Hepatocyte Growth Factor Induces Wnt
... been shown to be important in embryogenesis and carcinogenesis. The aim of this study was to elucidate the mechanism of functional similarities observed in the two pathways. We used normal rat liver, primary hepatocyte cultures and a dominant-negative Met expression system to study the effect of HGF ...
... been shown to be important in embryogenesis and carcinogenesis. The aim of this study was to elucidate the mechanism of functional similarities observed in the two pathways. We used normal rat liver, primary hepatocyte cultures and a dominant-negative Met expression system to study the effect of HGF ...
Intraflagellar transport molecules in ciliary and nonciliary cells of the
... evidence indicates that kinesin-II family members serve as anterograde transport motors in IFT (Kozminski et al., 1995; Cole et al., 1998; Snow et al., 2004), whereas the cytoplasmic dynein 2/1b mediates IFT in the retrograde direction (Pazour et al., 1998, 1999; Signor et al., 1999a). Biochemical a ...
... evidence indicates that kinesin-II family members serve as anterograde transport motors in IFT (Kozminski et al., 1995; Cole et al., 1998; Snow et al., 2004), whereas the cytoplasmic dynein 2/1b mediates IFT in the retrograde direction (Pazour et al., 1998, 1999; Signor et al., 1999a). Biochemical a ...
Chapter 10
... and sacs (cisternae) that extends from the nuclear membrane throughout the cytoplasm (Figure 10.1). The entire endoplasmic reticulum is enclosed by a continuous membrane and is the largest organelle of most eukaryotic cells. Its membrane may account for about half of all cell membranes, and the spac ...
... and sacs (cisternae) that extends from the nuclear membrane throughout the cytoplasm (Figure 10.1). The entire endoplasmic reticulum is enclosed by a continuous membrane and is the largest organelle of most eukaryotic cells. Its membrane may account for about half of all cell membranes, and the spac ...
Jasmonate Controls Leaf Growth by Repressing
... is merely a consequence of organ growth and to a large extent facultative (Massonnet et al., 2010). In the plant Arabidopsis, two types of cell cycle have been identified: the mitotic cell cycle and the endocycle (or endoreduplication cycle). The process of endoreduplication, which is an increase of ...
... is merely a consequence of organ growth and to a large extent facultative (Massonnet et al., 2010). In the plant Arabidopsis, two types of cell cycle have been identified: the mitotic cell cycle and the endocycle (or endoreduplication cycle). The process of endoreduplication, which is an increase of ...
Here - Events
... pauses cell cycle progression to partition the nuclei into individual cells and to assign those cells distinct developmental fates. The pause in cell cycle is analogous to the midblastula transition observed in many organisms and is associated with the degradation of a subset of maternally supplied ...
... pauses cell cycle progression to partition the nuclei into individual cells and to assign those cells distinct developmental fates. The pause in cell cycle is analogous to the midblastula transition observed in many organisms and is associated with the degradation of a subset of maternally supplied ...
Ameba Coloring - Learn District 196
... flagella, but the ameba has an unusual way of creeping along by stretching its cytoplasm into fingerlike extensions called pseudopodia. (The word "pseudopodia" means "false foot".) On the coloring sheet, there are several pseudopodia, use a yellow highlighter or pencil to highlight each of them (col ...
... flagella, but the ameba has an unusual way of creeping along by stretching its cytoplasm into fingerlike extensions called pseudopodia. (The word "pseudopodia" means "false foot".) On the coloring sheet, there are several pseudopodia, use a yellow highlighter or pencil to highlight each of them (col ...
Strio-pallidal projection in the monkey
... the resulting gliosis in the globus pallidus in several for a short distance into the internal segment; just of the brains are similar both in their site and extent, as its medio-lateral and supero-inferior limits are only a small number of representative experiments sharply defined so it stops quit ...
... the resulting gliosis in the globus pallidus in several for a short distance into the internal segment; just of the brains are similar both in their site and extent, as its medio-lateral and supero-inferior limits are only a small number of representative experiments sharply defined so it stops quit ...
Stochastic and reversible aggregation of mRNA with expanded CUG
... Unlike protein aggregates, which have been extensively studied using biochemical and cytological approaches, little is known about the mechanism of RNA aggregation. More and more RNA aggregates or foci have been identified in different pathologies, such as Myotonic Dystrophy type 1 (DM1) (Davis et a ...
... Unlike protein aggregates, which have been extensively studied using biochemical and cytological approaches, little is known about the mechanism of RNA aggregation. More and more RNA aggregates or foci have been identified in different pathologies, such as Myotonic Dystrophy type 1 (DM1) (Davis et a ...
View
... DNA-binding C2H2 zinc finger proteins contain proteinbinding domains that provide the basis for the assembly of regulatory complexes involved in chromatin remodeling and transcriptional regulation (Aasland et al., 1995; David et al., 1998). They are frequently expressed in distinct spatial and tempo ...
... DNA-binding C2H2 zinc finger proteins contain proteinbinding domains that provide the basis for the assembly of regulatory complexes involved in chromatin remodeling and transcriptional regulation (Aasland et al., 1995; David et al., 1998). They are frequently expressed in distinct spatial and tempo ...
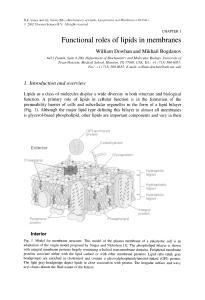
Functional Roles Of Lipids In membranes - IJS
... of self-associated monomers in equilibrium with a constant amount of free monomer. This point of self-association and the remaining constant free monomer concentration is the critical micelle concentration [6]. The larger the hydrophobic domain, the lower the critical micelle concentration due to th ...
... of self-associated monomers in equilibrium with a constant amount of free monomer. This point of self-association and the remaining constant free monomer concentration is the critical micelle concentration [6]. The larger the hydrophobic domain, the lower the critical micelle concentration due to th ...
Characterization of a 30S Ribsomal Subunit Intermediate Found in
... stimulate the misreading of mRNA by binding to the decoding site of 16S rRNA in the 30S ribosomal subunit. Recent work has shown that both antibiotics also inhibit 30S subunit assembly in Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus cells. This work describes the characteristics of an assembly interme ...
... stimulate the misreading of mRNA by binding to the decoding site of 16S rRNA in the 30S ribosomal subunit. Recent work has shown that both antibiotics also inhibit 30S subunit assembly in Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus cells. This work describes the characteristics of an assembly interme ...
Giant nuclei is essential in the cell cycle transition from meiosis to
... DNA replication in gnu eggs and embryos might be continuous or cyclic, with gaps in which there is no replication. To determine between these possibilities, we examined the distribution of the DNA polymerase-δ processivity factor, PCNA (Yamaguchi et al., 1991) and nuclear lamins in gnu embryos. In g ...
... DNA replication in gnu eggs and embryos might be continuous or cyclic, with gaps in which there is no replication. To determine between these possibilities, we examined the distribution of the DNA polymerase-δ processivity factor, PCNA (Yamaguchi et al., 1991) and nuclear lamins in gnu embryos. In g ...
Mechanisms and roles of the RNA-based gene silencing
... characteristic of PTGS in plants and fungi is that diffusible trans-acting molecules mediate it, which is able to mediate gene silencing between nuclei in heterokaryotic strains. The small sense and antisense RNAs associated with silencing derive from cleavage of dsRNA and both polarities are though ...
... characteristic of PTGS in plants and fungi is that diffusible trans-acting molecules mediate it, which is able to mediate gene silencing between nuclei in heterokaryotic strains. The small sense and antisense RNAs associated with silencing derive from cleavage of dsRNA and both polarities are though ...
