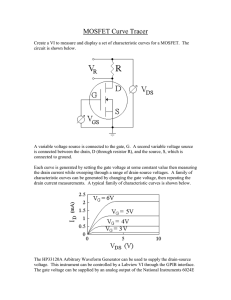
MOSFET Curve Tracer
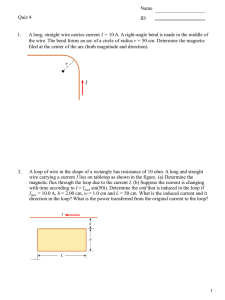
... A variable voltage source is connected to the gate, G. A second variable voltage source is connected between the drain, D (through resistor R), and the source, S, which is connected to ground. Each curve is generated by setting the gate voltage at some constant value then measuring the drain current ...
... A variable voltage source is connected to the gate, G. A second variable voltage source is connected between the drain, D (through resistor R), and the source, S, which is connected to ground. Each curve is generated by setting the gate voltage at some constant value then measuring the drain current ...
CR circuit - schoolphysics
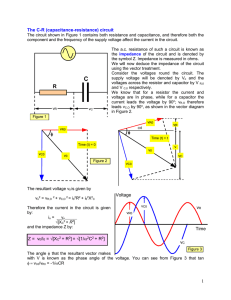
... The circuit shown in Figure 1 contains both resistance and capacitance, and therefore both the component and the frequency of the supply voltage affect the current in the circuit. The a.c. resistance of such a circuit is known as the impedance of the circuit and is denoted by the symbol Z. Impedance ...
... The circuit shown in Figure 1 contains both resistance and capacitance, and therefore both the component and the frequency of the supply voltage affect the current in the circuit. The a.c. resistance of such a circuit is known as the impedance of the circuit and is denoted by the symbol Z. Impedance ...
Measuring_Voltage_an..
... The students can either set up the circuit to measure current and voltage, or the circuit can be set up for them in advance. The students connect up the voltmeter and ammeter to measure the current through the circuit and the voltage across the resistor, or observe and explain why they are set up th ...
... The students can either set up the circuit to measure current and voltage, or the circuit can be set up for them in advance. The students connect up the voltmeter and ammeter to measure the current through the circuit and the voltage across the resistor, or observe and explain why they are set up th ...
ECEN 405 Assignment 3 Due: 1 April Worth: 3% 1. Design a buck
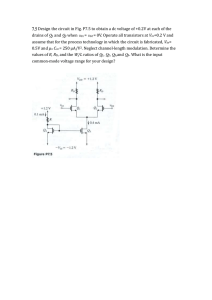
... inductor and the capacitor, peak voltage rating of each device, and the rms current in the inductor and the capacitor. 2. In a buck converter, L = 25µH, and is operating in DC steady state under the following conditions: Vin = 42V, D = 0.3, Po = 24W and fs = 400kHz. Assume ideal components. i. Calcu ...
... inductor and the capacitor, peak voltage rating of each device, and the rms current in the inductor and the capacitor. 2. In a buck converter, L = 25µH, and is operating in DC steady state under the following conditions: Vin = 42V, D = 0.3, Po = 24W and fs = 400kHz. Assume ideal components. i. Calcu ...
ap physics b lesson 72 kirchoff`s laws
... Kirchoff’s Loop (current) Law • Kirchoff’s Current Law – The same amount of charge must enter a junction in a given time interval as the amount of charge that leave the junction in the same time interval. – Itotal = I1 + I2 + I3 …… ...
... Kirchoff’s Loop (current) Law • Kirchoff’s Current Law – The same amount of charge must enter a junction in a given time interval as the amount of charge that leave the junction in the same time interval. – Itotal = I1 + I2 + I3 …… ...
Building a Simple Circuit
... Are electronics so complicated? Electronic devices are more easily ...
... Are electronics so complicated? Electronic devices are more easily ...
Ohm`s Law
... What is the voltage across a 680 W resistor if the current is 0.25 A? 170 V If you need to solve for resistance, Ohm’s law is: What is the resistance of the bulb? 132 W ...
