Ch.7.4 Homeostasis Notes
... o Fungi – yeast Multicellular organisms are composed of specialized cells that work together and communicate to maintain homeostasis. Cell specialization – a specific job a cell has within the organism The shape of a cell can determine the role it will have within the organism. Levels of organizat ...
... o Fungi – yeast Multicellular organisms are composed of specialized cells that work together and communicate to maintain homeostasis. Cell specialization – a specific job a cell has within the organism The shape of a cell can determine the role it will have within the organism. Levels of organizat ...
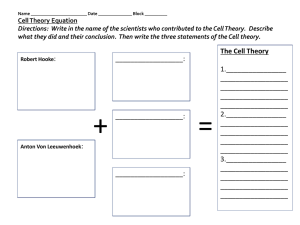
Robert Hooke (1665) saw cells while looking at a piece of cork
... Robert Hooke (1665) saw cells while looking at a piece of cork under the microscope. Anton Von Leeuwenhoek (1673) saw animalcules (“little animals”) in pond scum. Theodor Schwann (mid 1800’s) Cell Theory: 1. all organisms are composed of one or more cells. 2. the cell is the basic unit of life in al ...
... Robert Hooke (1665) saw cells while looking at a piece of cork under the microscope. Anton Von Leeuwenhoek (1673) saw animalcules (“little animals”) in pond scum. Theodor Schwann (mid 1800’s) Cell Theory: 1. all organisms are composed of one or more cells. 2. the cell is the basic unit of life in al ...
ISLET-1+ HEART PROGENITORS: A PARABLE OF
... Cardiogenesis requires the formation of a diverse spectrum of muscle and non-muscle cell lineages in specific tissue compartments of the heart. Regenerative stem cell therapies for heart disease necessitate a deep understanding of the molecular mechanisms that govern the fates and differentiation of ...
... Cardiogenesis requires the formation of a diverse spectrum of muscle and non-muscle cell lineages in specific tissue compartments of the heart. Regenerative stem cell therapies for heart disease necessitate a deep understanding of the molecular mechanisms that govern the fates and differentiation of ...
review for second six weeks common assessment
... 2. Passive and Active Transport 3. Diffusion, Osmosis 4. Functions of the cell membrane 5. Differences between plant and animal cells 6. What causes cells to stop growing when grown in a petri dish? 7. Cell organelle responsible for photosynthesis 8. Vascular vs. Nonvascular plants 9. How do angiosp ...
... 2. Passive and Active Transport 3. Diffusion, Osmosis 4. Functions of the cell membrane 5. Differences between plant and animal cells 6. What causes cells to stop growing when grown in a petri dish? 7. Cell organelle responsible for photosynthesis 8. Vascular vs. Nonvascular plants 9. How do angiosp ...
http://en
... CELLS Visit this web page: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cell_%28biology%29 and answer the questions. ...
... CELLS Visit this web page: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cell_%28biology%29 and answer the questions. ...
Homework: Respiration - Fall River Public Schools
... Cell Biologist’s Name: _________________________________ Class: 8__ Date: ______________ Mrs. Bouchard– 8th Grade Science ...
... Cell Biologist’s Name: _________________________________ Class: 8__ Date: ______________ Mrs. Bouchard– 8th Grade Science ...
Cell Review
... 1. All living things are made of cells 2. Cells are the basic unit of function in all living things 3. All cells come from preexisting cells Exceptions 1. Virus- can not reproduce on their own 2. Mitochondria and Chloroplasts contain their own DNA Organelles ...
... 1. All living things are made of cells 2. Cells are the basic unit of function in all living things 3. All cells come from preexisting cells Exceptions 1. Virus- can not reproduce on their own 2. Mitochondria and Chloroplasts contain their own DNA Organelles ...
Cellular specialization and differentiation
... Differentiation: the process through which cells become specialized for specific functions ...
... Differentiation: the process through which cells become specialized for specific functions ...
Biology Packet 5: Cell Growth and Division
... Define cell growth and division. Explain why cells divide. Define cell cycle. Name the main events of the cell cycle. Describe what happens during the four phases of mitosis. Identify a factor that can stop cells from growing. Describe how the cell cycle is regulated. Explain how cancer cells are di ...
... Define cell growth and division. Explain why cells divide. Define cell cycle. Name the main events of the cell cycle. Describe what happens during the four phases of mitosis. Identify a factor that can stop cells from growing. Describe how the cell cycle is regulated. Explain how cancer cells are di ...
Specification of the neural tube and neural crest
... Reading – NB these texts mostly describe embryology and do not discuss cellular developmental events Nolte (4th Ed), pgs 36-49 Fitzgerald, pgs 1-7 Crossman and Neary, pgs 3-8 Kiernan, pgs 4-11, 39-40 ...
... Reading – NB these texts mostly describe embryology and do not discuss cellular developmental events Nolte (4th Ed), pgs 36-49 Fitzgerald, pgs 1-7 Crossman and Neary, pgs 3-8 Kiernan, pgs 4-11, 39-40 ...
Chap 19 - Iowa State University
... Iowa State University Date: The science of developmental genetics is concerned with understanding how gene expression controls the process of development. ...
... Iowa State University Date: The science of developmental genetics is concerned with understanding how gene expression controls the process of development. ...
An Inside Look: Lysosome
... variation in size and shape as a result of differences in the materials that have been taken up for digestion. This organelle is mainly found in animal cells but are sometimes found in plant cells ...
... variation in size and shape as a result of differences in the materials that have been taken up for digestion. This organelle is mainly found in animal cells but are sometimes found in plant cells ...
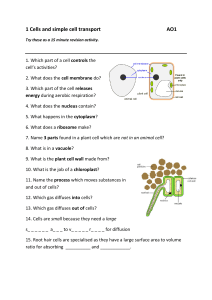
1 Cells and simple cell transport AO1
... 1. Which part of a cell controls the cell’s activities? 2. What does the cell membrane do? 3. Which part of the cell releases energy during aerobic respiration? 4. What does the nucleus contain? 5. What happens in the cytoplasm? 6. What does a ribosome make? 7. Name 3 parts found in a plant cell whi ...
... 1. Which part of a cell controls the cell’s activities? 2. What does the cell membrane do? 3. Which part of the cell releases energy during aerobic respiration? 4. What does the nucleus contain? 5. What happens in the cytoplasm? 6. What does a ribosome make? 7. Name 3 parts found in a plant cell whi ...
Chapter 7 test review 2015
... 12. Know what it means for a solution to be hypertonic, hypotonic, and isotonic and how it affects cells. Draw what cells look like after being in each solution and where the water is moving. ...
... 12. Know what it means for a solution to be hypertonic, hypotonic, and isotonic and how it affects cells. Draw what cells look like after being in each solution and where the water is moving. ...
The Cell Cycle - Haiku Learning
... What are the 3 phases of the cell cycle? What are the 4 phases of Mitosis? What is differentiation? ...
... What are the 3 phases of the cell cycle? What are the 4 phases of Mitosis? What is differentiation? ...
Cellular differentiation

In developmental biology, cellular differentiation isa cell changes from one cell type to another. Most commonly this is a less specialized type becoming a more specialized type, such as during cell growth. Differentiation occurs numerous times during the development of a multicellular organism as it changes from a simple zygote to a complex system of tissues and cell types. Differentiation continues in adulthood as adult stem cells divide and create fully differentiated daughter cells during tissue repair and during normal cell turnover. Some differentiation occurs in response to antigen exposure. Differentiation dramatically changes a cell's size, shape, membrane potential, metabolic activity, and responsiveness to signals. These changes are largely due to highly controlled modifications in gene expression and are the study of epigenetics. With a few exceptions, cellular differentiation almost never involves a change in the DNA sequence itself. Thus, different cells can have very different physical characteristics despite having the same genome.A cell that can differentiate into all cell types of the adult organism is known as pluripotent. Such cells are called embryonic stem cells in animals and meristematic cells in higher plants. A cell that can differentiate into all cell types, including the placental tissue, is known as totipotent. In mammals, only the zygote and subsequent blastomeres are totipotent, while in plants many differentiated cells can become totipotent with simple laboratory techniques. In cytopathology, the level of cellular differentiation is used as a measure of cancer progression. ""Grade"" is a marker of how differentiated a cell in a tumor is.