Document
... D.) No difference in transcription rate when an activator protein was present. E.) Negative control of transcription. ...
... D.) No difference in transcription rate when an activator protein was present. E.) Negative control of transcription. ...
Genetic Modification of Plants using Agrobacterium
... 6. A culture of this GM Agrobacterium is grown. 7. Transfection – the bacterium is made to infect plant tissue (this process can also be called transformation). This can be done in 3 different ways: Soaking leaf discs in the Agrobacterium culture & then growing these discs on agar containing kanamy ...
... 6. A culture of this GM Agrobacterium is grown. 7. Transfection – the bacterium is made to infect plant tissue (this process can also be called transformation). This can be done in 3 different ways: Soaking leaf discs in the Agrobacterium culture & then growing these discs on agar containing kanamy ...
Card Match
... When an organism produces offspring that are clones of itself. The offspring have just one parent. ...
... When an organism produces offspring that are clones of itself. The offspring have just one parent. ...
Repair of Damaged DNA
... DNA with closely related sequences 2. Site-specific 3. Transposition - occurs between unrelated sequences (e.g. Transposons; jumping genes ) Homologous Recombination Three purposes: 1. Recombinational DNA repair 2. DNA organization during meiosis (eukaryotes) 3. Genetic diversity (exchanging alleles ...
... DNA with closely related sequences 2. Site-specific 3. Transposition - occurs between unrelated sequences (e.g. Transposons; jumping genes ) Homologous Recombination Three purposes: 1. Recombinational DNA repair 2. DNA organization during meiosis (eukaryotes) 3. Genetic diversity (exchanging alleles ...
Inheritance and biotechnology assessment statements
... Topic 3.5 Genetic modification and biotechnology 3.5.1 Explain the process of DNA profiling including the processes of PCR and gel electrophoresis 3.5.2. Describe the process of cloning using one parent cell 3.5.3 Compare benefits and problems of genetic modification of species 3.5.4 Discuss the ris ...
... Topic 3.5 Genetic modification and biotechnology 3.5.1 Explain the process of DNA profiling including the processes of PCR and gel electrophoresis 3.5.2. Describe the process of cloning using one parent cell 3.5.3 Compare benefits and problems of genetic modification of species 3.5.4 Discuss the ris ...
DNA Unit Study Guide 2017 - Liberty Union High School District
... DNA T A C T A T T C C T C G T C T C G G C G T A T T mRNA_______________________________________________________________________ tRNA________________________________________________________________________ rRNA/aa______________________________________________________________________ 24. What is a gen ...
... DNA T A C T A T T C C T C G T C T C G G C G T A T T mRNA_______________________________________________________________________ tRNA________________________________________________________________________ rRNA/aa______________________________________________________________________ 24. What is a gen ...
Functional genomics and drug discovery: use of alternative model
... over the world to determine the complete genomic sequences of various organisms. This exercise has resulted in the generation of enormous sequence database comprising of the genome sequences of the various model organisms such as E coli, yeast, C. elegans, Drosophila, Arabidopsis, mouse, etc. One of ...
... over the world to determine the complete genomic sequences of various organisms. This exercise has resulted in the generation of enormous sequence database comprising of the genome sequences of the various model organisms such as E coli, yeast, C. elegans, Drosophila, Arabidopsis, mouse, etc. One of ...
Heredity and Genetics Vocabulary
... The following document is a running list of vocabulary terms for the Carbohydrate, Lipid and Protein unit for Biology. The unit is one of the larger units and contains a lot of vocabulary to keep straight. In order the help the students I have created this study option for home. ...
... The following document is a running list of vocabulary terms for the Carbohydrate, Lipid and Protein unit for Biology. The unit is one of the larger units and contains a lot of vocabulary to keep straight. In order the help the students I have created this study option for home. ...
Gene Mapping Techniques - Nestlé Nutrition Institute
... gene coding for the light chain of myosin very close to the mouse Idh-1 locus (chromosome 1) using sexual reproduction (and thus meiotic recombination) and two different mouse species: Mus musculus domesticus (the normal laboratory mouse) and Mus spretus (a line derived from a wild population of mic ...
... gene coding for the light chain of myosin very close to the mouse Idh-1 locus (chromosome 1) using sexual reproduction (and thus meiotic recombination) and two different mouse species: Mus musculus domesticus (the normal laboratory mouse) and Mus spretus (a line derived from a wild population of mic ...
L8 cells PPt - Moodle
... Mutations (changes in sequence of DNA bases) may result in changed properties of proteins for which they code caused by e.g. errors of ‘copying’ ...
... Mutations (changes in sequence of DNA bases) may result in changed properties of proteins for which they code caused by e.g. errors of ‘copying’ ...
AS90459 Version 2 Describe genetic variation and change Level 2
... Biological concepts and processes relating to genetic change, ie where the gene pool is affected, will be selected from: ...
... Biological concepts and processes relating to genetic change, ie where the gene pool is affected, will be selected from: ...
A Platform for Cluster Analysis of Next
... The purpose of gene expression data clustering analysis is clustered genes with the same or similar functions to help explore the gene function and regulatory network. The past is mainly based on microarray gene expression data, in recent years due to the development of next-generation sequencing te ...
... The purpose of gene expression data clustering analysis is clustered genes with the same or similar functions to help explore the gene function and regulatory network. The past is mainly based on microarray gene expression data, in recent years due to the development of next-generation sequencing te ...
Genes
... Tay-Sachs Disease: Causes destruction of nervous system, blindness, and death during early childhood. Cystic Fibrosis: Makes breathing and digestion difficult, its caused by abnormal genes, one from each parent. Down Syndrome: Caused by a chromosomal abnormality known as Trisony-21,( the presence of ...
... Tay-Sachs Disease: Causes destruction of nervous system, blindness, and death during early childhood. Cystic Fibrosis: Makes breathing and digestion difficult, its caused by abnormal genes, one from each parent. Down Syndrome: Caused by a chromosomal abnormality known as Trisony-21,( the presence of ...
DNA marker analysis - Central Magnet School
... The region of the DNA that is the known STR marker is amplified (and the BRCA unknown gene version with it) The amplified DNA is then run on a gel. ...
... The region of the DNA that is the known STR marker is amplified (and the BRCA unknown gene version with it) The amplified DNA is then run on a gel. ...
Problem 3: Why do pre-mRNAs get smaller during RNA processing?
... Promoters for eukaryotic mRNA genes: A. are more complex than prokaryotic promoters B. can require binding of multiple transcription factors to form a transcription complex C. have specific DNA sequences such as the "TATA" box that are recognized by proteins D. are the stretches of DNA to which RNA ...
... Promoters for eukaryotic mRNA genes: A. are more complex than prokaryotic promoters B. can require binding of multiple transcription factors to form a transcription complex C. have specific DNA sequences such as the "TATA" box that are recognized by proteins D. are the stretches of DNA to which RNA ...
B. Sc. Part- II (GENETICS)
... PAPER- V : MOLECULAR GENETICS-I Max. Marks: 45 Internal Assessment:5 Time: 3 Hours Note: Question 1 will be compulsory and short answer type covering entire syllabi. Four questions will be set from each Section. Candidates have to answer five questions in all selecting two from each section. SECTION ...
... PAPER- V : MOLECULAR GENETICS-I Max. Marks: 45 Internal Assessment:5 Time: 3 Hours Note: Question 1 will be compulsory and short answer type covering entire syllabi. Four questions will be set from each Section. Candidates have to answer five questions in all selecting two from each section. SECTION ...
Dow Agrosciences Australia - PDF 170 KB
... Using EXZACT™ Delete, no repair template is needed. Once the targeted DNA sequence has been cleaved by EXZACT™ ZFNs, the cell will use another DNA-repair process known as Non-Homologous End-Joining (NHEJ) to resolve the double stranded break. This repair process sometimes results in short nucleotide ...
... Using EXZACT™ Delete, no repair template is needed. Once the targeted DNA sequence has been cleaved by EXZACT™ ZFNs, the cell will use another DNA-repair process known as Non-Homologous End-Joining (NHEJ) to resolve the double stranded break. This repair process sometimes results in short nucleotide ...
Why-do-cells
... like anything else, cells get worn out. They need repair, and, just like an old car, eventually need replacement. The best way to fix what ails a cell is to replace that cell all together. ...
