Activated T cells
... Activated T cells In this video we can see a T cell that becomes activate when interacts with a dendritic cell. The T cell is label with a dye, the fluorescent when it binds calcium ions at the moment the T cell is not activated, its intracellular calcium concentrations are low and so little green f ...
... Activated T cells In this video we can see a T cell that becomes activate when interacts with a dendritic cell. The T cell is label with a dye, the fluorescent when it binds calcium ions at the moment the T cell is not activated, its intracellular calcium concentrations are low and so little green f ...
Cell Wall
... Prokaryotic Cells • Lack membrane bound nucleus • DNA found in nucleoid region • Like many eukaryotic cells, these cells have cell walls, plasma membranes, flagella and ribosomes • Unlike eukaryotic cells, they may have a capsule and pili ...
... Prokaryotic Cells • Lack membrane bound nucleus • DNA found in nucleoid region • Like many eukaryotic cells, these cells have cell walls, plasma membranes, flagella and ribosomes • Unlike eukaryotic cells, they may have a capsule and pili ...
cell structure review sheet
... List and explain the characteristics of life. Discuss 3 main differences between plant and animal cells. Fill in the chart and be able to identify the organelles on a plant or animal cell diagram: CELL ORGANELLE ...
... List and explain the characteristics of life. Discuss 3 main differences between plant and animal cells. Fill in the chart and be able to identify the organelles on a plant or animal cell diagram: CELL ORGANELLE ...
Notes-Organelles - Svetz-wiki
... --flattened stacks of membranes --functions in collection, packaging and distribution of molecules made in the cell and used elsewhere -- front end (cis) faces the ER, and the back end (trans) faces the cell membrane --the folded stacks are called cisternae --unprocessed proteins enter the Golgi app ...
... --flattened stacks of membranes --functions in collection, packaging and distribution of molecules made in the cell and used elsewhere -- front end (cis) faces the ER, and the back end (trans) faces the cell membrane --the folded stacks are called cisternae --unprocessed proteins enter the Golgi app ...
Name Cell Parts Section
... The ____________ is the combination of the ____________ and the organelles that float within this watery substance. Each _____________ carries out a specific function within the cell. Read What are cell proteins? and answer the questions below. Proteins are built from _______ _________. There are __ ...
... The ____________ is the combination of the ____________ and the organelles that float within this watery substance. Each _____________ carries out a specific function within the cell. Read What are cell proteins? and answer the questions below. Proteins are built from _______ _________. There are __ ...
Cell Power Point Questions
... 2) ___________ came up with the term cells. 3) ___________ was the first to record observations of what we know as bacteria from the plaque of teeth and he called these ____________. 4) The three scientists that contributed to cell theory are: - _______________ - _______________ - _______________ 5) ...
... 2) ___________ came up with the term cells. 3) ___________ was the first to record observations of what we know as bacteria from the plaque of teeth and he called these ____________. 4) The three scientists that contributed to cell theory are: - _______________ - _______________ - _______________ 5) ...
Intro to Cells / Microscopes
... • Prokaryotes - no true nucleus – DNA is not separated from the rest of the cell (no nuclear membrane) but is concentrated in a nucleoid region ...
... • Prokaryotes - no true nucleus – DNA is not separated from the rest of the cell (no nuclear membrane) but is concentrated in a nucleoid region ...
the study of cells - Greer Middle College
... Cells have two main parts - NUCLEUS & CYTOPLASM, Enclosed in a CELL MEMBRANE (also called PLASMA MEMBRANE), which is extremely thin, often has folds and pouches, and allows certain substances to pass through it. _______________________ = controls what enters and leaves the cell, it allows some thing ...
... Cells have two main parts - NUCLEUS & CYTOPLASM, Enclosed in a CELL MEMBRANE (also called PLASMA MEMBRANE), which is extremely thin, often has folds and pouches, and allows certain substances to pass through it. _______________________ = controls what enters and leaves the cell, it allows some thing ...
Cell organelle powerpoint
... Mitochondrion is like a crankshaft because it helps turn the motor and give it power ...
... Mitochondrion is like a crankshaft because it helps turn the motor and give it power ...
Cellular Biology Crossword
... organelles called ribosomes to produce proteins from amino acids. 14 - Protein packaging plant -Sends vesicles of macromolecules to destination in cell. ...
... organelles called ribosomes to produce proteins from amino acids. 14 - Protein packaging plant -Sends vesicles of macromolecules to destination in cell. ...
BIOL 150 - HCC Learning Web
... 25. The process that uses energy to move molecules or ions across a concentration gradient from an area of lower concentration to an area of higher concentration is called? ...
... 25. The process that uses energy to move molecules or ions across a concentration gradient from an area of lower concentration to an area of higher concentration is called? ...
The spreading out of particles from an area of high concentration to
... The remains of plants and animals made from the gradual replacement of hard parts with minerals (or from casts and impressions or, by preservation when no decay occurs). ...
... The remains of plants and animals made from the gradual replacement of hard parts with minerals (or from casts and impressions or, by preservation when no decay occurs). ...
review-cell-structur..