Chromatin Fibers Observed In Situ in Frozen Hydrated Sections
... et al., 1993), and dextran cryoprotectant but not fixed. For comparison, the same material after GA fixation and conventional epoxy embedding is shown in Fig. 3 b. Both the frozen hydrated and conventionally prepared cells have nuclei filled with chromatin fibers, and, in general, features seen in t ...
... et al., 1993), and dextran cryoprotectant but not fixed. For comparison, the same material after GA fixation and conventional epoxy embedding is shown in Fig. 3 b. Both the frozen hydrated and conventionally prepared cells have nuclei filled with chromatin fibers, and, in general, features seen in t ...
this PDF file
... bacterial themselves de novo. Although most DNA in the form of the fibrillar nucleoid is present in the riboplasm, some DNA appearing in the anammoxosome have been confirmed by analysis using anti-DNA antibody [9]. This small amount of DNA within anammoxosome might be speculated to be relic DNA of t ...
... bacterial themselves de novo. Although most DNA in the form of the fibrillar nucleoid is present in the riboplasm, some DNA appearing in the anammoxosome have been confirmed by analysis using anti-DNA antibody [9]. This small amount of DNA within anammoxosome might be speculated to be relic DNA of t ...
Dev Biol 364(2), 138-48. PDF
... 2010; Dard et al., 2009; Plusa et al., 2005), although their roles in controlling TE differentiation and blastocyst formation are still unclear. The functional relationship between PCP components and aPKC/PAR complex proteins, the key players in AB polarity formation, are also unclear. However, evid ...
... 2010; Dard et al., 2009; Plusa et al., 2005), although their roles in controlling TE differentiation and blastocyst formation are still unclear. The functional relationship between PCP components and aPKC/PAR complex proteins, the key players in AB polarity formation, are also unclear. However, evid ...
Fatty acid
... • Steroids have a ring structure rather than linear • They are based mainly on the cholesterol molecule which is one reason you can not completely cut cholesterol out of your diet • As you saw before, many steroids act as hormones and small changes in structure can mean a big difference in function ...
... • Steroids have a ring structure rather than linear • They are based mainly on the cholesterol molecule which is one reason you can not completely cut cholesterol out of your diet • As you saw before, many steroids act as hormones and small changes in structure can mean a big difference in function ...
Copyright Information of the Article Published Online
... endosymbiotic theory indicates that mitochondria were initially free-living prokaryotes that entered eukaryotic cells and became organelles. However, this theory has not always been accepted by the scientific community; it was first proposed for plastids at the beginning of the 20th century, but was ...
... endosymbiotic theory indicates that mitochondria were initially free-living prokaryotes that entered eukaryotic cells and became organelles. However, this theory has not always been accepted by the scientific community; it was first proposed for plastids at the beginning of the 20th century, but was ...
Tese Hugo Fraga
... propagation. Plant tissue culture encompasses a range of biotechnology tools that enable the conservation and plant breeding. The somatic embryogenesis (SE) morphogenetic route can be employed for mass clonal propagation of elite genotypes, conservation of endangered species, and for the study of ph ...
... propagation. Plant tissue culture encompasses a range of biotechnology tools that enable the conservation and plant breeding. The somatic embryogenesis (SE) morphogenetic route can be employed for mass clonal propagation of elite genotypes, conservation of endangered species, and for the study of ph ...
the Internal Capsule - Turkish Neurosurgery
... signs by involving the parts of the internal capsule or by pressure over it. In fact, in the studies and management of the intrinsic brain lesion such as the gliomas, the 3-dimensional microanatomy of the white matter tracts is more important than the anatomy of the sulci (8) The knowledge and exper ...
... signs by involving the parts of the internal capsule or by pressure over it. In fact, in the studies and management of the intrinsic brain lesion such as the gliomas, the 3-dimensional microanatomy of the white matter tracts is more important than the anatomy of the sulci (8) The knowledge and exper ...
PKC in limb development
... both present in the cytoplasm and in the nuclei. Gold particles attached to RACK1 or to activated PKC were associated with nuclear pores (Fig. 2A-C, inserts), raising the possibility that RACK1 and activated PKC are transported between cytoplasm and nucleus. The immunohistochemical analyses demonstr ...
... both present in the cytoplasm and in the nuclei. Gold particles attached to RACK1 or to activated PKC were associated with nuclear pores (Fig. 2A-C, inserts), raising the possibility that RACK1 and activated PKC are transported between cytoplasm and nucleus. The immunohistochemical analyses demonstr ...
Ca Signaling11
... - Incr of synaptic activity synaptic NMDA receptordependent transient Ca2+ currents and long-lasting LTP in hipp (CA1 region) activate (phosphorylate) CREB txn factor CaMKII and MAPK (ERK) signalling pathways • Serum response element (SRE). - Induce expression of c-fos promotor activation of L ...
... - Incr of synaptic activity synaptic NMDA receptordependent transient Ca2+ currents and long-lasting LTP in hipp (CA1 region) activate (phosphorylate) CREB txn factor CaMKII and MAPK (ERK) signalling pathways • Serum response element (SRE). - Induce expression of c-fos promotor activation of L ...
Boundless Study Slides
... • growth factor a naturally-occurring substance capable of stimulating cellular growth, proliferation, and cellular differentiation • GTP-binding protein a protein which binds GTP and catalyzes its conversion to GDP • hydrophobic lacking an affinity for water; unable to absorb, or be wetted by water ...
... • growth factor a naturally-occurring substance capable of stimulating cellular growth, proliferation, and cellular differentiation • GTP-binding protein a protein which binds GTP and catalyzes its conversion to GDP • hydrophobic lacking an affinity for water; unable to absorb, or be wetted by water ...
Ultrastructural studies of t /t mouse embryos
... lethal periods, (2) their nuclear inclusions, and (3) the presence or absence of mitochondrial variants. Both homozygotes can be distinguished from their litter-mates as early as the 2-cell stage by the presence of nuclear lipid droplets and excessive cytoplasmic lipid. In addition, both homozygous ...
... lethal periods, (2) their nuclear inclusions, and (3) the presence or absence of mitochondrial variants. Both homozygotes can be distinguished from their litter-mates as early as the 2-cell stage by the presence of nuclear lipid droplets and excessive cytoplasmic lipid. In addition, both homozygous ...
Cell nucleus

In cell biology, the nucleus (pl. nuclei; from Latin nucleus or nuculeus, meaning kernel) is a membrane-enclosed organelle found in eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotes usually have a single nucleus, but a few cell types have no nuclei, and a few others have many.Cell nuclei contain most of the cell's genetic material, organized as multiple long linear DNA molecules in complex with a large variety of proteins, such as histones, to form chromosomes. The genes within these chromosomes are the cell's nuclear genome. The function of the nucleus is to maintain the integrity of these genes and to control the activities of the cell by regulating gene expression—the nucleus is, therefore, the control center of the cell. The main structures making up the nucleus are the nuclear envelope, a double membrane that encloses the entire organelle and isolates its contents from the cellular cytoplasm, and the nucleoskeleton (which includes nuclear lamina), a network within the nucleus that adds mechanical support, much like the cytoskeleton, which supports the cell as a whole.Because the nuclear membrane is impermeable to large molecules, nuclear pores are required that regulate nuclear transport of molecules across the envelope. The pores cross both nuclear membranes, providing a channel through which larger molecules must be actively transported by carrier proteins while allowing free movement of small molecules and ions. Movement of large molecules such as proteins and RNA through the pores is required for both gene expression and the maintenance of chromosomes. The interior of the nucleus does not contain any membrane-bound sub compartments, its contents are not uniform, and a number of sub-nuclear bodies exist, made up of unique proteins, RNA molecules, and particular parts of the chromosomes. The best-known of these is the nucleolus, which is mainly involved in the assembly of ribosomes. After being produced in the nucleolus, ribosomes are exported to the cytoplasm where they translate mRNA.