... What is the voltage across a 680 W resistor if the current is 0.25 A? 170 V If you need to solve for resistance, Ohm’s law is: What is the resistance of the bulb? 132 W ...
Physics 536 - Assignment #7
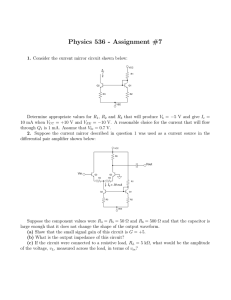
... Suppose the component values were R4 = R5 = 50 Ω and R6 = 500 Ω and that the capacitor is large enough that it does not change the shape of the output waveform. (a) Show that the small signal gain of this circuit is G = +5. (b) What is the output impedance of this circuit? (c) If the circuit were co ...
... Suppose the component values were R4 = R5 = 50 Ω and R6 = 500 Ω and that the capacitor is large enough that it does not change the shape of the output waveform. (a) Show that the small signal gain of this circuit is G = +5. (b) What is the output impedance of this circuit? (c) If the circuit were co ...
Physics 132 Name_________________________________ Recitation Instructor (circle one): Dick
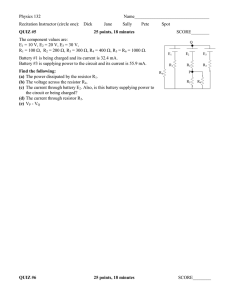
... Physics 132 Recitation Instructor (circle one): Dick QUIZ #5 ...
... Physics 132 Recitation Instructor (circle one): Dick QUIZ #5 ...
Exercise 3
... applied to the circuit? ___________ 4. Verify that the voltage drop across each resistor is proportional to the ratio of its resistance to the total resistance: e.g., ...
... applied to the circuit? ___________ 4. Verify that the voltage drop across each resistor is proportional to the ratio of its resistance to the total resistance: e.g., ...
The law
... When working with actual circuits, please remember this guideline: The input impedance of a voltmeter should be at least 100 times greater than the Thevenin resistance to avoid loading error. ...
... When working with actual circuits, please remember this guideline: The input impedance of a voltmeter should be at least 100 times greater than the Thevenin resistance to avoid loading error. ...
AP_Physics_B_-_Planck_s_Constant_lab
... In this lab we will be introduced to TWO new schematic symbols, This is called a variable resistance, also known as a dimmer switch. There are THREE connections, one on each end and one in the middle. This is called an LED, light emitting diode. This is a great example to illustrate the photoelectri ...
... In this lab we will be introduced to TWO new schematic symbols, This is called a variable resistance, also known as a dimmer switch. There are THREE connections, one on each end and one in the middle. This is called an LED, light emitting diode. This is a great example to illustrate the photoelectri ...
Portable Appliance Testing Course Pre-Study Revision
... The candidate will need to understand basic numeric prefixes used with electrical symbols and measurement units i.e.… milli (m) a thousandth e.g. 3mA : three thousandths of an amp kilo (k) a thousand times e.g. 100k : one hundred thousand ohms mega (M) a million times e.g. 2M : two million ohms ...
... The candidate will need to understand basic numeric prefixes used with electrical symbols and measurement units i.e.… milli (m) a thousandth e.g. 3mA : three thousandths of an amp kilo (k) a thousand times e.g. 100k : one hundred thousand ohms mega (M) a million times e.g. 2M : two million ohms ...
What property of electric current allowed Edison*s first light bulb to
... through a wire or conductor. Voltage difference – The force that causes electric charges to flow; charges flow from high voltage to low voltage. ...
... through a wire or conductor. Voltage difference – The force that causes electric charges to flow; charges flow from high voltage to low voltage. ...
Current source
A current source is an electronic circuit that delivers or absorbs an electric current which is independent of the voltage across it.A current source is the dual of a voltage source. The term constant-current 'sink' is sometimes used for sources fed from a negative voltage supply. Figure 1 shows the schematic symbol for an ideal current source, driving a resistor load. There are two types - an independent current source (or sink) delivers a constant current. A dependent current source delivers a current which is proportional to some other voltage or current in the circuit.