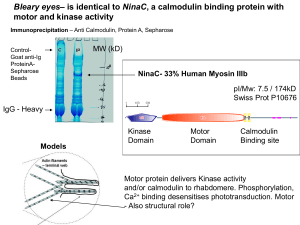
Jeff Errington L-form bacteria: life without walls or a division machine
... The peptidoglycan cell wall is a defining feature of bacterial cells. It has a wide range of important functions and is usually essential for cell viability. It is the target for our best antibiotics and fragments of the wall are recognised as danger signals by our innate immune systems. The wall wa ...
... The peptidoglycan cell wall is a defining feature of bacterial cells. It has a wide range of important functions and is usually essential for cell viability. It is the target for our best antibiotics and fragments of the wall are recognised as danger signals by our innate immune systems. The wall wa ...
Cell Theory, Cell Structure and Cellular Transport
... large vesicles formed by the Golgi. They contain hydrolytic enzymes that could destroy the cell. Lysosome contents function in the extracellular breakdown of materials. ...
... large vesicles formed by the Golgi. They contain hydrolytic enzymes that could destroy the cell. Lysosome contents function in the extracellular breakdown of materials. ...
From Biomarkers to Companion Diagnostics: Mitochondrial
... protein via a direct association with VDAC1 localized at the outer mitochondrial membrane and functioning as a gatekeeper for the entry and exit of mitochondrial metabolites, thereby controlling crosstalk between mitochondria and the rest of the cell. VDAC1 also plays a key role in mitochondria-medi ...
... protein via a direct association with VDAC1 localized at the outer mitochondrial membrane and functioning as a gatekeeper for the entry and exit of mitochondrial metabolites, thereby controlling crosstalk between mitochondria and the rest of the cell. VDAC1 also plays a key role in mitochondria-medi ...
Title: Co-expression of urokinase-type plasminogen activator and its
... (HEp3), which usually showed 40 to 50% invasiveness, The 3 other cell lines all produced MMP-2 and MMP-9, but only AGS showed moderate invasiveness (24.2 +/8.8%). While antibodies to u-PA were significantly effective in reducing CAM invasiveness of Hs746T cells by approximately 40%, the invasiveness ...
... (HEp3), which usually showed 40 to 50% invasiveness, The 3 other cell lines all produced MMP-2 and MMP-9, but only AGS showed moderate invasiveness (24.2 +/8.8%). While antibodies to u-PA were significantly effective in reducing CAM invasiveness of Hs746T cells by approximately 40%, the invasiveness ...
Unit 3 Biochemistry - The Naked Science Society
... Living things require millions of chemical reactions within the body, just to survive. Metabolism = all the chemical reactions occurring in the body. Organic molecules: ...
... Living things require millions of chemical reactions within the body, just to survive. Metabolism = all the chemical reactions occurring in the body. Organic molecules: ...
Cell Structure Vocab/Synonyms
... a tiny cell structure that carries out a specific function in a organelle cell unicellular a type of organism that is made up of one cell multicellular an organism made up of many cells a rod-shaped cell structure that produces most of the energy mitochondrion needed to carry out the cell's function ...
... a tiny cell structure that carries out a specific function in a organelle cell unicellular a type of organism that is made up of one cell multicellular an organism made up of many cells a rod-shaped cell structure that produces most of the energy mitochondrion needed to carry out the cell's function ...
Presentation
... Receptors – react to hormones, etc. to trigger metabolic changes; __________________ transduction ...
... Receptors – react to hormones, etc. to trigger metabolic changes; __________________ transduction ...
Biochemistry
... • Used by cells for: – energy – Support and structure • Cellular membrane: lipid bilayer ...
... • Used by cells for: – energy – Support and structure • Cellular membrane: lipid bilayer ...
II. The Cell - Quakertown Community School District
... The Nucleus Nucleus—control center - enclosed by nuclear envelope - contains most of the genes that control the entire cell - DNA organized with proteins into chromatin - nucleolus-produces ribosomes ...
... The Nucleus Nucleus—control center - enclosed by nuclear envelope - contains most of the genes that control the entire cell - DNA organized with proteins into chromatin - nucleolus-produces ribosomes ...
Investigating Cell Migration Under Microgravity Conditions
... ● E-cadherin (membrane protein) → involved in cell to cell adhesion ...
... ● E-cadherin (membrane protein) → involved in cell to cell adhesion ...
Plasma Membrane/Cell Transport Powerpoint
... G) Sugars: Helps as an ID tag for the cell H) Skip I) Skip J) Cytoskeleton fibers: Cell Structure ...
... G) Sugars: Helps as an ID tag for the cell H) Skip I) Skip J) Cytoskeleton fibers: Cell Structure ...
Answers to exam 1 review #2
... 45. Are glucose and fructose a structural or steroisomer? Structural 46. Hydrophobic forces cause which protein structure? Tertiary structure 47. The two types of electron microscopes are TSM and SEM? F 48. Myosin is a molecular motor moving along an actin filament T F 49. What does cholesterol do t ...
... 45. Are glucose and fructose a structural or steroisomer? Structural 46. Hydrophobic forces cause which protein structure? Tertiary structure 47. The two types of electron microscopes are TSM and SEM? F 48. Myosin is a molecular motor moving along an actin filament T F 49. What does cholesterol do t ...
Cell Organelles and Functions
... hair-like organelles, identical in structure to flagella, that line the surfaces of certain cells and beat in rhythmic waves, providing locomotion to ciliate protozoans and moving liquids along internal epithelial tissue in humans and animals. ...
... hair-like organelles, identical in structure to flagella, that line the surfaces of certain cells and beat in rhythmic waves, providing locomotion to ciliate protozoans and moving liquids along internal epithelial tissue in humans and animals. ...
Protein Structure:
... The PDGF receptor tyrosine kinase becomes phosphorylated on tyrosine residues when activated by ligand (PDGF) binding. The phospho-tyrosines (shown in red) are located in specific regions of the PDGF receptor (shown in green). Receptor phosphotyosines serve to recruit other molecules such as phospho ...
... The PDGF receptor tyrosine kinase becomes phosphorylated on tyrosine residues when activated by ligand (PDGF) binding. The phospho-tyrosines (shown in red) are located in specific regions of the PDGF receptor (shown in green). Receptor phosphotyosines serve to recruit other molecules such as phospho ...
Dr. Vincent Giampapa Receives Nobel Prize Nomination for Stem
... The Nobel Prize Nomination was awarded for the potential impact Dr. Giampapa’s technology may have on the global aging epidemic as well as the financial impact of future health care in all countries with aging demographics, especially in the United States. After 2 years of research on the effects of ...
... The Nobel Prize Nomination was awarded for the potential impact Dr. Giampapa’s technology may have on the global aging epidemic as well as the financial impact of future health care in all countries with aging demographics, especially in the United States. After 2 years of research on the effects of ...
Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling
... Sensory neurons transmit information from the eyes and other sensors that detect stimuli to the brain or spinal cord for processing. Interneurons connect sensory and motor neurons or make local connections in the brain and spinal cord. Motor neurons transmit signals to effectors, such as muscl ...
... Sensory neurons transmit information from the eyes and other sensors that detect stimuli to the brain or spinal cord for processing. Interneurons connect sensory and motor neurons or make local connections in the brain and spinal cord. Motor neurons transmit signals to effectors, such as muscl ...
Signal transduction
Signal transduction occurs when an extracellular signaling molecule activates a specific receptor located on the cell surface or inside the cell. In turn, this receptor triggers a biochemical chain of events inside the cell, creating a response. Depending on the cell, the response alters the cell's metabolism, shape, gene expression, or ability to divide. The signal can be amplified at any step. Thus, one signaling molecule can cause many responses.