The Parts of A Cell - Lemoore Elementary School
... • Some cells, like plants and fungi have a rigid cell wall. • Cell walls provide shape, support, and protection for the cell. • Animal cells DO NOT have cell walls. ...
... • Some cells, like plants and fungi have a rigid cell wall. • Cell walls provide shape, support, and protection for the cell. • Animal cells DO NOT have cell walls. ...
Cell Surface/Intercell Communication Division
... Extracellular Matrix (ECM) Definition: A substance that contains collagen, elastin, proteoglycans, glycosaminoglycans, and fluid that is produced by cells and in which the cells are embedded. ● Secreted by chondroblasts which is responsible for the properties of forming cartilage. ● Osteoblasts for ...
... Extracellular Matrix (ECM) Definition: A substance that contains collagen, elastin, proteoglycans, glycosaminoglycans, and fluid that is produced by cells and in which the cells are embedded. ● Secreted by chondroblasts which is responsible for the properties of forming cartilage. ● Osteoblasts for ...
Cell Unit Project (Chapters 1-2)
... Directions: Be sure to add colored pictures (provide websites) and be creative. All foldables must be colored. Characteristics of all Living Things 1. List the characteristics of all living things (4) 2. List the needs of all living things (3) 3. What are the components of the Cell Theory? Contribut ...
... Directions: Be sure to add colored pictures (provide websites) and be creative. All foldables must be colored. Characteristics of all Living Things 1. List the characteristics of all living things (4) 2. List the needs of all living things (3) 3. What are the components of the Cell Theory? Contribut ...
Understanding cell and tissue size and shape regulation in a stem
... use a computational morphodynamics approach, where live imaging is combined with mathematical modeling, to better understand the regulation of differentiation and cell growth in the meristem tissue. I will discuss how the number of stem cells is scaling with the size and shape of the niche tissue. O ...
... use a computational morphodynamics approach, where live imaging is combined with mathematical modeling, to better understand the regulation of differentiation and cell growth in the meristem tissue. I will discuss how the number of stem cells is scaling with the size and shape of the niche tissue. O ...
1 - Evolving Sciences
... The Chloroplast are specialised organelles filled with chlorophyll. They are found in plant cells and their main role is to assist in photosynthesis. Another specific feature to plant cells is a cell wall made of cellulose. Organelles like the nucleus and ribosome, float in the cytoplasm. A jelly li ...
... The Chloroplast are specialised organelles filled with chlorophyll. They are found in plant cells and their main role is to assist in photosynthesis. Another specific feature to plant cells is a cell wall made of cellulose. Organelles like the nucleus and ribosome, float in the cytoplasm. A jelly li ...
File
... Unit 3: Cell Biology Scale Learning Goal/Bio Benchmark: I can compare and contrast the general structures of plant and animal cells and the general structures of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. I can also relate structure to function for the components of plant and animal cells. Finally, I can exp ...
... Unit 3: Cell Biology Scale Learning Goal/Bio Benchmark: I can compare and contrast the general structures of plant and animal cells and the general structures of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. I can also relate structure to function for the components of plant and animal cells. Finally, I can exp ...
The Cell
... ◦ 2. filtration-movement of water and other solutes from high to low concentration Based on a difference in water pressure between external and internal environment ...
... ◦ 2. filtration-movement of water and other solutes from high to low concentration Based on a difference in water pressure between external and internal environment ...
Cells PPt 2
... Cellular respiration occurs here to release energy for the cell to use Bound by a double membrane Inner folds= cristae Has its own strand of DNA ...
... Cellular respiration occurs here to release energy for the cell to use Bound by a double membrane Inner folds= cristae Has its own strand of DNA ...
Tunneling nanotubes meso abstract
... Background: Research efforts to understand communication mechanisms that influence cancer growth and metastasis have been focused on gap junctions, exosomes and microvesicles, and cytokine signaling interactions between cells. Currently there is limited understanding of how efficient cell-to-cell co ...
... Background: Research efforts to understand communication mechanisms that influence cancer growth and metastasis have been focused on gap junctions, exosomes and microvesicles, and cytokine signaling interactions between cells. Currently there is limited understanding of how efficient cell-to-cell co ...
The cell is the smallest unit of life
... The _________ is the smallest unit of life. Anything smaller is not alive. ___________ living things are made of cells. There are three basic types of cells. ________________,________________, &_______________. Cells contain tiny structures that perform specific functions that are called ___________ ...
... The _________ is the smallest unit of life. Anything smaller is not alive. ___________ living things are made of cells. There are three basic types of cells. ________________,________________, &_______________. Cells contain tiny structures that perform specific functions that are called ___________ ...
Cell Structure & Function
... • The lipid bilayer has carbohydrates AND proteins embedded within! ...
... • The lipid bilayer has carbohydrates AND proteins embedded within! ...
