Cellular Organelles Quiz
... 1_______ The structure in the nucleus which manufactures ribosomes for protein synthesis. 2_______ Cellular structure that regulates what enters and leaves the cell. 3_______ Organelles that store materials such as water, salts, and carbohydrates. They may occupy a large space within plant cells. 4_ ...
... 1_______ The structure in the nucleus which manufactures ribosomes for protein synthesis. 2_______ Cellular structure that regulates what enters and leaves the cell. 3_______ Organelles that store materials such as water, salts, and carbohydrates. They may occupy a large space within plant cells. 4_ ...
Cellular Organelles Quiz
... products to be used at another cellular local. 4_______ The organelle responsible for manufacturing proteins. (Be specific!) 5_______ The information and control center of the cell. Contains genetic information. 6_______ The structure in the nucleus which manufactures ribosomes for protein synthesis ...
... products to be used at another cellular local. 4_______ The organelle responsible for manufacturing proteins. (Be specific!) 5_______ The information and control center of the cell. Contains genetic information. 6_______ The structure in the nucleus which manufactures ribosomes for protein synthesis ...
Name: Date: Biology Chapter 6: A Tour of the Cell Review Sheet
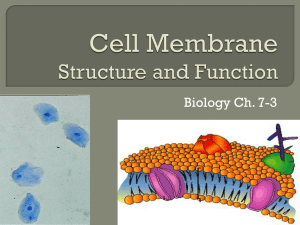
... 1. What are the three components of the cell theory? 2. Compare (similarities) and contrast (differences) prokaryotes and eukaryotes. 3. Compare and contrast animal and plant cells. 6.2 Cell membrane 1. Know all terms. 2. Draw the cell membrane and label and briefly describe the function of the foll ...
... 1. What are the three components of the cell theory? 2. Compare (similarities) and contrast (differences) prokaryotes and eukaryotes. 3. Compare and contrast animal and plant cells. 6.2 Cell membrane 1. Know all terms. 2. Draw the cell membrane and label and briefly describe the function of the foll ...
File
... What are the three parts of the cell theory? How are molecules, organelles, cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, and organisms related? List them in to order from least to most complex. What is cell specialization (differentiation)? How is a cell’s specialized shape related to its speciali ...
... What are the three parts of the cell theory? How are molecules, organelles, cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, and organisms related? List them in to order from least to most complex. What is cell specialization (differentiation)? How is a cell’s specialized shape related to its speciali ...
Cell Cycle Control System
... • Loss of function of p53 gene (apoptosis gene) – if the cells stay in the same location they are said to be benign – if the tumor invades an organ and impair its function, it is said to be malignant – when the cancer cells travel to different locations they are metastatic (process is ...
... • Loss of function of p53 gene (apoptosis gene) – if the cells stay in the same location they are said to be benign – if the tumor invades an organ and impair its function, it is said to be malignant – when the cancer cells travel to different locations they are metastatic (process is ...
Ch. 7 GN - Jamestown Public Schools
... Levels of Organization - The __________ of organization in a ________________ organism are individual ______, tissues, ___________, & __________ systems - Tissue – a group of similar _______ that perform a particular ___________ - Organ – many groups of __________ working ______________ - Organ syst ...
... Levels of Organization - The __________ of organization in a ________________ organism are individual ______, tissues, ___________, & __________ systems - Tissue – a group of similar _______ that perform a particular ___________ - Organ – many groups of __________ working ______________ - Organ syst ...
Cytology
... • To describe the characteristics and identify the monomers of lipids, proteins, carbohydrates, and nucleic acids and to define their role in biochemical processes. • To analyze and explain the chemical reactions the provide energy for the body. • To investigate and describe the integration of the c ...
... • To describe the characteristics and identify the monomers of lipids, proteins, carbohydrates, and nucleic acids and to define their role in biochemical processes. • To analyze and explain the chemical reactions the provide energy for the body. • To investigate and describe the integration of the c ...
Cell Content Statement 1 Study Guide
... Know the definition of the following organelles: (Use “The Cell: The Basic Unit of Life” Packet) Cell wall Cell membrane Cytoplasm Vacuoles Nucleus Chromosomes Chloroplasts Endoplasmic Reticulum Ribosome Mitochondria ...
... Know the definition of the following organelles: (Use “The Cell: The Basic Unit of Life” Packet) Cell wall Cell membrane Cytoplasm Vacuoles Nucleus Chromosomes Chloroplasts Endoplasmic Reticulum Ribosome Mitochondria ...
Biology- ch. 7
... • All living things are composed of cells • Cells are the basic units of structure and organization in living things • New cells are produced from existing cells with cells passing copies of their genetic material down to their daughter cells ...
... • All living things are composed of cells • Cells are the basic units of structure and organization in living things • New cells are produced from existing cells with cells passing copies of their genetic material down to their daughter cells ...
Cells
... All living things are made of one or more cells The cell is the smallest unit of life All new cells come from preexisting cells ...
... All living things are made of one or more cells The cell is the smallest unit of life All new cells come from preexisting cells ...
Introduction to Cells
... him of the little rooms where monks prayed. This is his actual drawing of what he saw. So what is Hooke remembered for? ...
... him of the little rooms where monks prayed. This is his actual drawing of what he saw. So what is Hooke remembered for? ...
1 - Cork
... Do red blood cells have The long fibers of a Do bacteria have a a nucleus? nerve cell make nucleus? hundreds of connections with other nerve cells. What do they control? Do white blood cells have a nucleus? What is the study of bacteria called? ...
... Do red blood cells have The long fibers of a Do bacteria have a a nucleus? nerve cell make nucleus? hundreds of connections with other nerve cells. What do they control? Do white blood cells have a nucleus? What is the study of bacteria called? ...
Extra cellular components 15
... Animal cell lack cell walls but they have elaborate extra cellular matrix (ECM). ECM consists of glycoproteins secreted by the cell. i.e. Collagen which form strong fiber out side the cells. Collagen accounts half of the total proteins in the cell. Collagen fibers are embedded in network of pro ...
... Animal cell lack cell walls but they have elaborate extra cellular matrix (ECM). ECM consists of glycoproteins secreted by the cell. i.e. Collagen which form strong fiber out side the cells. Collagen accounts half of the total proteins in the cell. Collagen fibers are embedded in network of pro ...
logcsscibap_2_1_2_d_..
... Spirogyra is an alga. It is made up of cells joined by their cell walls to form long filaments. If a single cell is detached from the filament it can survive and grow to form a new filament. a ...
... Spirogyra is an alga. It is made up of cells joined by their cell walls to form long filaments. If a single cell is detached from the filament it can survive and grow to form a new filament. a ...
Biology_Semester_2_Learning_Targets
... 1. Explain what chemical compounds are and why they are important. a. Describe properties of water that makes it important to life. b. Explain what chemical compounds are and why they are important to living organisms. c. Describe the composition and role of carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucl ...
... 1. Explain what chemical compounds are and why they are important. a. Describe properties of water that makes it important to life. b. Explain what chemical compounds are and why they are important to living organisms. c. Describe the composition and role of carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucl ...
HyStem Hydrogels for Stem Cell Research
... The immobilized heparin in the HyStem-HP hydrogel mimics the heparin sulfate proteoglycans normally present in the extracellular matrix. Heparin forms an ionic bond with proteins which protects them from proteolysis and facilitates their slow release into the cell culture medium. This significantly ...
... The immobilized heparin in the HyStem-HP hydrogel mimics the heparin sulfate proteoglycans normally present in the extracellular matrix. Heparin forms an ionic bond with proteins which protects them from proteolysis and facilitates their slow release into the cell culture medium. This significantly ...
Ribosomes 2
... Located on the Rough ER and in the cytoplasm in eukaryotic cells and move freely in prokaryotic cells ...
... Located on the Rough ER and in the cytoplasm in eukaryotic cells and move freely in prokaryotic cells ...
Chemistry of Macromolecules
... • Fatty acid tail Used for: • Long term energy storage • Insulation • Major component of ...
... • Fatty acid tail Used for: • Long term energy storage • Insulation • Major component of ...
Biology: Cell Unit Review
... Cell Structure • Form follows function: Shapes evolve to allow cells to perform their function. • Sizes range from nm to 2 m in length, but average cells are 10 – 50 mm. • Surface-area-to-volume ratio limits size. – Volume increases more quickly. – Cells’ need for nutrient intake & waste disposal d ...
... Cell Structure • Form follows function: Shapes evolve to allow cells to perform their function. • Sizes range from nm to 2 m in length, but average cells are 10 – 50 mm. • Surface-area-to-volume ratio limits size. – Volume increases more quickly. – Cells’ need for nutrient intake & waste disposal d ...
Ch 6 Organelles
... a. __________________ May be free or attached b. __________________Site of photosynthesis c. __________________ A double membrane encloses nucleus d. __________________ Stores water in plant cells e. _________________ Contains enzymes, one of which is catalase f. __________________Thickest fiber of ...
... a. __________________ May be free or attached b. __________________Site of photosynthesis c. __________________ A double membrane encloses nucleus d. __________________ Stores water in plant cells e. _________________ Contains enzymes, one of which is catalase f. __________________Thickest fiber of ...
L*_*__*__dF - IES Alyanub
... biomolecule: smallest unit an organism can be divided into multicellular: containing more than one cell eukaryote: organism made of cells that have a nucleus heterotrophic: obtaining nutrition from compounds that already exist organelle: special compartment inside a eukaryotic cell that performs a s ...
... biomolecule: smallest unit an organism can be divided into multicellular: containing more than one cell eukaryote: organism made of cells that have a nucleus heterotrophic: obtaining nutrition from compounds that already exist organelle: special compartment inside a eukaryotic cell that performs a s ...
Extracellular matrix

In biology, the extracellular matrix (ECM) is a collection of extracellular molecules secreted by cells that provides structural and biochemical support to the surrounding cells. Because multicellularity evolved independently in different multicellular lineages, the composition of ECM varies between multicellular structures; however, cell adhesion, cell-to-cell communication and differentiation are common functions of the ECM.The animal extracellular matrix includes the interstitial matrix and the basement membrane. Interstitial matrix is present between various animal cells (i.e., in the intercellular spaces). Gels of polysaccharides and fibrous proteins fill the interstitial space and act as a compression buffer against the stress placed on the ECM. Basement membranes are sheet-like depositions of ECM on which various epithelial cells rest.The plant ECM includes cell wall components, like cellulose, in addition to more complex signaling molecules. Some single-celled organisms adopt multicelluar biofilms in which the cells are embedded in an ECM composed primarily of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS).