PDF
... embryos, antagonism of Wnt signaling allows the formation of anterior structures at the expense of posterior ones (Leyns et al., 1997; Glinka et al., 1998). This is also true for zebrafish: morpholino knockdown of wnt8a results in embryos that predominantly form head but lack posterior structures (E ...
... embryos, antagonism of Wnt signaling allows the formation of anterior structures at the expense of posterior ones (Leyns et al., 1997; Glinka et al., 1998). This is also true for zebrafish: morpholino knockdown of wnt8a results in embryos that predominantly form head but lack posterior structures (E ...
Spt4 modulates Rad26 requirement in transcription
... In human cells, TCR requires the CSB gene product. The hereditary recessive disorder Cockayne syndrome can be caused by a mutation in the CSB gene (Troelstra et al., 1992), and cells derived from Cockayne syndrome patients show a defect speci®cally in the TCR pathway (Venema et al., 1990). Previousl ...
... In human cells, TCR requires the CSB gene product. The hereditary recessive disorder Cockayne syndrome can be caused by a mutation in the CSB gene (Troelstra et al., 1992), and cells derived from Cockayne syndrome patients show a defect speci®cally in the TCR pathway (Venema et al., 1990). Previousl ...
Active Transport of the Survival Motor Neuron Protein and
... SMN is localized to both the nucleus and cytoplasm, and considerable attention has focused on concentration of SMN in nuclear dot-like structures termed gems (Liu and Dreyfuss, 1996) and coiled (Cajal) bodies (Carvalho et al., 1999; Young et al., 2000). There have been extensive studies, in various ...
... SMN is localized to both the nucleus and cytoplasm, and considerable attention has focused on concentration of SMN in nuclear dot-like structures termed gems (Liu and Dreyfuss, 1996) and coiled (Cajal) bodies (Carvalho et al., 1999; Young et al., 2000). There have been extensive studies, in various ...
Ribosome Profiling Provides Evidence that Large Please share
... mature RNA after the snoRNAs have been extracted from intronic regions (Smith and Steitz, 1998). Thus, it is important to develop strategies for using the 80S footprint data provided by ribosome profiling experiments to distinguish true messengers that encode functional proteins from those that are ...
... mature RNA after the snoRNAs have been extracted from intronic regions (Smith and Steitz, 1998). Thus, it is important to develop strategies for using the 80S footprint data provided by ribosome profiling experiments to distinguish true messengers that encode functional proteins from those that are ...
Det här verket är upphovrättskyddat enligt Lagen (1960
... The improved knowledge of the unique structure of the thyroid follicle achieved in recent years by electron micro scopical studies has greatly promoted the understanding of the physiology of the follicle (18, 20). It is now possible to re late the processes of formation, storage and secretion of t ...
... The improved knowledge of the unique structure of the thyroid follicle achieved in recent years by electron micro scopical studies has greatly promoted the understanding of the physiology of the follicle (18, 20). It is now possible to re late the processes of formation, storage and secretion of t ...
Lineage-specific stem cells, signals and asymmetries
... Fig. 1. Stomatal development in Arabidopsis. (A) Cell transitions and key regulatory pathways within the stomatal lineage. In the developing epidermis of photosynthetic tissues, an undifferentiated protodermal cell adopts a meristemoid mother cell (MMC, purple) identity and undergoes an asymmetric c ...
... Fig. 1. Stomatal development in Arabidopsis. (A) Cell transitions and key regulatory pathways within the stomatal lineage. In the developing epidermis of photosynthetic tissues, an undifferentiated protodermal cell adopts a meristemoid mother cell (MMC, purple) identity and undergoes an asymmetric c ...
Shaping mitotic chromosomes: From classical concepts to molecular
... daughter cells during mitotic divisions is one of the most spectacular events of the cell division cycle. Successful segregation requires the extensive reorganization of chromatin fibers into compact cylindrical mitotic chromosomes. Although this “condensation” process has fascinated scientists sinc ...
... daughter cells during mitotic divisions is one of the most spectacular events of the cell division cycle. Successful segregation requires the extensive reorganization of chromatin fibers into compact cylindrical mitotic chromosomes. Although this “condensation” process has fascinated scientists sinc ...
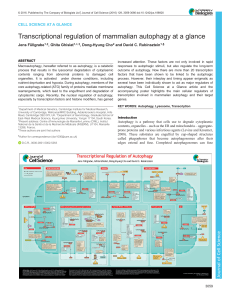
Transcriptional regulation of mammalian autophagy at a glance
... referred to as p53) has been described to inhibit mTORC1 and thus to activate autophagy, several studies have shown that cytoplasmic p53 is a potent inhibitor of autophagy. The mechanisms for this inhibition are largely unknown (Green and Kroemer, 2009); however, post-transcriptional downregulation ...
... referred to as p53) has been described to inhibit mTORC1 and thus to activate autophagy, several studies have shown that cytoplasmic p53 is a potent inhibitor of autophagy. The mechanisms for this inhibition are largely unknown (Green and Kroemer, 2009); however, post-transcriptional downregulation ...
Diverse roles of the Mediator complex in plants
... eukaryotic lineages, Bourbon, (2008) showed that Mediator subunits from very diverse phyla could be identified using evolutionary conserved signature sequence motifs (SSMs). Using these analyses, Bourbon (2008) identified all but two Mediator subunits in plants and all of the human subunits in the d ...
... eukaryotic lineages, Bourbon, (2008) showed that Mediator subunits from very diverse phyla could be identified using evolutionary conserved signature sequence motifs (SSMs). Using these analyses, Bourbon (2008) identified all but two Mediator subunits in plants and all of the human subunits in the d ...
Control of convergent yolk syncytial layer nuclear movement in
... Up⬇1 μm/minute is the speed with which the progenitor patch moves. Since the time scale for cortical flow is much longer than that for elastic relaxation, the cortex may be described as an incompressible viscous fluid for the present purpose. In general, the flow profile is a function of the Reynold ...
... Up⬇1 μm/minute is the speed with which the progenitor patch moves. Since the time scale for cortical flow is much longer than that for elastic relaxation, the cortex may be described as an incompressible viscous fluid for the present purpose. In general, the flow profile is a function of the Reynold ...
Control of convergent yolk syncytial layer nuclear movement in
... Up⬇1 μm/minute is the speed with which the progenitor patch moves. Since the time scale for cortical flow is much longer than that for elastic relaxation, the cortex may be described as an incompressible viscous fluid for the present purpose. In general, the flow profile is a function of the Reynold ...
... Up⬇1 μm/minute is the speed with which the progenitor patch moves. Since the time scale for cortical flow is much longer than that for elastic relaxation, the cortex may be described as an incompressible viscous fluid for the present purpose. In general, the flow profile is a function of the Reynold ...
Systematic Characterisation of Cellular Localisation and
... Copyright: ß 2009 Juncker et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited. Funding: This work is supported ...
... Copyright: ß 2009 Juncker et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited. Funding: This work is supported ...
Tracing the Archaeal Origins of Eukaryotic Membrane
... 2007; Dacks et al. 2008). Therefore, despite the apparent complexity of the modern trafficking machinery, the paralogous nature of the proteins involved suggests that this machinery evolved from a smaller set of primordial vesicle formation and fusion proteins that were present in early stages of eu ...
... 2007; Dacks et al. 2008). Therefore, despite the apparent complexity of the modern trafficking machinery, the paralogous nature of the proteins involved suggests that this machinery evolved from a smaller set of primordial vesicle formation and fusion proteins that were present in early stages of eu ...
Cleavage furrow formation and ingression during animal cytokinesis
... successfully complete the first embryonic divisions, though cytokinesis fails in subsequent cell divisions (Verbrugghe and White, 2004). Second, Canman et al. showed that drug-induced monopolar spindles, which lack central spindle microtubules, in mammalian PtK1 cells initiate and complete cytokines ...
... successfully complete the first embryonic divisions, though cytokinesis fails in subsequent cell divisions (Verbrugghe and White, 2004). Second, Canman et al. showed that drug-induced monopolar spindles, which lack central spindle microtubules, in mammalian PtK1 cells initiate and complete cytokines ...
Structural insights into the coupling of virion assembly and rotavirus
... the rotavirus towards host cell egress. The lack of highresolution structures for rotavirus assembly intermediates had previously hampered our understanding of assembly state-mediated regulation of replication. In recent years, however, several studies using X‑ray crystallography and cryo-electron m ...
... the rotavirus towards host cell egress. The lack of highresolution structures for rotavirus assembly intermediates had previously hampered our understanding of assembly state-mediated regulation of replication. In recent years, however, several studies using X‑ray crystallography and cryo-electron m ...
Nucleation and Dynamics of Golgi-derived Microtubules
... et al., 2011; Ori-Mckenney et al., 2012; Maia et al., 2013), likely because it can recruit γ-TuRC either directly, or indirectly via CDK5Rap2 or myomegalin interactions. However, AKAP450 function is not essential for MT nucleation at the Golgi in myotubes, likely because γ-TuRC is recruited to the G ...
... et al., 2011; Ori-Mckenney et al., 2012; Maia et al., 2013), likely because it can recruit γ-TuRC either directly, or indirectly via CDK5Rap2 or myomegalin interactions. However, AKAP450 function is not essential for MT nucleation at the Golgi in myotubes, likely because γ-TuRC is recruited to the G ...
Vesicular transport of newly synthesized opsin from the Golgi
... Each day, rod photoreceptors of the vertebrate retina synthesize rhodopsin and insert it into new membranes of the rod outer segment (ROS). The authors determined which components of the rod cell transport opsin from the Golgi to the ROS by a combined EM autoradiographic and immunocytochemical study ...
... Each day, rod photoreceptors of the vertebrate retina synthesize rhodopsin and insert it into new membranes of the rod outer segment (ROS). The authors determined which components of the rod cell transport opsin from the Golgi to the ROS by a combined EM autoradiographic and immunocytochemical study ...
Genetic and molecular identification of genes
... observed, ranging from defects in different stages of early embryo sac development to mutants with apparently normal embryo sacs, but exhibiting defects in processes such as pollen tube guidance, fertilization or early embryo development. Unexpectedly, nearly half of the mutants isolated in this stu ...
... observed, ranging from defects in different stages of early embryo sac development to mutants with apparently normal embryo sacs, but exhibiting defects in processes such as pollen tube guidance, fertilization or early embryo development. Unexpectedly, nearly half of the mutants isolated in this stu ...
Indicate structure that belongs to pelvis as a whole
... What is the function of the external obliquemuscle of the abdomen? A. During bilateral contraction this muscle lowers the ribs and bends the spine. During unilateral contraction it turns the body to the opposite side B. When the pelvis is fixed, bilateral contraction this muscle lowers the ribs. Dur ...
... What is the function of the external obliquemuscle of the abdomen? A. During bilateral contraction this muscle lowers the ribs and bends the spine. During unilateral contraction it turns the body to the opposite side B. When the pelvis is fixed, bilateral contraction this muscle lowers the ribs. Dur ...
A nucleus-encoded chloroplast protein regulated by iron availability
... domain may be functionally important (Supplemental Table S1). Altogether, these observations suggest that TAA1 could be involved in RNA metabolism. A comparison of the cDNA sequences of the wild-type TAA1 and of the taa1 mutant, obtained by RT-PCR, revealed a single base substitution, which changes ...
... domain may be functionally important (Supplemental Table S1). Altogether, these observations suggest that TAA1 could be involved in RNA metabolism. A comparison of the cDNA sequences of the wild-type TAA1 and of the taa1 mutant, obtained by RT-PCR, revealed a single base substitution, which changes ...
Coordination of peptidoglycan synthesis and outer membrane
... a ‘pinch-point’ until the two halves of the cell have been separated. This process must be carefully controlled to ensure that the cell does not burst open at any point. Some bacteria known as ‘Gram-negative’ bacteria have a second membrane on the other side of the cell wall. These cells divide in t ...
... a ‘pinch-point’ until the two halves of the cell have been separated. This process must be carefully controlled to ensure that the cell does not burst open at any point. Some bacteria known as ‘Gram-negative’ bacteria have a second membrane on the other side of the cell wall. These cells divide in t ...
Cell nucleus

In cell biology, the nucleus (pl. nuclei; from Latin nucleus or nuculeus, meaning kernel) is a membrane-enclosed organelle found in eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotes usually have a single nucleus, but a few cell types have no nuclei, and a few others have many.Cell nuclei contain most of the cell's genetic material, organized as multiple long linear DNA molecules in complex with a large variety of proteins, such as histones, to form chromosomes. The genes within these chromosomes are the cell's nuclear genome. The function of the nucleus is to maintain the integrity of these genes and to control the activities of the cell by regulating gene expression—the nucleus is, therefore, the control center of the cell. The main structures making up the nucleus are the nuclear envelope, a double membrane that encloses the entire organelle and isolates its contents from the cellular cytoplasm, and the nucleoskeleton (which includes nuclear lamina), a network within the nucleus that adds mechanical support, much like the cytoskeleton, which supports the cell as a whole.Because the nuclear membrane is impermeable to large molecules, nuclear pores are required that regulate nuclear transport of molecules across the envelope. The pores cross both nuclear membranes, providing a channel through which larger molecules must be actively transported by carrier proteins while allowing free movement of small molecules and ions. Movement of large molecules such as proteins and RNA through the pores is required for both gene expression and the maintenance of chromosomes. The interior of the nucleus does not contain any membrane-bound sub compartments, its contents are not uniform, and a number of sub-nuclear bodies exist, made up of unique proteins, RNA molecules, and particular parts of the chromosomes. The best-known of these is the nucleolus, which is mainly involved in the assembly of ribosomes. After being produced in the nucleolus, ribosomes are exported to the cytoplasm where they translate mRNA.