Lab #7
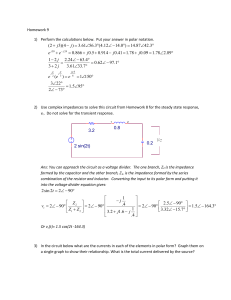
... – The multimeter is used to measure the RMS (root mean square) voltage (or effective DC voltage because it supplies as much power as a DC voltage source would.) – The DMM can also measure the frequency of the source. ...
... – The multimeter is used to measure the RMS (root mean square) voltage (or effective DC voltage because it supplies as much power as a DC voltage source would.) – The DMM can also measure the frequency of the source. ...
Chapter 7 Review
... • The statement that current is equal to voltage difference divided by the resistance of an object is ______ law. • Ohm’s ...
... • The statement that current is equal to voltage difference divided by the resistance of an object is ______ law. • Ohm’s ...
Slide 1
... Length – short wires have less resistance Area- thick wires have less resistance Material- different materials have different conductivity of charge Temperature- heat slows the flow of charge. ...
... Length – short wires have less resistance Area- thick wires have less resistance Material- different materials have different conductivity of charge Temperature- heat slows the flow of charge. ...
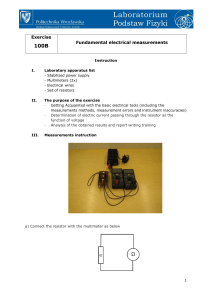
Exercise Fundamental electrical measurements
... measurements methods, measurement errors and instrument inaccuracies) Determination of electric current passing through the resistor as the function of voltage Analysis of the obtained results and report writing training ...
... measurements methods, measurement errors and instrument inaccuracies) Determination of electric current passing through the resistor as the function of voltage Analysis of the obtained results and report writing training ...
PHYS1120ExamIIReview.. - University of Colorado Boulder
... elements in parallel always have the same voltage: Ibig V same across both R's ...
... elements in parallel always have the same voltage: Ibig V same across both R's ...
ENG 220
... Understand the “rounding rule”. Less than 5; Go to lower value, Greater than 5, go to next higher value. 2. Know the definition of Current in Coulombs/Second and Volts in Joules/Coulomb 3. Know the relationship between Joule*Seconds and Watts. 4. Know the relationship between Watts and Volt*Amperes. ...
... Understand the “rounding rule”. Less than 5; Go to lower value, Greater than 5, go to next higher value. 2. Know the definition of Current in Coulombs/Second and Volts in Joules/Coulomb 3. Know the relationship between Joule*Seconds and Watts. 4. Know the relationship between Watts and Volt*Amperes. ...
ET 12
... 1. A 100 kW, 460V shunt generator on board ship was run as a motor on no load at its rated voltage and speed. The total current taken was 9.8A, including a shunt current of 2.7A. The resistance of the armature circuit at normal working temperature was 0.11. Calculate the efficiencies at (a) full lo ...
... 1. A 100 kW, 460V shunt generator on board ship was run as a motor on no load at its rated voltage and speed. The total current taken was 9.8A, including a shunt current of 2.7A. The resistance of the armature circuit at normal working temperature was 0.11. Calculate the efficiencies at (a) full lo ...
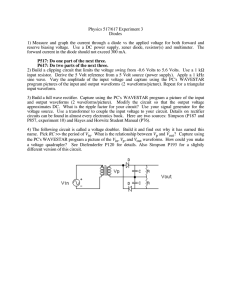
Physics 517/617 Experiment 3 Diodes
... input resistor. Derive the 5 Volt reference from a 5 Volt source (power supply). Apply a 1 kHz sine wave. Vary the amplitude of the input voltage and capture using the PC's WAVESTAR program pictures of the input and output waveforms (2 waveforms/picture). Repeat for a triangular input waveform. 3) B ...
... input resistor. Derive the 5 Volt reference from a 5 Volt source (power supply). Apply a 1 kHz sine wave. Vary the amplitude of the input voltage and capture using the PC's WAVESTAR program pictures of the input and output waveforms (2 waveforms/picture). Repeat for a triangular input waveform. 3) B ...
hw8
... diode voltage at constant current is -1.5mV/K, and that at room temperature the diode voltage necessary to pass 10uA through a single diode is 0.7V. a. What is the room-temperature voltage necessary for 10 diodes in parallel to pass 10uA? b. What is the room-temperature voltage across R1 (assuming a ...
... diode voltage at constant current is -1.5mV/K, and that at room temperature the diode voltage necessary to pass 10uA through a single diode is 0.7V. a. What is the room-temperature voltage necessary for 10 diodes in parallel to pass 10uA? b. What is the room-temperature voltage across R1 (assuming a ...
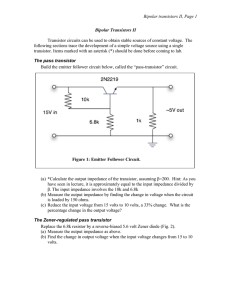
Bipolar transistors II, Page 1 Bipolar Transistors II
... Figure 4: Feedback Voltage Regulator. load conditions are variable. These can give output impedances less than an ohm and high stability against temperature variation. Figure 4 is a common example of a negative-feedback circuit. Transistor Q1 is normally conducting because of the bias current throug ...
... Figure 4: Feedback Voltage Regulator. load conditions are variable. These can give output impedances less than an ohm and high stability against temperature variation. Figure 4 is a common example of a negative-feedback circuit. Transistor Q1 is normally conducting because of the bias current throug ...
Electricity & Optics Physics 24100 Lecture 11 – Chapter 25 sec. 4-5
... the parallel combination of ' and ( ? ...
... the parallel combination of ' and ( ? ...
14.1 Series Circuits
... out when the switch is opened? Explain. 3. What happens to c circuit’s resistance as more resistors are added in series? 4. A series circuit contains a 9-volt battery and three identical bulbs. What is the voltage drop across each bulb? ...
... out when the switch is opened? Explain. 3. What happens to c circuit’s resistance as more resistors are added in series? 4. A series circuit contains a 9-volt battery and three identical bulbs. What is the voltage drop across each bulb? ...
Notes18
... through which electric current flows (p374). There must of source of electrical potential difference (voltage)—such as a battery—in order to produce a current flow. Other components in the circuit dissipate this change in potential energy (caused by the battery), by doing work or dissipating the ene ...
... through which electric current flows (p374). There must of source of electrical potential difference (voltage)—such as a battery—in order to produce a current flow. Other components in the circuit dissipate this change in potential energy (caused by the battery), by doing work or dissipating the ene ...
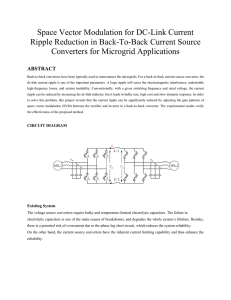
abstract - Innovetech
... This project mainly focuses on the microgrid applications, where the voltages on both sides are generally controlled within a safe range for critical loads. Additionally, in contrast to the voltage source converter, the modulation index is generally controlled high to reduce the converter loss for t ...
... This project mainly focuses on the microgrid applications, where the voltages on both sides are generally controlled within a safe range for critical loads. Additionally, in contrast to the voltage source converter, the modulation index is generally controlled high to reduce the converter loss for t ...
Multi-functional Packaged Antennas for Next
... Basic Operation in the Active Region – Cont’d Basic Operation in the Active Region: An npn transistor (CE configuration) with variable voltage sources operating in the active region: VBE ≈ 0.6 V to forward bias the BE junction VCE >VBE - the base collector junction is reverse biased ...
... Basic Operation in the Active Region – Cont’d Basic Operation in the Active Region: An npn transistor (CE configuration) with variable voltage sources operating in the active region: VBE ≈ 0.6 V to forward bias the BE junction VCE >VBE - the base collector junction is reverse biased ...
secondary.mysdhc.org
... We have already learned that POWER is the rate at which work (energy) is done. Circuits that are a prime example of this as batteries only last for a certain amount of time AND we get charged an energy bill each month based on the amount of energy we used over the course of a ...
... We have already learned that POWER is the rate at which work (energy) is done. Circuits that are a prime example of this as batteries only last for a certain amount of time AND we get charged an energy bill each month based on the amount of energy we used over the course of a ...
lecture10
... thyristors thatdcthe voltage are inductance triggered ED williswith be sufficiently function the same of large, delay firing soangle, angle: that each hence Scr conducts they share thefor load a period current ofequally. 180 degree.( The load conduction currentcurrent is shownis continuous). to be c ...
... thyristors thatdcthe voltage are inductance triggered ED williswith be sufficiently function the same of large, delay firing soangle, angle: that each hence Scr conducts they share thefor load a period current ofequally. 180 degree.( The load conduction currentcurrent is shownis continuous). to be c ...
Current source
A current source is an electronic circuit that delivers or absorbs an electric current which is independent of the voltage across it.A current source is the dual of a voltage source. The term constant-current 'sink' is sometimes used for sources fed from a negative voltage supply. Figure 1 shows the schematic symbol for an ideal current source, driving a resistor load. There are two types - an independent current source (or sink) delivers a constant current. A dependent current source delivers a current which is proportional to some other voltage or current in the circuit.