Chapter 4: A Tour of the Cell
... 16. What do we mean by the fluid mosaic model of the cell membrane? “Fluid in the membrane’s molecular wanderings and mosaic in the diversity of proteins that float like icebergs in the sea of phospholipids.” 17. Define the following: a. selectively permeable the membrane allows some substances to c ...
... 16. What do we mean by the fluid mosaic model of the cell membrane? “Fluid in the membrane’s molecular wanderings and mosaic in the diversity of proteins that float like icebergs in the sea of phospholipids.” 17. Define the following: a. selectively permeable the membrane allows some substances to c ...
Part B: Cell Organelles Structure and Function
... 1. State the three parts to the traditional cell theory: a. b. c. 2. Describe what Anton van Leeuwenhoek and Robert Hooke did to contribute to the cell theory. ...
... 1. State the three parts to the traditional cell theory: a. b. c. 2. Describe what Anton van Leeuwenhoek and Robert Hooke did to contribute to the cell theory. ...
Cells: basic unit of Life
... 2. Organelle-tiny structures inside cells that perform specific functions 3. Cell membrane- outside covering of cells; controls what goes in and out of a cell 4. Cytoplasm-gel-like fluid inside cells 5. Nucleus-control center of the cell 6. DNA-genetic material of an organism ...
... 2. Organelle-tiny structures inside cells that perform specific functions 3. Cell membrane- outside covering of cells; controls what goes in and out of a cell 4. Cytoplasm-gel-like fluid inside cells 5. Nucleus-control center of the cell 6. DNA-genetic material of an organism ...
Chapter 4 Eukaryotic Cell
... Made up of two subunits. Each subunit is made up of proteins and ribosomal RNA. • Eukaryotic cell has 80s ribosomes. • Larger and denser than prokarytoic ribosomes. ...
... Made up of two subunits. Each subunit is made up of proteins and ribosomal RNA. • Eukaryotic cell has 80s ribosomes. • Larger and denser than prokarytoic ribosomes. ...
The Function of Organelles
... ATP Most of cell’s ATP made here Animal cells can’t make own food so we need these to break down sugar for energy ...
... ATP Most of cell’s ATP made here Animal cells can’t make own food so we need these to break down sugar for energy ...
Histology Practical 1
... Identify the connective tissue described. 8. A vascular connective tissue consisting of cells sitting in a calcium rich matrix with many collagen fibers laid down in lamellae. 9. An avascular connective tissue, cells occupy a potential space termed a lacuna, associated with movable joints, and is t ...
... Identify the connective tissue described. 8. A vascular connective tissue consisting of cells sitting in a calcium rich matrix with many collagen fibers laid down in lamellae. 9. An avascular connective tissue, cells occupy a potential space termed a lacuna, associated with movable joints, and is t ...
Cellular specialization and differentiation
... words. Provide an example. (It doesn’t have to be an example from biology). ...
... words. Provide an example. (It doesn’t have to be an example from biology). ...
Development of a Production Process of Viral Particles –Kinetic
... The cells have been adapted to a commercially available serum-free medium. In addition, all products of animal origin have been replaced. The growth surface was provided by micro carriers for the cultivation of adherent cells in stirred systems. Similar maximum titers were reached for cell-associate ...
... The cells have been adapted to a commercially available serum-free medium. In addition, all products of animal origin have been replaced. The growth surface was provided by micro carriers for the cultivation of adherent cells in stirred systems. Similar maximum titers were reached for cell-associate ...
Institute for Genetics of the University of Cologne Christoph Möhl
... Active movement of single cells plays a central role in various biological processes such as tissue development, cancer metastasis and immune response. In contrast to e.g. flagellar movement, cell migration is not driven by a distinct organelle, but rather by the concerted integration of multiple dy ...
... Active movement of single cells plays a central role in various biological processes such as tissue development, cancer metastasis and immune response. In contrast to e.g. flagellar movement, cell migration is not driven by a distinct organelle, but rather by the concerted integration of multiple dy ...
Review Sheet – Biology
... Functions and locations in the cell of the following in prokaryotes: cell wall, cell membrane, cytoplasm, nucleoid, ribosomes, pili, flagella ...
... Functions and locations in the cell of the following in prokaryotes: cell wall, cell membrane, cytoplasm, nucleoid, ribosomes, pili, flagella ...
webquest answer sheet
... cause any problems because they are not part of the cell's genes.” (Hyperlinks in this definition link directly to the meaning of these terms. DNA: acronym used to refer to deoxyribonucleic acid, the molecule found in the nucleus of cells that contains genetic information about an organism. Mitosis: ...
... cause any problems because they are not part of the cell's genes.” (Hyperlinks in this definition link directly to the meaning of these terms. DNA: acronym used to refer to deoxyribonucleic acid, the molecule found in the nucleus of cells that contains genetic information about an organism. Mitosis: ...
Product Information
... phase of the cell cycle. Thereby a cell in the interphase (“resting phase”) of G 418-BC is less affected than in the mitosis (“separating phase”). But also on separating-active cells, the cells’ death occurs only after 3 to 7 days. The recommended concentration at G 418-BC in the medium has for euka ...
... phase of the cell cycle. Thereby a cell in the interphase (“resting phase”) of G 418-BC is less affected than in the mitosis (“separating phase”). But also on separating-active cells, the cells’ death occurs only after 3 to 7 days. The recommended concentration at G 418-BC in the medium has for euka ...
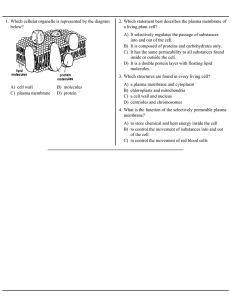
A) cell wall B) molecules C) plasma membrane D) protein 1. Which
... 2. Which statement best describes the plasma membrane of a living plant cell? A) It selectively regulates the passage of substances into and out of the cell. B) It is composed of proteins and carbohydrates only. C) It has the same permeability to all substances found inside or outside the cell. D) I ...
... 2. Which statement best describes the plasma membrane of a living plant cell? A) It selectively regulates the passage of substances into and out of the cell. B) It is composed of proteins and carbohydrates only. C) It has the same permeability to all substances found inside or outside the cell. D) I ...
biochem ch 49 [2-9
... Types of collagen that do not form fibrils perform a series of distinct roles Fibril-associated collagens bind to surface of collagen fibrils and link them to other matrix-forming components Transmembrane collagens form anchoring fibrils that link components of extracellular matrix to underlyi ...
... Types of collagen that do not form fibrils perform a series of distinct roles Fibril-associated collagens bind to surface of collagen fibrils and link them to other matrix-forming components Transmembrane collagens form anchoring fibrils that link components of extracellular matrix to underlyi ...
Cell Cycle and Facts
... Through the process of mitosis (cell division) our body ensures the numbers of chromosomes stay the same throughout the body ...
... Through the process of mitosis (cell division) our body ensures the numbers of chromosomes stay the same throughout the body ...
Cell Structure and Function
... 1. Cell Wall Cell Wall -ALL Cells have a Cell membrane, but plant cells ALSO have a Cell Wall -It is made of cellulose -It gives shape, support, and structure to the plant cell ...
... 1. Cell Wall Cell Wall -ALL Cells have a Cell membrane, but plant cells ALSO have a Cell Wall -It is made of cellulose -It gives shape, support, and structure to the plant cell ...
Name - Humble ISD
... Discuss the structures of a typical cell and the functions of each structure What is the molecular structure of and function of cell membranes? Chapter 4 Physiology of Cells What are the similarities and differences between diffusion, dialysis, osmosis and filtration? What is the difference between ...
... Discuss the structures of a typical cell and the functions of each structure What is the molecular structure of and function of cell membranes? Chapter 4 Physiology of Cells What are the similarities and differences between diffusion, dialysis, osmosis and filtration? What is the difference between ...
Unit 6 Objectives Chapter 4 • Understand the basic tenets of the cell
... the general function of each ...
... the general function of each ...
Across 1. an organelle within the nucleus that produces ribosomes 3
... 12. thinnest filaments found in eukaryotic cells (made of actin) 14. an organelle unique to plant cells that is green in colour 15. a complex combination of DNA, RNA, and protein that makes up chromosomes 16. allow transport between the cytoplasm and ...
... 12. thinnest filaments found in eukaryotic cells (made of actin) 14. an organelle unique to plant cells that is green in colour 15. a complex combination of DNA, RNA, and protein that makes up chromosomes 16. allow transport between the cytoplasm and ...
Extracellular matrix

In biology, the extracellular matrix (ECM) is a collection of extracellular molecules secreted by cells that provides structural and biochemical support to the surrounding cells. Because multicellularity evolved independently in different multicellular lineages, the composition of ECM varies between multicellular structures; however, cell adhesion, cell-to-cell communication and differentiation are common functions of the ECM.The animal extracellular matrix includes the interstitial matrix and the basement membrane. Interstitial matrix is present between various animal cells (i.e., in the intercellular spaces). Gels of polysaccharides and fibrous proteins fill the interstitial space and act as a compression buffer against the stress placed on the ECM. Basement membranes are sheet-like depositions of ECM on which various epithelial cells rest.The plant ECM includes cell wall components, like cellulose, in addition to more complex signaling molecules. Some single-celled organisms adopt multicelluar biofilms in which the cells are embedded in an ECM composed primarily of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS).