Series and Parallel Circuits
... • For the series circuit the same current flows through both loads. • The loads can be added together to calculate the total load. • Rtot = R1 + R2, where Rtot is the total resistance, R1 is the resistance of one load, and R2 is the resistance of the other. • The total load (resistance) in a series ...
... • For the series circuit the same current flows through both loads. • The loads can be added together to calculate the total load. • Rtot = R1 + R2, where Rtot is the total resistance, R1 is the resistance of one load, and R2 is the resistance of the other. • The total load (resistance) in a series ...
Ohms Law - Ms. Jefford`s Homework Page
... ammeter. Explore what happens when other resistors are added i.e. more lamps. Could add batteries to explore voltage and current readings. This would show relationships between current, voltage and resistance and discover that the amount of current in a circuit is directly proportional to the voltag ...
... ammeter. Explore what happens when other resistors are added i.e. more lamps. Could add batteries to explore voltage and current readings. This would show relationships between current, voltage and resistance and discover that the amount of current in a circuit is directly proportional to the voltag ...
Electronics_exercises_files/extra 2
... What must Vt be for this device? If a device for which Vt is 0.5V less is used, what does Vs become? What bias current results? ...
... What must Vt be for this device? If a device for which Vt is 0.5V less is used, what does Vs become? What bias current results? ...
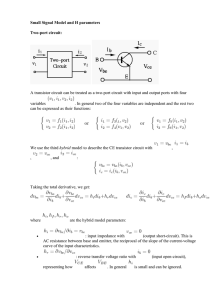
Small Signal Model and H parameters
... A transistor circuit can be treated as a two-port circuit with input and output ports with four variables . In general two of the four variables are independent and the rest two can be expressed as their functions: ...
... A transistor circuit can be treated as a two-port circuit with input and output ports with four variables . In general two of the four variables are independent and the rest two can be expressed as their functions: ...
Written - Rose
... resistance circuit. The two resistors can be combine into a since they are in series. For the parallel circuit, the current through one of the resistor is proportional to the total current. The proportionality is the equivalent resistance of the parallel resistors divided by its resistance. The equi ...
... resistance circuit. The two resistors can be combine into a since they are in series. For the parallel circuit, the current through one of the resistor is proportional to the total current. The proportionality is the equivalent resistance of the parallel resistors divided by its resistance. The equi ...
MS Word
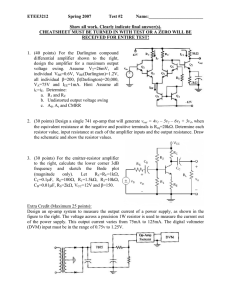
... A MOSFET connected in a common-source configuration has transconductance gm = 5 mA/V (mS). When a source resistor RS is connected to the source terminal, the effective transconductance g’m is reduced to 2 mA/V (mS). Estimate the value of this resistor RS. [Note: Source resistor RS is not bypassed wi ...
... A MOSFET connected in a common-source configuration has transconductance gm = 5 mA/V (mS). When a source resistor RS is connected to the source terminal, the effective transconductance g’m is reduced to 2 mA/V (mS). Estimate the value of this resistor RS. [Note: Source resistor RS is not bypassed wi ...
Solid State Relais
... positioned in between one of the 115/220V AC wires although it is common practice to leave the neutral wire the way it is and switch the phase or hot wire. See diagram for 'LOAD'. As long as thereis no dc voltage present (left side of circuit diagram), the phototransistor within the TIL111 blocks an ...
... positioned in between one of the 115/220V AC wires although it is common practice to leave the neutral wire the way it is and switch the phase or hot wire. See diagram for 'LOAD'. As long as thereis no dc voltage present (left side of circuit diagram), the phototransistor within the TIL111 blocks an ...
Exercise 1:
... Exercise 1: Ohm’s Law Begin by reading the material on measuring voltage prepared by Prof E. J. Mastascusa at Bucknell University. Next create the following circuit on your breadboard: ...
... Exercise 1: Ohm’s Law Begin by reading the material on measuring voltage prepared by Prof E. J. Mastascusa at Bucknell University. Next create the following circuit on your breadboard: ...
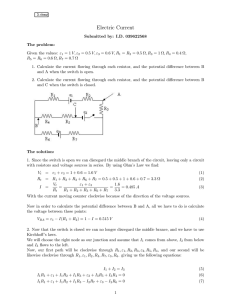
Electric Current
... Electric Current Submitted by: I.D. 039622568 The problem: Given the values: ε1 = 1 V, ε2 = 0.5 V, ε3 = 0.6 V, R1 = R2 = 0.5 Ω, R3 = 1 Ω, R4 = 0.4 Ω, R5 = R6 = 0.6 Ω, R7 = 0.7 Ω 1. Calculate the current flowing through each resistor, and the potential difference between B and A when the switch is open ...
... Electric Current Submitted by: I.D. 039622568 The problem: Given the values: ε1 = 1 V, ε2 = 0.5 V, ε3 = 0.6 V, R1 = R2 = 0.5 Ω, R3 = 1 Ω, R4 = 0.4 Ω, R5 = R6 = 0.6 Ω, R7 = 0.7 Ω 1. Calculate the current flowing through each resistor, and the potential difference between B and A when the switch is open ...
Voltage: Current: Resistance: Ohm`s Law:
... 1. A stove is connected to a 180 – V outlet. If the heating element has a resistance of 18 ohms, calculate the current flowing through it. ...
... 1. A stove is connected to a 180 – V outlet. If the heating element has a resistance of 18 ohms, calculate the current flowing through it. ...
Solar Powered Phone Charger
... Cell Phone through Ni-Cd or Lead Acid Battery. The charge produced by the 12V Solar panel is fed to the 6V, 4.5Ah Rechargeable Battery through the Voltage Regulator LM 317. The charger has voltage and current regulation and over voltage cut-off facilities. A Variable Resistor is placed between the a ...
... Cell Phone through Ni-Cd or Lead Acid Battery. The charge produced by the 12V Solar panel is fed to the 6V, 4.5Ah Rechargeable Battery through the Voltage Regulator LM 317. The charger has voltage and current regulation and over voltage cut-off facilities. A Variable Resistor is placed between the a ...
File
... 2. PE/q; ΔPE/q between points 3. Pressure difference; potential difference 4. Flow of charge 5. Flow of 1 coulomb per second 6. Electric “pressure”, PE/q, which produces electric current 7. 120 J/C = 120 V 8. Flows through a circuit 9. Established across, only charge flows 10. That which resists flo ...
... 2. PE/q; ΔPE/q between points 3. Pressure difference; potential difference 4. Flow of charge 5. Flow of 1 coulomb per second 6. Electric “pressure”, PE/q, which produces electric current 7. 120 J/C = 120 V 8. Flows through a circuit 9. Established across, only charge flows 10. That which resists flo ...
In the circuit shown below, the switch closes at t = 0. a) Find iL(t → ∞).
... The switch bypasses the current source and resistor. If we consider a voltage loop around the outside, we have only R2. Thus, the voltage drop across R2 must be zero. It follows from Ohm's law that the current in R2 must be zero. Since the current in R2 is the same as the current in L, we must have ...
... The switch bypasses the current source and resistor. If we consider a voltage loop around the outside, we have only R2. Thus, the voltage drop across R2 must be zero. It follows from Ohm's law that the current in R2 must be zero. Since the current in R2 is the same as the current in L, we must have ...
Current source
A current source is an electronic circuit that delivers or absorbs an electric current which is independent of the voltage across it.A current source is the dual of a voltage source. The term constant-current 'sink' is sometimes used for sources fed from a negative voltage supply. Figure 1 shows the schematic symbol for an ideal current source, driving a resistor load. There are two types - an independent current source (or sink) delivers a constant current. A dependent current source delivers a current which is proportional to some other voltage or current in the circuit.