Cell Motility - Cochran`s Half Acre
... Components of the Cytoskeleton: • Intermediate Filaments – Only in animal cells of specific tissues – Mechanically strengthen cells or cell parts and help maintain shape ...
... Components of the Cytoskeleton: • Intermediate Filaments – Only in animal cells of specific tissues – Mechanically strengthen cells or cell parts and help maintain shape ...
single cell. - Sonoma Valley High School
... ways to perform different tasks for the whole organism. Cells communicate and cooperate with each other ...
... ways to perform different tasks for the whole organism. Cells communicate and cooperate with each other ...
File
... Directions: Answer the following questions in complete sentences on a separate sheet of paper. 1. What are the differences between plant cells and animal cells? 2. How do waste products, such as carbon dioxide leave cells? 3. What are cells? 4. Which part of a plant cell provides rigid support for t ...
... Directions: Answer the following questions in complete sentences on a separate sheet of paper. 1. What are the differences between plant cells and animal cells? 2. How do waste products, such as carbon dioxide leave cells? 3. What are cells? 4. Which part of a plant cell provides rigid support for t ...
Flow of Matter_04_Sample Quiz Questions
... 2) Make sure you also include at least one observation from our Cell Diversity Lab (Lab 02) as evidence to support your explanation. ...
... 2) Make sure you also include at least one observation from our Cell Diversity Lab (Lab 02) as evidence to support your explanation. ...
Homeostasis and the Cell
... • The tendency of a system to maintain its internal stability. • We sweat or shiver to maintain our body’s core temperature. • Homeostasis happens, as well, at a cellular level in order to maintain the stability of the cells. ...
... • The tendency of a system to maintain its internal stability. • We sweat or shiver to maintain our body’s core temperature. • Homeostasis happens, as well, at a cellular level in order to maintain the stability of the cells. ...
WebQuest 1 - The Cell - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... 5) What do the following types of blood cells do inside the human body? a) Red blood cells. b) White blood cells. 6) List three functions of bone cells in the human body. 7) Describe how brain cells are different from other human body cells. 8) a) Which cells in the human body have the longest life ...
... 5) What do the following types of blood cells do inside the human body? a) Red blood cells. b) White blood cells. 6) List three functions of bone cells in the human body. 7) Describe how brain cells are different from other human body cells. 8) a) Which cells in the human body have the longest life ...
Cells - Denton ISD
... difficult it is to get things in and out of it. •If cells grow too large they would not be able to supply their own needs, and growth would come to a stop. ...
... difficult it is to get things in and out of it. •If cells grow too large they would not be able to supply their own needs, and growth would come to a stop. ...
Videomicroscopic study of cell motility and proliferation in vitro
... II. This tumor cell cultures were also used to model the effect of therapeutic irradiation in vitro. Dose-dependent cell enlargement and inhibition of cell proliferation was found within one week following a single irradiation. A controversial motility enhancing effect of sublethal radiation was obs ...
... II. This tumor cell cultures were also used to model the effect of therapeutic irradiation in vitro. Dose-dependent cell enlargement and inhibition of cell proliferation was found within one week following a single irradiation. A controversial motility enhancing effect of sublethal radiation was obs ...
Exam III Sample Questions
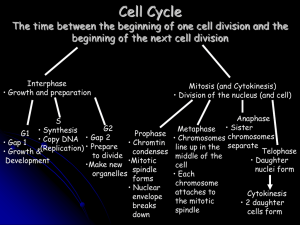
... 1. M-CDK activity is required for the metaphase to anaphase transition to occur during Mitosis 2. Duplication of DNA and Centrioles occurs during S phase. 3. Activation of initiator caspases can only occur as a result of cytochrome C release from the mitochondria inner membrane space. 4. Assembly of ...
... 1. M-CDK activity is required for the metaphase to anaphase transition to occur during Mitosis 2. Duplication of DNA and Centrioles occurs during S phase. 3. Activation of initiator caspases can only occur as a result of cytochrome C release from the mitochondria inner membrane space. 4. Assembly of ...
Extracellular matrix

In biology, the extracellular matrix (ECM) is a collection of extracellular molecules secreted by cells that provides structural and biochemical support to the surrounding cells. Because multicellularity evolved independently in different multicellular lineages, the composition of ECM varies between multicellular structures; however, cell adhesion, cell-to-cell communication and differentiation are common functions of the ECM.The animal extracellular matrix includes the interstitial matrix and the basement membrane. Interstitial matrix is present between various animal cells (i.e., in the intercellular spaces). Gels of polysaccharides and fibrous proteins fill the interstitial space and act as a compression buffer against the stress placed on the ECM. Basement membranes are sheet-like depositions of ECM on which various epithelial cells rest.The plant ECM includes cell wall components, like cellulose, in addition to more complex signaling molecules. Some single-celled organisms adopt multicelluar biofilms in which the cells are embedded in an ECM composed primarily of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS).