CellStructureFunction
... 1. Cell (plasma) membrane - barrier between inside and outside (skin) 2. Cytoplasm - organelles, free proteins, ions (guts) 3. Nucleus - Control center for decision-making, responding to environment and replicating genetic material (nervous system) ...
... 1. Cell (plasma) membrane - barrier between inside and outside (skin) 2. Cytoplasm - organelles, free proteins, ions (guts) 3. Nucleus - Control center for decision-making, responding to environment and replicating genetic material (nervous system) ...
Function
... phosphate “head” which is hydrophilic (waterloving) and two non-polar fatty-acid “tails” that are hydrophobic (water-fearing); arranged in a bilayer with the hydrophilic heads facing the inside and the outside of the cell – Fluid mosaic model – plasma membrane behaves more like a fluid than a solid; ...
... phosphate “head” which is hydrophilic (waterloving) and two non-polar fatty-acid “tails” that are hydrophobic (water-fearing); arranged in a bilayer with the hydrophilic heads facing the inside and the outside of the cell – Fluid mosaic model – plasma membrane behaves more like a fluid than a solid; ...
Cell Trafficking
... Integrins and receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) are cell surface receptors mediating biological functions such as cell survival, proliferation and cell migration. Integrins, through direct binding to extracellular molecules, provide a physical link between the cell cytoskeleton and the surrounding en ...
... Integrins and receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) are cell surface receptors mediating biological functions such as cell survival, proliferation and cell migration. Integrins, through direct binding to extracellular molecules, provide a physical link between the cell cytoskeleton and the surrounding en ...
Answers to Cells and Membrane Transport Quiz Review 1. Cells are
... 3. Prokaryotic cells do not have a nucleus and eukaryotic cells do. 4. Cell membrane 5. 1 - Endoplasmic reticulum 2 – Nucleus 3 – Mitochondria 4 – Cell Membrane 5 – Golgi body ...
... 3. Prokaryotic cells do not have a nucleus and eukaryotic cells do. 4. Cell membrane 5. 1 - Endoplasmic reticulum 2 – Nucleus 3 – Mitochondria 4 – Cell Membrane 5 – Golgi body ...
1 06 Parts of Cell E.. - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... Lysosomes patrol the cytoplasm, cleaning up. They contain special proteins that are used to break down large molecules into many smaller molecules. The smaller molecules can be reused as building blocks for other large molecules. In humans and other animals, lysosomes are also used to kill and diges ...
... Lysosomes patrol the cytoplasm, cleaning up. They contain special proteins that are used to break down large molecules into many smaller molecules. The smaller molecules can be reused as building blocks for other large molecules. In humans and other animals, lysosomes are also used to kill and diges ...
Quiz5ch5new.doc
... e. the phospholipids and proteins move from place to place within the bilayer 2. Which of the following types of molecules must pass through membranes via the aqueous pores formed by membrane proteins? a. gases such as carbon dioxide and ...
... e. the phospholipids and proteins move from place to place within the bilayer 2. Which of the following types of molecules must pass through membranes via the aqueous pores formed by membrane proteins? a. gases such as carbon dioxide and ...
Cell Membrane Nucleus Cytoplasm Cell Wall Ribosome Reticulum
... other materials from the ER. Packages them and distributes them to other parts of the cell stores water and nutrients needed by cell and also stores waste Contains enzymes (chemicals) to digest wastes, foods, and worn or damaged cells. ...
... other materials from the ER. Packages them and distributes them to other parts of the cell stores water and nutrients needed by cell and also stores waste Contains enzymes (chemicals) to digest wastes, foods, and worn or damaged cells. ...
Chapter 7-3
... ●Regulates what comes in and out of the cell ●Main components: proteins and phospholipids ...
... ●Regulates what comes in and out of the cell ●Main components: proteins and phospholipids ...
Cellular, Element, and Molecular Building Blocks of Living Systems
... • Provide a mechanism for storage of genetic information. ...
... • Provide a mechanism for storage of genetic information. ...
Printing – LAB Organic Molecule – Lipid
... 2. A wide variety of proteins are located in and around membranes. These proteins can associate with membranes in a variety of ways. 3. Integral proteins extend through one or both layers of the phospholipid bilayer. 4. Some proteins are attached to lipid molecules which anchor them to the membrane. ...
... 2. A wide variety of proteins are located in and around membranes. These proteins can associate with membranes in a variety of ways. 3. Integral proteins extend through one or both layers of the phospholipid bilayer. 4. Some proteins are attached to lipid molecules which anchor them to the membrane. ...
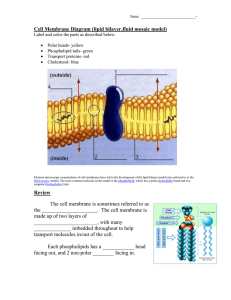
Cell Membrane Diagram (lipid bilayer,fluid mosaic model)
... Polar heads- yellow Phospholipid tails- green Transport proteins- red Cholesterol- blue ...
... Polar heads- yellow Phospholipid tails- green Transport proteins- red Cholesterol- blue ...
CH3- part2
... When cells die, lysosomes within burst open and enzymes are released into the cytosol. ◦ Enzymes digest organelles and nucleus of the cell (____________). ...
... When cells die, lysosomes within burst open and enzymes are released into the cytosol. ◦ Enzymes digest organelles and nucleus of the cell (____________). ...
BIOL108 LECTURE NOTES
... o Hydrogen bonding keeps water liquid – between 0 and 100C o Water is a universal solvent – facilitates chemical reactions o Hydrogen bonding gives water cohesion – used for transport o Hydrogen bonding means that large amounts of energy must be gained or lost for water temperature to change signifi ...
... o Hydrogen bonding keeps water liquid – between 0 and 100C o Water is a universal solvent – facilitates chemical reactions o Hydrogen bonding gives water cohesion – used for transport o Hydrogen bonding means that large amounts of energy must be gained or lost for water temperature to change signifi ...
Metabotropic Neurot
... Functional Roles for mGluR • All 3 classes inhibit L-type voltage sensitive Ca2+ channels • mGluR activation also closes K+ channels, leading to slow repolarization (prolong excitation) HPC and cortex • Opposite effect in cerebellum • Pre-synaptic mGluRs are inhibitory-on both Glutamate and GABA ne ...
... Functional Roles for mGluR • All 3 classes inhibit L-type voltage sensitive Ca2+ channels • mGluR activation also closes K+ channels, leading to slow repolarization (prolong excitation) HPC and cortex • Opposite effect in cerebellum • Pre-synaptic mGluRs are inhibitory-on both Glutamate and GABA ne ...
Cells - Seattle Central College
... Questions for the cell • What structure controls which proteins, lipids & RNA are produced and when? • Where do cells get Energy? Which structures harness is? • What structures move stuff around the cell? • Where are proteins and lipids built? • How does the cell move stuff in and out? • How does i ...
... Questions for the cell • What structure controls which proteins, lipids & RNA are produced and when? • Where do cells get Energy? Which structures harness is? • What structures move stuff around the cell? • Where are proteins and lipids built? • How does the cell move stuff in and out? • How does i ...
Diffusion/Osmosis
... Passive Transport-movement of any substance across a membrane w/o use of chemical energy Facilitated Diffusion: transport proteins help move materials across cell membrane Gated Channel: protein controlled opening (channel), some are permanently open ...
... Passive Transport-movement of any substance across a membrane w/o use of chemical energy Facilitated Diffusion: transport proteins help move materials across cell membrane Gated Channel: protein controlled opening (channel), some are permanently open ...
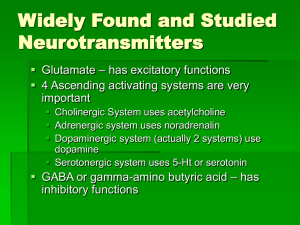
Widely Found and Studied Neurotransmitters
... block or enhance the reuptake and reuse of the neurotransmitter Altering the actions of second messegers ...
... block or enhance the reuptake and reuse of the neurotransmitter Altering the actions of second messegers ...
Widely Found and Studied Neurotransmitters
... • block or enhance the reuptake and reuse of the neurotransmitter • Altering the actions of second messegers ...
... • block or enhance the reuptake and reuse of the neurotransmitter • Altering the actions of second messegers ...
Team Publications
... The small GTP-binding protein ADP-ribosylation factor 6 (ARF6) controls the endocytic recycling pathway of several plasma membrane receptors. We analyzed the localization and GDP/GTP cycle of GFP-tagged ARF6 by total internal reflection fluorescent microscopy. We found that ARF6-GFP associates with cl ...
... The small GTP-binding protein ADP-ribosylation factor 6 (ARF6) controls the endocytic recycling pathway of several plasma membrane receptors. We analyzed the localization and GDP/GTP cycle of GFP-tagged ARF6 by total internal reflection fluorescent microscopy. We found that ARF6-GFP associates with cl ...
Lecture 9: Biological Pathway Simulation
... Peptides / Proteins- Growth Factors Amino acid derivatives - epinephrine, histamine Other small biomolecules - ATP Steroids, prostaglandins Gases - Nitric Oxide (NO) Photons Damaged DNA Odorants, tastants Signal = LIGAND Ligand- A molecule that binds to a specific site on another molecule, usually a ...
... Peptides / Proteins- Growth Factors Amino acid derivatives - epinephrine, histamine Other small biomolecules - ATP Steroids, prostaglandins Gases - Nitric Oxide (NO) Photons Damaged DNA Odorants, tastants Signal = LIGAND Ligand- A molecule that binds to a specific site on another molecule, usually a ...
P014 Using Simulation Cell Theory to Calculate the Thermody
... The association of molecules is of central importance in biology and pharmacology. Methods to predict the affinity of such associations would be of great practical value. However, entropic changes upon binding are difficult to estimate and are often neglected. Here we apply our recently developed me ...
... The association of molecules is of central importance in biology and pharmacology. Methods to predict the affinity of such associations would be of great practical value. However, entropic changes upon binding are difficult to estimate and are often neglected. Here we apply our recently developed me ...
File
... Inside the cell is a semi-fluid medium called the cytoplasm, composed of water, salts, and dissolved organic molecules. The cell membrane regulates the entrance and exit of molecules into and out of the cytoplasm. Cell Walls Some eukaryotic cells have permeable but protective cell walls in addition ...
... Inside the cell is a semi-fluid medium called the cytoplasm, composed of water, salts, and dissolved organic molecules. The cell membrane regulates the entrance and exit of molecules into and out of the cytoplasm. Cell Walls Some eukaryotic cells have permeable but protective cell walls in addition ...
CELLS
... take nutrients/energy from environment for their own use can repair themselves can reproduce Cell is an organized container of chemicals that behaves in a way that we say is living. 3 parts of the cell: ...
... take nutrients/energy from environment for their own use can repair themselves can reproduce Cell is an organized container of chemicals that behaves in a way that we say is living. 3 parts of the cell: ...
Signal transduction
Signal transduction occurs when an extracellular signaling molecule activates a specific receptor located on the cell surface or inside the cell. In turn, this receptor triggers a biochemical chain of events inside the cell, creating a response. Depending on the cell, the response alters the cell's metabolism, shape, gene expression, or ability to divide. The signal can be amplified at any step. Thus, one signaling molecule can cause many responses.