Immunology Lab
... Specificity of B and T cells depends on their ability to recognize ___________ ______________. They have the ability to do this because their surface is covered with 10,000 to 100,000 __________________________ receptors. All of these receptors on a specific B cell are identical; thus, the cells bin ...
... Specificity of B and T cells depends on their ability to recognize ___________ ______________. They have the ability to do this because their surface is covered with 10,000 to 100,000 __________________________ receptors. All of these receptors on a specific B cell are identical; thus, the cells bin ...
INTRODUCTION TO THE CELL NOTES
... 3. Describe the relationship between a cell’s shape and its function. ...
... 3. Describe the relationship between a cell’s shape and its function. ...
“The Physiology of Excitable Cells”
... we follow the trajectories of interacting ions in the potassium channel. With a fast supercomputer, we simulate the motion of 26 potassium ions and 26 chloride ions interacting through the intermolecular potential. Here we apply a potential difference across the channel such that inside is positive ...
... we follow the trajectories of interacting ions in the potassium channel. With a fast supercomputer, we simulate the motion of 26 potassium ions and 26 chloride ions interacting through the intermolecular potential. Here we apply a potential difference across the channel such that inside is positive ...
Final Review- Semester 1
... bisphosphate (RuBP) carboxylase, reduction of glycerate 3-phosphate (OP) to triose phosphate (TP), NADPH + H, ATP, regeneration of RuBP and synthesis of carbohydrates (glucose). ...
... bisphosphate (RuBP) carboxylase, reduction of glycerate 3-phosphate (OP) to triose phosphate (TP), NADPH + H, ATP, regeneration of RuBP and synthesis of carbohydrates (glucose). ...
File osmosis @ diffusion guided notes 6b
... 3. Active ________________Diffusion – is the process by which _________________________ of __________________________ to an area of lower concentration – diffusion is the main method by which small molecules move across the cell membrane! What causes diffusion? Molecules are always moving and as a r ...
... 3. Active ________________Diffusion – is the process by which _________________________ of __________________________ to an area of lower concentration – diffusion is the main method by which small molecules move across the cell membrane! What causes diffusion? Molecules are always moving and as a r ...
Exam 1 Fa08 Key
... 21. How do scientists know that all life is linked evolutionarily (e.g., what are some characteristics that are shared by all forms of known life)? (3 pts) [You must have at least mentioned DNA - all organisms have DNA built from the same 4 nucleic acids. You may also have mentioned a very similar b ...
... 21. How do scientists know that all life is linked evolutionarily (e.g., what are some characteristics that are shared by all forms of known life)? (3 pts) [You must have at least mentioned DNA - all organisms have DNA built from the same 4 nucleic acids. You may also have mentioned a very similar b ...
Biology-The study of the life
... * Biology : the study of the life or a natural science concerned with the study of life and living organisms, including their structure, function, growth, origin, evolution, distribution, and taxonomy. * Discovery of Cells: Robert Hooke and Anton Van Leeuwenhoek * Two fundamental classes of Cells: 1 ...
... * Biology : the study of the life or a natural science concerned with the study of life and living organisms, including their structure, function, growth, origin, evolution, distribution, and taxonomy. * Discovery of Cells: Robert Hooke and Anton Van Leeuwenhoek * Two fundamental classes of Cells: 1 ...
Unit 3 Powerpoint
... •Tissue is called tumor, growth, neoplasm •Oncology – The study of •Cancerous is called malignant •Non-cancerous is benign – does not spread to other parts and may be removed ...
... •Tissue is called tumor, growth, neoplasm •Oncology – The study of •Cancerous is called malignant •Non-cancerous is benign – does not spread to other parts and may be removed ...
Homework Exercise 6 1(a). Name the “building blocks” of a protein
... 3. Are proteins that control all of the reactions taking place in a cell. ...
... 3. Are proteins that control all of the reactions taking place in a cell. ...
3 - Coastalzone
... All organisms are composed of one or more cells. The cell is the basic living unit of organization for all living things All cells arise from preexisting cells Cells contain all of the hereditary information 3 basic structures of all cell types: 1. plasma membrane - a physical boundary that separate ...
... All organisms are composed of one or more cells. The cell is the basic living unit of organization for all living things All cells arise from preexisting cells Cells contain all of the hereditary information 3 basic structures of all cell types: 1. plasma membrane - a physical boundary that separate ...
Skills Worksheet
... 3. What is diffusion? Why is diffusion an example of passive transport? _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ ____________________________________ ...
... 3. What is diffusion? Why is diffusion an example of passive transport? _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ ____________________________________ ...
Cell parts practice
... and leaves the cell ______ Found outside of the cell membrane in plants & bacteria; provides support & protection ...
... and leaves the cell ______ Found outside of the cell membrane in plants & bacteria; provides support & protection ...
STUDY GUIDE Cells/Membrane Transport Cell Organelles What`s
... ● Why do scientists think mitochondria were once freeliving organisms? they contain their own DNA and have 2 membranes ...
