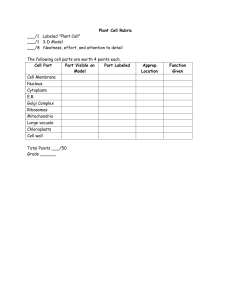
Anatomy of Plants
... • Site of protein synthesis • Two types: Rough ER has ribosomes and Smooth ER does not have ribosomes or very few. • Proteins produced by ribosomes are passed through the ER membrane into the ER lumen, where they are sealed in vesicles for transport to the cell organelles. ...
... • Site of protein synthesis • Two types: Rough ER has ribosomes and Smooth ER does not have ribosomes or very few. • Proteins produced by ribosomes are passed through the ER membrane into the ER lumen, where they are sealed in vesicles for transport to the cell organelles. ...
ppt - University of Kentucky
... many cases more than one type of cells; collectively perform all the functions of the organism. E.g. Higher plants and animals ...
... many cases more than one type of cells; collectively perform all the functions of the organism. E.g. Higher plants and animals ...
Nonspecific Immunity
... effectors produce antibodies or T cells which are antigen specific. This requires selection of effectors of appropriate specificity for clonal expansion before an effective response can be observed. In contrast, other immune responses can be evoked by infectious agents or injury in a generalized, an ...
... effectors produce antibodies or T cells which are antigen specific. This requires selection of effectors of appropriate specificity for clonal expansion before an effective response can be observed. In contrast, other immune responses can be evoked by infectious agents or injury in a generalized, an ...
Explain how cell size and shape affect the overall rate of nutrient
... Explain passive transport across membranes by simple diffusion and facilitated diffusion. Explain the role of protein pumps and ATP in active transport across membranes. Explain how vesicles are used to transport materials within a cell between the rough endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus and pl ...
... Explain passive transport across membranes by simple diffusion and facilitated diffusion. Explain the role of protein pumps and ATP in active transport across membranes. Explain how vesicles are used to transport materials within a cell between the rough endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus and pl ...
Cellular mechanotransduction: role of the nucleus Cells exploit
... Cells exploit traction forces to sense the physical characteristics of their microenvironments, which co-regulates a variety of cellular processes like stem cell differentiation, development and cancer progression. Mechanical forces, rising from the extracellular environment or from the contractile ...
... Cells exploit traction forces to sense the physical characteristics of their microenvironments, which co-regulates a variety of cellular processes like stem cell differentiation, development and cancer progression. Mechanical forces, rising from the extracellular environment or from the contractile ...
College 5
... All cells are enclosed in a plasma membrane. This container acts as a selective barrier that enables the cell to concentrate nutrients gathered from its environment and retain the products it has synthesized for its own use, while excreting waste products. Without its plasma membrane the cell could ...
... All cells are enclosed in a plasma membrane. This container acts as a selective barrier that enables the cell to concentrate nutrients gathered from its environment and retain the products it has synthesized for its own use, while excreting waste products. Without its plasma membrane the cell could ...
Ashley Ajayi
... nucleoli depending n the species and the stage in the cell’s reproductive cycle. Chromatin is material consisting of DNA and proteins. It is visible as individual chromosomes in a dividing cell. The Plasma membrane encloses the cell. Ribosomes are nonmembranous organelles that consist of ribosomal D ...
... nucleoli depending n the species and the stage in the cell’s reproductive cycle. Chromatin is material consisting of DNA and proteins. It is visible as individual chromosomes in a dividing cell. The Plasma membrane encloses the cell. Ribosomes are nonmembranous organelles that consist of ribosomal D ...
Name: ____________________________ ... Biology
... C. experience a decrease in turgor pressure. D. be at equilibrium. ...
... C. experience a decrease in turgor pressure. D. be at equilibrium. ...
Cells and Tissues - Mrs. Hille`s FunZone
... Cells are the building blocks of all living things Tissues are groups of cells that are similar in structure and function Anatomy of the Cell Cells are not all the same All cells share general structures Cells are organized into three main regions Nucleus Cytoplasm Plasma membrane ...
... Cells are the building blocks of all living things Tissues are groups of cells that are similar in structure and function Anatomy of the Cell Cells are not all the same All cells share general structures Cells are organized into three main regions Nucleus Cytoplasm Plasma membrane ...
Biol 178 Lecture 10
... “The proteins span the membrane with the polar regions on the outside and the non-polar regions on the inside”. ...
... “The proteins span the membrane with the polar regions on the outside and the non-polar regions on the inside”. ...
Organic Molecules - Riverdale Middle School
... – Cholesterol – found in your blood – Phosopholipids – make up cell membrane ...
... – Cholesterol – found in your blood – Phosopholipids – make up cell membrane ...
Biology- ch. 7
... – Chromatin: DNA bound to proteins – Nucleolus: ribosome assembly occurs here – Nuclear envelope: double membrane protecting the nucleus – Nuclear pores: holes in nuclear envelope that control substances passing into and out of nucleus ...
... – Chromatin: DNA bound to proteins – Nucleolus: ribosome assembly occurs here – Nuclear envelope: double membrane protecting the nucleus – Nuclear pores: holes in nuclear envelope that control substances passing into and out of nucleus ...
cell theory
... Huge in ________________cells, small in ___________ cells, NOT in ______________________ cells. ...
... Huge in ________________cells, small in ___________ cells, NOT in ______________________ cells. ...
Biochemistry Review Sheet
... 10. What is diffusion? 11. What is the difference between simple and facilitated diffusion? 12. What is osmosis? 13. Draw three cells: one surrounded by hypotonic solution, one surrounded by hypertonic solution, and one surrounded by isotonic solution. Label the direction of solute movement and wate ...
... 10. What is diffusion? 11. What is the difference between simple and facilitated diffusion? 12. What is osmosis? 13. Draw three cells: one surrounded by hypotonic solution, one surrounded by hypertonic solution, and one surrounded by isotonic solution. Label the direction of solute movement and wate ...
PDF datasheet
... *Heneberg P, Lebduska P, Draberova L, Korb J, Draber P: Topography of plasma membrane microdomains and its consequences for mast cell signaling. Eur J Immunol. 2006 Oct;36(10):2795-806. *Lebduska P, Korb J, Tůmová M, Heneberg P, Dráber P: Topography of signaling molecules as detected by electron mic ...
... *Heneberg P, Lebduska P, Draberova L, Korb J, Draber P: Topography of plasma membrane microdomains and its consequences for mast cell signaling. Eur J Immunol. 2006 Oct;36(10):2795-806. *Lebduska P, Korb J, Tůmová M, Heneberg P, Dráber P: Topography of signaling molecules as detected by electron mic ...
Human Liver Stem Cells for Assessing AhR
... human HepG2 and mouse Hepa1c1c7 hepatoma cell lines identified 75 genes and 18 orthologs common to HL1-1 cells, respectively. Further comparison of temporal gene expression in HL1-1 with hepatic tissue from immature ovariectomized C57BL/6 mice treated with 30 g/kg TCDD identified 32 commonly regula ...
... human HepG2 and mouse Hepa1c1c7 hepatoma cell lines identified 75 genes and 18 orthologs common to HL1-1 cells, respectively. Further comparison of temporal gene expression in HL1-1 with hepatic tissue from immature ovariectomized C57BL/6 mice treated with 30 g/kg TCDD identified 32 commonly regula ...
Organelle Notes
... Lecture, reading/chapter/novel/article during class, power point, movies (if need to collect info.) ...
... Lecture, reading/chapter/novel/article during class, power point, movies (if need to collect info.) ...
Study Guide I
... *Animal and plant cells are considered eukaryotic cells, while bacteria are considered prokaryotic cells that belong only to the kingdom “Monera”. *Living bacterial cells are considered prokaryotic cells because they only contain DNA without any nuclear envelope around it. *All living cells must con ...
... *Animal and plant cells are considered eukaryotic cells, while bacteria are considered prokaryotic cells that belong only to the kingdom “Monera”. *Living bacterial cells are considered prokaryotic cells because they only contain DNA without any nuclear envelope around it. *All living cells must con ...
News Release
... pharmaceutically effective peptides (small protein molecules) that are attached to tailor-made, geometric-like structures called “scaffolding.” Each scaffold is specifically designed to combine the peptides in such a way that they will form an effective medicinal combination and so that they will bi ...
... pharmaceutically effective peptides (small protein molecules) that are attached to tailor-made, geometric-like structures called “scaffolding.” Each scaffold is specifically designed to combine the peptides in such a way that they will form an effective medicinal combination and so that they will bi ...
Day 2: Protein Sequence Analysis
... Proteins destined for particular subcellular localizations have distinct amino acid properties particularly in their N-terminal regions. ...
... Proteins destined for particular subcellular localizations have distinct amino acid properties particularly in their N-terminal regions. ...
The Human Genome Project
... – Only about 2% of these code for proteins – One gene is able to code for many proteins – About 8 million single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) ...
... – Only about 2% of these code for proteins – One gene is able to code for many proteins – About 8 million single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) ...
Signal transduction
Signal transduction occurs when an extracellular signaling molecule activates a specific receptor located on the cell surface or inside the cell. In turn, this receptor triggers a biochemical chain of events inside the cell, creating a response. Depending on the cell, the response alters the cell's metabolism, shape, gene expression, or ability to divide. The signal can be amplified at any step. Thus, one signaling molecule can cause many responses.