... 17. The small, membrane-bound structures inside a cell are ____________________. 18. In a typical animal cell, the nuclear sap and nucleolus occupies the area (above, inside, surrounding, outside, adjacent to) the nucleus. 19. Cells that have the same function are organized into (tissues, organs, or ...
... 17. The small, membrane-bound structures inside a cell are ____________________. 18. In a typical animal cell, the nuclear sap and nucleolus occupies the area (above, inside, surrounding, outside, adjacent to) the nucleus. 19. Cells that have the same function are organized into (tissues, organs, or ...
Mitochondrion 2
... • Main function is to produce energy in the form of ATP • Adenosine Triphosphate • Formed by metabolizing sugar • Cellular respiration • Oxidative metabolism • Proteins on inner membrane carry out this process ...
... • Main function is to produce energy in the form of ATP • Adenosine Triphosphate • Formed by metabolizing sugar • Cellular respiration • Oxidative metabolism • Proteins on inner membrane carry out this process ...
Name: Date: Block: Science 8 Chapter 1 Review Answer the
... Answer the following questions in full sentences on a separate piece of lined paper. 1. What are the 5 characteristics of living things? 2. What is the cell theory? 3. What is the field of view? Which objective lens will show you the greatest field of view? 4. What is the nucleus of a cell? 5. Expla ...
... Answer the following questions in full sentences on a separate piece of lined paper. 1. What are the 5 characteristics of living things? 2. What is the cell theory? 3. What is the field of view? Which objective lens will show you the greatest field of view? 4. What is the nucleus of a cell? 5. Expla ...
diffusion
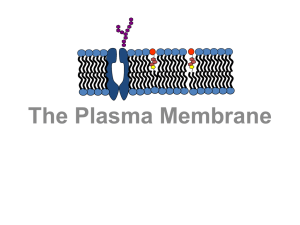
... The theory by which the properties of the plasma membrane are explained Mosaic: mixture of phospholipids, sterols (cholesterol), proteins, glycoproteins Fluid: the components are not fixed in place and may move or shift but are kept ordered due to hydrophobic forces ...
... The theory by which the properties of the plasma membrane are explained Mosaic: mixture of phospholipids, sterols (cholesterol), proteins, glycoproteins Fluid: the components are not fixed in place and may move or shift but are kept ordered due to hydrophobic forces ...
Cell Biology
... The movement of a molecules down a concentration gradient from a high concentration to a lower concentration. • Diffusion is an example of passive transport; Passive transport is the movement of molecules down a concentration gradient from a high concentration to a lower concentration, and does not ...
... The movement of a molecules down a concentration gradient from a high concentration to a lower concentration. • Diffusion is an example of passive transport; Passive transport is the movement of molecules down a concentration gradient from a high concentration to a lower concentration, and does not ...
CELL TRANSPORT - Oncourse : Gateway : Home
... Plasmolysis – loss of turgor pressure Plants wilt ...
... Plasmolysis – loss of turgor pressure Plants wilt ...
the cell lab2 part 1 and 2
... • (1839)Theodor Schwann & Matthias Schleiden “ all living things are made of cells” • (50 yrs. later) Rudolf Virchow “all cells come from cells” ...
... • (1839)Theodor Schwann & Matthias Schleiden “ all living things are made of cells” • (50 yrs. later) Rudolf Virchow “all cells come from cells” ...
Lecture 11
... Inactive protein kinase A Active protein kinase A (104) Inactive phosphorylase kinase Active phosphorylase kinase (105) Inactive glycogen phosphorylase ...
... Inactive protein kinase A Active protein kinase A (104) Inactive phosphorylase kinase Active phosphorylase kinase (105) Inactive glycogen phosphorylase ...
G-protein coupled receptor over-expression in
... GPCRs are the single largest protein family in the mammalian genome, and the largest class of drug targets. Unfortunately, they are only available in minute quantities in the cell (typically less than 0.1% of the protein complement). It is therefore recognised by the scientific community that the on ...
... GPCRs are the single largest protein family in the mammalian genome, and the largest class of drug targets. Unfortunately, they are only available in minute quantities in the cell (typically less than 0.1% of the protein complement). It is therefore recognised by the scientific community that the on ...
Slide 1
... Diverse molecular families control the growth and guidance of developing axons. A. A large family of classical cadherins promote cell and axonal adhesion, primarily through homophilic interactions between cadherin molecules on adjacent neurons. Adhesive interactions are mediated through interactions ...
... Diverse molecular families control the growth and guidance of developing axons. A. A large family of classical cadherins promote cell and axonal adhesion, primarily through homophilic interactions between cadherin molecules on adjacent neurons. Adhesive interactions are mediated through interactions ...
Signal transduction
Signal transduction occurs when an extracellular signaling molecule activates a specific receptor located on the cell surface or inside the cell. In turn, this receptor triggers a biochemical chain of events inside the cell, creating a response. Depending on the cell, the response alters the cell's metabolism, shape, gene expression, or ability to divide. The signal can be amplified at any step. Thus, one signaling molecule can cause many responses.