The Cell and Its Structures
... - every cell must carry out basic functions to stay alive (obtaining materials and supplies for energy, making products and getting rid of wastes) - to carry out these functions, cells must have certain internal structures known as organelles A – Cell membrane – surrounds and protects the contents o ...
... - every cell must carry out basic functions to stay alive (obtaining materials and supplies for energy, making products and getting rid of wastes) - to carry out these functions, cells must have certain internal structures known as organelles A – Cell membrane – surrounds and protects the contents o ...
Outline
... Survey of Organelles and Cell Structures Plasma Membrane (cell membrane) outside limit of each cell semi-permeable Cell Wall in plants, fungi and prokaryotes no cell walls in animal cells not a permeability barrier Nucleus, nuclear pores and nucleolus Mitochondria – two membranes, inner and outer. I ...
... Survey of Organelles and Cell Structures Plasma Membrane (cell membrane) outside limit of each cell semi-permeable Cell Wall in plants, fungi and prokaryotes no cell walls in animal cells not a permeability barrier Nucleus, nuclear pores and nucleolus Mitochondria – two membranes, inner and outer. I ...
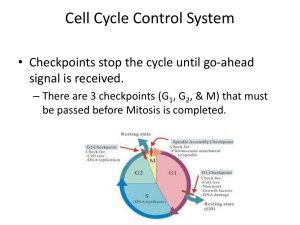
Cell Cycle Control System - Santa Susana High School
... • Cdks - cyclin-dependent kinase (remember that a kinase is an enzyme that activate or inactivate by phosphorylating) – cyclin is always present in the cell and is activated when phosphorylated – synthesized during the S-phase ...
... • Cdks - cyclin-dependent kinase (remember that a kinase is an enzyme that activate or inactivate by phosphorylating) – cyclin is always present in the cell and is activated when phosphorylated – synthesized during the S-phase ...
cells cells - Springwater River Otters
... The main structures- yeah, we call them organelles. Now let's break it down and get some information- How do cells work? It's a crazy combination! -ChorusThe cell membrane is the border patrol, Who can cross over? The membrane lets 'em know The gooey stuff inside, is called the cytoplasm It holds th ...
... The main structures- yeah, we call them organelles. Now let's break it down and get some information- How do cells work? It's a crazy combination! -ChorusThe cell membrane is the border patrol, Who can cross over? The membrane lets 'em know The gooey stuff inside, is called the cytoplasm It holds th ...
Cellular Organization
... Cells are units of structure and function All cells arise from pre-existing cells ...
... Cells are units of structure and function All cells arise from pre-existing cells ...
Cell Theory - OnMyCalendar
... The Center for Disease Control, or CDC, has had to respond to several concerns about various outbreaks of disease across the state. In order to better understand the diseases and how to deal with them, the CDC, has established a series of monetary grants in which they will pay people to do the cell ...
... The Center for Disease Control, or CDC, has had to respond to several concerns about various outbreaks of disease across the state. In order to better understand the diseases and how to deal with them, the CDC, has established a series of monetary grants in which they will pay people to do the cell ...
cell_structure_tt
... pressure of the cell wall prevents more water entering, the cell is said to be turgid. ...
... pressure of the cell wall prevents more water entering, the cell is said to be turgid. ...
Unit 2 Part 1: The Cell Test Review 1. What is the function of a cell`s
... 12. What organelle in plant cells makes it possible for plants to carry out photosynthesis? 13. What does the structure of the endoplasmic reticulum look like? 14. How does the cell membrane function like a security gate? 15. What gets energy by absorbing materials and does not have chloroplast? 16. ...
... 12. What organelle in plant cells makes it possible for plants to carry out photosynthesis? 13. What does the structure of the endoplasmic reticulum look like? 14. How does the cell membrane function like a security gate? 15. What gets energy by absorbing materials and does not have chloroplast? 16. ...
cell organelle webquest
... Objective: Upon completion of this activity, you should be able to describe the cell and identify its parts (organelles). You should be able to distinguish between plant and animal cells. PART I Go to: www.wisc-online.com/objects/index_tj.asp?objid=AP11604 Click “Next” to begin the activity. Answer ...
... Objective: Upon completion of this activity, you should be able to describe the cell and identify its parts (organelles). You should be able to distinguish between plant and animal cells. PART I Go to: www.wisc-online.com/objects/index_tj.asp?objid=AP11604 Click “Next” to begin the activity. Answer ...
Diffusion with Eggs Lab
... • As chemicals pass into and out of a cell, they move from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration. This process is called diffusion. • Water can also move into and out of the cell by osmosis. ...
... • As chemicals pass into and out of a cell, they move from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration. This process is called diffusion. • Water can also move into and out of the cell by osmosis. ...
Cells
... Cell Surfaces • Cell wall, plasma membrane, or capsules • Plant cell wall – Cellulose fibers for ...
... Cell Surfaces • Cell wall, plasma membrane, or capsules • Plant cell wall – Cellulose fibers for ...
Note taking guide
... Lies within the cytoplasmic membrane. It’s featureless under electron microscope, has a gel-like consistency with different properties, and holds many cellular constituents. Cytoplasm is the medium in which many functions for cell growth, metabolism, and replication are carried out. ...
... Lies within the cytoplasmic membrane. It’s featureless under electron microscope, has a gel-like consistency with different properties, and holds many cellular constituents. Cytoplasm is the medium in which many functions for cell growth, metabolism, and replication are carried out. ...
Cell Theory-
... Cell Theory The cell is the basic unit of life All organisms are made up of cells All cells come from other cells Organelle- “tiny organs” within the cytoplasm Cell Wall- rigid, outer layer that provides support & structure Only in PLANTS, fungi, bacteria “brick wall or support beams” ...
... Cell Theory The cell is the basic unit of life All organisms are made up of cells All cells come from other cells Organelle- “tiny organs” within the cytoplasm Cell Wall- rigid, outer layer that provides support & structure Only in PLANTS, fungi, bacteria “brick wall or support beams” ...
1. All living things are made of cell
... 3. What process creates new cells for growth and repair through cell division that are identical to the parent cell? Mitosis ...
... 3. What process creates new cells for growth and repair through cell division that are identical to the parent cell? Mitosis ...
Jeopardy
... Which part of the cell allows certain materials to enter the cell and other materials to ...
... Which part of the cell allows certain materials to enter the cell and other materials to ...
Extracellular matrix

In biology, the extracellular matrix (ECM) is a collection of extracellular molecules secreted by cells that provides structural and biochemical support to the surrounding cells. Because multicellularity evolved independently in different multicellular lineages, the composition of ECM varies between multicellular structures; however, cell adhesion, cell-to-cell communication and differentiation are common functions of the ECM.The animal extracellular matrix includes the interstitial matrix and the basement membrane. Interstitial matrix is present between various animal cells (i.e., in the intercellular spaces). Gels of polysaccharides and fibrous proteins fill the interstitial space and act as a compression buffer against the stress placed on the ECM. Basement membranes are sheet-like depositions of ECM on which various epithelial cells rest.The plant ECM includes cell wall components, like cellulose, in addition to more complex signaling molecules. Some single-celled organisms adopt multicelluar biofilms in which the cells are embedded in an ECM composed primarily of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS).