examples ...
... • Metabotropic PSPs typically require multiple stimuli at high frequencies – 10 stimuli at 66 Hz (15 ms intervals) in these examples ...
CELL MEMBRANES
... Draw another beaker 2/3 full of water Draw more molecules such that they are submerged and surrounded by water, but also able to contain water ...
... Draw another beaker 2/3 full of water Draw more molecules such that they are submerged and surrounded by water, but also able to contain water ...
Cell Review Cell Theory Levels of Organization Organelle
... M - Pre-existing cells make cells. L - All living organisms are made of cells B - Basic structure and function of life. ...
... M - Pre-existing cells make cells. L - All living organisms are made of cells B - Basic structure and function of life. ...
Abstract The cytoskeleton is a cellular structure comprised of three
... Abstract The cytoskeleton is a cellular structure comprised of three types of protein filaments called microfilaments, intermediate filaments and microtubules respectively. These filaments are highly dynamic and can change their organisation and properties according to the current needs of a cell. T ...
... Abstract The cytoskeleton is a cellular structure comprised of three types of protein filaments called microfilaments, intermediate filaments and microtubules respectively. These filaments are highly dynamic and can change their organisation and properties according to the current needs of a cell. T ...
Lysosome small round structures that break down large food
... Lysosome small round structures that break down large food molecules ...
... Lysosome small round structures that break down large food molecules ...
Lesson
... * Amino acid structure & properties * Stages involved with formation of proteins * Primary, secondary, tertiary & quaternary structures ...
... * Amino acid structure & properties * Stages involved with formation of proteins * Primary, secondary, tertiary & quaternary structures ...
CELLS QQ#2 (TOC#4) HW: CELLS Notes (TOC#5)
... Inner membrane • Embedded with proteins • Pores that serve as molecular channels that restricts passage of molecules except RNA and some proteins. ...
... Inner membrane • Embedded with proteins • Pores that serve as molecular channels that restricts passage of molecules except RNA and some proteins. ...
3. Facilitated Diffusion (Assisted diffusion) 4. Diffusion Through Ion
... __nonpolar interior ______________ of membrane some ion channels are always open; others open and close (gated channels) o opening/closing may be controlled by 1. membrane stretching 2. electrical signals 3. chemical signals examples of some common ions: ...
... __nonpolar interior ______________ of membrane some ion channels are always open; others open and close (gated channels) o opening/closing may be controlled by 1. membrane stretching 2. electrical signals 3. chemical signals examples of some common ions: ...
Signal transduction
Signal transduction occurs when an extracellular signaling molecule activates a specific receptor located on the cell surface or inside the cell. In turn, this receptor triggers a biochemical chain of events inside the cell, creating a response. Depending on the cell, the response alters the cell's metabolism, shape, gene expression, or ability to divide. The signal can be amplified at any step. Thus, one signaling molecule can cause many responses.