... ● Why do scientists think mitochondria were once freeliving organisms? they contain their own DNA and have 2 membranes ...
TOPIC 2: Cells and Cellular Organization Please use the Khan
... TOPIC 2: Cells and Cellular Organization Please use the Khan Academy Parts of a Cell video (compliments of Council Rock High School) to guide you. This video can be found at http://www.crsd.org/Page/31715 ...
... TOPIC 2: Cells and Cellular Organization Please use the Khan Academy Parts of a Cell video (compliments of Council Rock High School) to guide you. This video can be found at http://www.crsd.org/Page/31715 ...
Cells
... disease. He also developed the first vaccines. • Koch – rules to test if a germ is the cause of a specific disease • Margulis – tested DNA in mitochondria and found it was the same as bacteria DNA ...
... disease. He also developed the first vaccines. • Koch – rules to test if a germ is the cause of a specific disease • Margulis – tested DNA in mitochondria and found it was the same as bacteria DNA ...
Dynamic analysis of ErbB signal transduction pathways
... define the cell behavior corresponding to the different cellular conditions. To reveal the regulation mechanism of ErbB signaling, we performed the experimental data-based modeling of ErbB signaling network and molecular dynamics (MD) simulation of the receptor-protein interactions in the signaling ...
... define the cell behavior corresponding to the different cellular conditions. To reveal the regulation mechanism of ErbB signaling, we performed the experimental data-based modeling of ErbB signaling network and molecular dynamics (MD) simulation of the receptor-protein interactions in the signaling ...
7.2 Organelles
... Modify, sort, and package proteins and other materials from er for storage in cell or secretion What does it look like? Pancake stacks ...
... Modify, sort, and package proteins and other materials from er for storage in cell or secretion What does it look like? Pancake stacks ...
Biology Microbes / Classification 2012 – 2013 #4
... Bacterial anatomy A. Cell Wall = not like that of a plant 1. Gram + have typical cell wall - stain purple 2. Gram - have an extra lipid layer ...
... Bacterial anatomy A. Cell Wall = not like that of a plant 1. Gram + have typical cell wall - stain purple 2. Gram - have an extra lipid layer ...
G protein
... • The molecules that relay a signal from receptor to response are mostly proteins • Like falling dominoes, the receptor activates another protein, which activates another, and so on, until the protein producing the response is activated • At each step, the signal is transduced into a different form, ...
... • The molecules that relay a signal from receptor to response are mostly proteins • Like falling dominoes, the receptor activates another protein, which activates another, and so on, until the protein producing the response is activated • At each step, the signal is transduced into a different form, ...
THE CELL
... 1) All living organisms are composed of one or more cells. 2) Cells are the basic living units within organisms. 3) All cells arise from preexisting cells. ...
... 1) All living organisms are composed of one or more cells. 2) Cells are the basic living units within organisms. 3) All cells arise from preexisting cells. ...
What do I need to know for Monday`s test? Prokaryotes Single cell
... Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER)- Covered with ribosomes, the RER processes the proteins created by the ribosomes Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (SER) = makes lipids and breaks down toxins Golgi body – packages proteins into vesicles and ships them out of the cell. Mitochondria = the power ho ...
... Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER)- Covered with ribosomes, the RER processes the proteins created by the ribosomes Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (SER) = makes lipids and breaks down toxins Golgi body – packages proteins into vesicles and ships them out of the cell. Mitochondria = the power ho ...
cell drinking
... primary structure of one protein • DNA : 4 type of nucleotides (ATCG), which differ by the bases (no the sugars of pgospate groups) • Gene : has a sequences of nucleotides, which ultimately encodes a sequences of amino acids. ...
... primary structure of one protein • DNA : 4 type of nucleotides (ATCG), which differ by the bases (no the sugars of pgospate groups) • Gene : has a sequences of nucleotides, which ultimately encodes a sequences of amino acids. ...
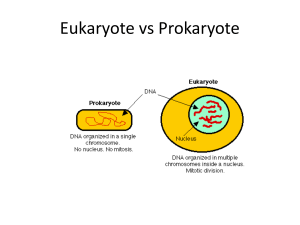
PROKARYOTES
... Types of Cells (Prokaryote and eukaryote) Are: • They both have DNA as their genetic material. • They are both membrane bound. • They both have ribosomes . • They have similar basic metabolism . • They are both amazingly diverse in forms. ...
... Types of Cells (Prokaryote and eukaryote) Are: • They both have DNA as their genetic material. • They are both membrane bound. • They both have ribosomes . • They have similar basic metabolism . • They are both amazingly diverse in forms. ...
Signal transduction
Signal transduction occurs when an extracellular signaling molecule activates a specific receptor located on the cell surface or inside the cell. In turn, this receptor triggers a biochemical chain of events inside the cell, creating a response. Depending on the cell, the response alters the cell's metabolism, shape, gene expression, or ability to divide. The signal can be amplified at any step. Thus, one signaling molecule can cause many responses.