... like anything else, cells get worn out. They need repair, and, just like an old car, eventually need replacement. The best way to fix what ails a cell is to replace that cell all together. ...
JF lect 5 12
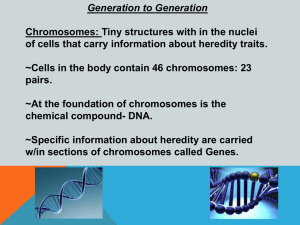
... 1902 – McClung – a particular chromosome (X) determines sex in insects (XO = male; XX = female) 1903 – Sutton and Boveri – chromosomes behave just like the ‘unit factors’ described by Mendel 1910 – Morgan – the “white” eye color gene of Drosophila is located on the X-chromosome - there are many othe ...
... 1902 – McClung – a particular chromosome (X) determines sex in insects (XO = male; XX = female) 1903 – Sutton and Boveri – chromosomes behave just like the ‘unit factors’ described by Mendel 1910 – Morgan – the “white” eye color gene of Drosophila is located on the X-chromosome - there are many othe ...
CHEMISTRY
... 18.4. What are viroids and what do they do? 18.5. What are prions and what do they do? 18.6. What is bacterial transformation and how does it happen? 18.7. Using a diagram, describe the process of transduction by viruses and mention some implications and uses of this process. 18.8. Explain what plas ...
... 18.4. What are viroids and what do they do? 18.5. What are prions and what do they do? 18.6. What is bacterial transformation and how does it happen? 18.7. Using a diagram, describe the process of transduction by viruses and mention some implications and uses of this process. 18.8. Explain what plas ...
gaining immense new power to heal
... How does gene therapy work? • In most gene therapy studies, a "normal" gene is inserted into the genome to replace an "abnormal," disease-causing gene. • A carrier molecule called a vector must be used to deliver the therapeutic gene to the patient's target cells. • Currently, the most common vecto ...
... How does gene therapy work? • In most gene therapy studies, a "normal" gene is inserted into the genome to replace an "abnormal," disease-causing gene. • A carrier molecule called a vector must be used to deliver the therapeutic gene to the patient's target cells. • Currently, the most common vecto ...
14.4 Gene Mutations
... If this occurs in somatic (body) cells, the change cannot be inherited. Only mutations in the DNA within gametes can be passed on to the next generation. ...
... If this occurs in somatic (body) cells, the change cannot be inherited. Only mutations in the DNA within gametes can be passed on to the next generation. ...
Introduction to Genetic - Home
... Methods for detecting genetic abnormalities, depend upon the size and nature of the mutation. Some techniques are applied to test for chromosomal DNA itself, some to the RNA copies and some to the protein product of the gene ...
... Methods for detecting genetic abnormalities, depend upon the size and nature of the mutation. Some techniques are applied to test for chromosomal DNA itself, some to the RNA copies and some to the protein product of the gene ...
Gene Interaction that produces novel Phenotype
... • Genomic imprinting: differential expression of genetic material depending on whether it is inherited from the male or female parent. • Epigenetics: Phenomena due to alterations to DNA that do not include changes in the base sequence; often affect the way in which the DNA sequences are expressed. ...
... • Genomic imprinting: differential expression of genetic material depending on whether it is inherited from the male or female parent. • Epigenetics: Phenomena due to alterations to DNA that do not include changes in the base sequence; often affect the way in which the DNA sequences are expressed. ...
Site-specific recombinase technology

Nearly every human gene has a counterpart in the mouse (regardless of the fact that a minor set of orthologues had to follow species specific selection routes). This made the mouse the major model for elucidating the ways in which our genetic material encodes information. In the late 1980s gene targeting in murine embryonic stem (ES-)cells enabled the transmission of mutations into the mouse germ line and emerged as a novel option to study the genetic basis of regulatory networks as they exist in the genome. Still, classical gene targeting proved to be limited in several ways as gene functions became irreversibly destroyed by the marker gene that had to be introduced for selecting recombinant ES cells. These early steps led to animals in which the mutation was present in all cells of the body from the beginning leading to complex phenotypes and/or early lethality. There was a clear need for methods to restrict these mutations to specific points in development and specific cell types. This dream became reality when groups in the USA were able to introduce bacteriophage and yeast-derived site-specific recombination (SSR-) systems into mammalian cells as well as into the mouse