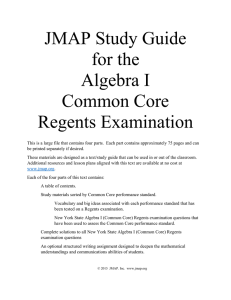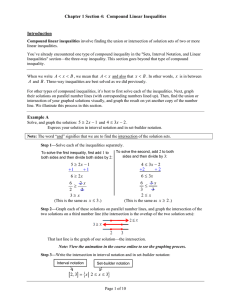
pdf [local copy]
... In this paper we aim at more general formulations. The expressive power in the title refers to, on the one hand, the recursion-theoretic complexity of the problem of kernel existence and, on the other hand, to the axiomatic strength of solvability of digraphs of various classes. These questions, app ...
... In this paper we aim at more general formulations. The expressive power in the title refers to, on the one hand, the recursion-theoretic complexity of the problem of kernel existence and, on the other hand, to the axiomatic strength of solvability of digraphs of various classes. These questions, app ...





![pdf [local copy]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/003897753_1-78a7dbe322dae43ae963f2a2fbd70110-300x300.png)