7 3-2DR - Groupfusion.net
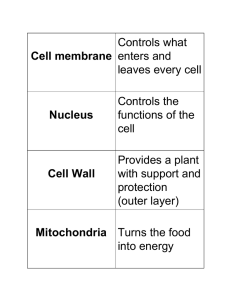
... ____ 9.What is the genetic material contained inside a cell’s nucleus? a. protein c. DNA b. lipids d. nucleolus _____ 10. The function of proteins in a cell is to a. control chemical reactions. c. cover the nucleus. b. store genetic information. d. copy messages from DNA. _____ 11. What is the nucle ...
... ____ 9.What is the genetic material contained inside a cell’s nucleus? a. protein c. DNA b. lipids d. nucleolus _____ 10. The function of proteins in a cell is to a. control chemical reactions. c. cover the nucleus. b. store genetic information. d. copy messages from DNA. _____ 11. What is the nucle ...
Directed Reading A
... ____9.What is the genetic material contained inside a cell’s nucleus? a. protein c. DNA b. lipids d. nucleolus _____ 10. The function of proteins in a cell is to a. control chemical reactions. c. cover the nucleus. b. store genetic information. d. copy messages from DNA. _____ 11. What is the nucleo ...
... ____9.What is the genetic material contained inside a cell’s nucleus? a. protein c. DNA b. lipids d. nucleolus _____ 10. The function of proteins in a cell is to a. control chemical reactions. c. cover the nucleus. b. store genetic information. d. copy messages from DNA. _____ 11. What is the nucleo ...
LEARNING GOALS - Cell Membranes
... Passive transport plays a primary role in the import of resources and the export of wastes. Membrane proteins play a role in facilitated diffusion of charged and polar molecules through a membrane. (Examples include glucose transport and Na+/K+ transport.) 3. External environments can be hypotonic, ...
... Passive transport plays a primary role in the import of resources and the export of wastes. Membrane proteins play a role in facilitated diffusion of charged and polar molecules through a membrane. (Examples include glucose transport and Na+/K+ transport.) 3. External environments can be hypotonic, ...
1. Cells have selectively permeable membranes that regulate what
... 6. Photosynthesis is the process that plants and other organisms (algae and some bacteria) use to convert light energy into chemical energy or sugars to be used as food. 7. Organisms that can’t make their own food are consumers/heterotrophs. 8. 2 products of photosynthesis are oxygen and glucose (su ...
... 6. Photosynthesis is the process that plants and other organisms (algae and some bacteria) use to convert light energy into chemical energy or sugars to be used as food. 7. Organisms that can’t make their own food are consumers/heterotrophs. 8. 2 products of photosynthesis are oxygen and glucose (su ...
Honors Biology Midterm Chapters and Topics 2014
... Types of microscopes and why they are used Prokaryotes verses Eukaryotes Comparing plant and animal cells Cell structures and functions Chapter 5 The Working Cell Plasma membrane structure and function Passive transport o Diffusion o Facilitated diffusion o Osmosis: hypotonic, hypertonic, isotonic s ...
... Types of microscopes and why they are used Prokaryotes verses Eukaryotes Comparing plant and animal cells Cell structures and functions Chapter 5 The Working Cell Plasma membrane structure and function Passive transport o Diffusion o Facilitated diffusion o Osmosis: hypotonic, hypertonic, isotonic s ...
Tutorial 7 – Secretory Pathway
... look at cell processes. • A labeled molecule can be located because its radioactivity develops the silver grains on a photographic emulsion. ...
... look at cell processes. • A labeled molecule can be located because its radioactivity develops the silver grains on a photographic emulsion. ...
Chemical Senses
... the equivalent of the vertebrate olfactory bulb. As you can see, the AL is composed of spheroidal structures, the glomeruli. While vertebrate olfactory bulbs may contain thousands of glomeruli, the fly AL contains only ~43 glomeruli. Furthermore, each glomerulus is uniquely identifiable, based on it ...
... the equivalent of the vertebrate olfactory bulb. As you can see, the AL is composed of spheroidal structures, the glomeruli. While vertebrate olfactory bulbs may contain thousands of glomeruli, the fly AL contains only ~43 glomeruli. Furthermore, each glomerulus is uniquely identifiable, based on it ...
Test questions used for assessment
... a. hydrophobic tails in the lipid bilayer stop water soluble molecules from passing, but allow water itself to get through b. proteins may function as channels, receptors, and enzymes c. carbohydrates are important in recognition of self and are sometimes part of CAMs d. all of the above e. b and c ...
... a. hydrophobic tails in the lipid bilayer stop water soluble molecules from passing, but allow water itself to get through b. proteins may function as channels, receptors, and enzymes c. carbohydrates are important in recognition of self and are sometimes part of CAMs d. all of the above e. b and c ...
Cell Structure and Function
... 10. The structure separating the interior of a cell from the outside environment. It is a semipermeable lipid bilayer found in all cells. 12. A threadlike, gene-carrying structure found in the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell. 13. Plural. An organelle in eukaryotic cells where cellular respiration occur ...
... 10. The structure separating the interior of a cell from the outside environment. It is a semipermeable lipid bilayer found in all cells. 12. A threadlike, gene-carrying structure found in the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell. 13. Plural. An organelle in eukaryotic cells where cellular respiration occur ...
Eukaryotic cells Section review model answers Ribosomes are
... series of folded membranes on which lipids, proteins, and other materials are made, and through which those materials are delivered to other places in the cell. 4. Plant cells have cell walls, but animal cells do not. Plant cells have chloroplasts, which animal cells do not have. Plant cells do not ...
... series of folded membranes on which lipids, proteins, and other materials are made, and through which those materials are delivered to other places in the cell. 4. Plant cells have cell walls, but animal cells do not. Plant cells have chloroplasts, which animal cells do not have. Plant cells do not ...
MICRONUCLEUS FORMATION AND CELL PROLIFERATION IN A
... e.g. use of high-LET new particle beams like carbon ions. To date, however, our knowledge regarding the importance of DNA DSB repair proteins and mechanisms in the response of human cells to high-LET radiation, is far from being complete. In this study we investigated the role of BRCA1 and 2, both i ...
... e.g. use of high-LET new particle beams like carbon ions. To date, however, our knowledge regarding the importance of DNA DSB repair proteins and mechanisms in the response of human cells to high-LET radiation, is far from being complete. In this study we investigated the role of BRCA1 and 2, both i ...
Cell Membrane
... The polar head is hydrophilic and likes water molecules. hydro = water Philic = loving ...
... The polar head is hydrophilic and likes water molecules. hydro = water Philic = loving ...
Cell Mates
... ● Job: perform _______________________________ ● ___________________________ molecules _____________________ sunlight, and convert water and CO2 into ________________. ● _____________________________ theory: were once free living organisms that became parts of modern cells. ...
... ● Job: perform _______________________________ ● ___________________________ molecules _____________________ sunlight, and convert water and CO2 into ________________. ● _____________________________ theory: were once free living organisms that became parts of modern cells. ...
Facile Kinase Activation with Membrane Permeable Small
... Facile Kinase Activation with Membrane Permeable Small Molecules ...
... Facile Kinase Activation with Membrane Permeable Small Molecules ...
Recombinant Human Neuregulin-1 (rh NRG-1)
... Recombinant Human Neuregulin-1 (rh NRG-1) Synonyms: Heregulin-β-1(HRG-b1) Introduction: Neuregulin/Heregulin is a family of structurally related polypeptide growth factors derived from alternatively spliced genes (NRG-1, NRG-2, NRG-3 and NRG-4). To date, there are over 14 soluble and transmembrane p ...
... Recombinant Human Neuregulin-1 (rh NRG-1) Synonyms: Heregulin-β-1(HRG-b1) Introduction: Neuregulin/Heregulin is a family of structurally related polypeptide growth factors derived from alternatively spliced genes (NRG-1, NRG-2, NRG-3 and NRG-4). To date, there are over 14 soluble and transmembrane p ...
Biological (organic) Molecules
... Simple sugars: monosaccharides Complex carbohydrates: disaccharides or polysaccharides ...
... Simple sugars: monosaccharides Complex carbohydrates: disaccharides or polysaccharides ...
Unit 5 Free Response
... DNA is the hereditary material. 2. 2000 Information transfer is fundamental to all living organism. For two of the following examples, explain in detail how the transfer of information is accomplished. a. The genetic material in one cell is copied and distributed to two identical daughter cells. b. ...
... DNA is the hereditary material. 2. 2000 Information transfer is fundamental to all living organism. For two of the following examples, explain in detail how the transfer of information is accomplished. a. The genetic material in one cell is copied and distributed to two identical daughter cells. b. ...
Slide ()
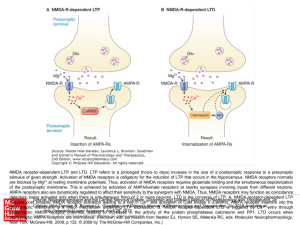
... NMDA receptor-dependent LTP and LTD. LTP refers to a prolonged (hours to days) increase in the size of a postsynaptic response to a presynaptic stimulus of given strength. Activation of NMDA receptors is obligatory for the induction of LTP that occurs in the hippocampus. NMDA receptors normally are ...
... NMDA receptor-dependent LTP and LTD. LTP refers to a prolonged (hours to days) increase in the size of a postsynaptic response to a presynaptic stimulus of given strength. Activation of NMDA receptors is obligatory for the induction of LTP that occurs in the hippocampus. NMDA receptors normally are ...
Transport across cell membranes
... vacuole as it is forming, and DYNAMIN ( a GTP-binding protein) causes the pinching-off of the vesicle’s neck This plays a role in internalizing many receptors and the ligands bound to them, as well as internalising low-density lipoprotein ...
... vacuole as it is forming, and DYNAMIN ( a GTP-binding protein) causes the pinching-off of the vesicle’s neck This plays a role in internalizing many receptors and the ligands bound to them, as well as internalising low-density lipoprotein ...
Workshop IV Signal Transduction Chair: Miguel Peñalva 100
... exposed to a highly variable environment with significant changes affecting, temperature, pH, oxygen, andwater and nutrient availability. Many of these changes occur during Trichoderma life cycle, triggering specific stress responses to external factors. In some cases, stress-related responses can a ...
... exposed to a highly variable environment with significant changes affecting, temperature, pH, oxygen, andwater and nutrient availability. Many of these changes occur during Trichoderma life cycle, triggering specific stress responses to external factors. In some cases, stress-related responses can a ...
Signal transduction
Signal transduction occurs when an extracellular signaling molecule activates a specific receptor located on the cell surface or inside the cell. In turn, this receptor triggers a biochemical chain of events inside the cell, creating a response. Depending on the cell, the response alters the cell's metabolism, shape, gene expression, or ability to divide. The signal can be amplified at any step. Thus, one signaling molecule can cause many responses.