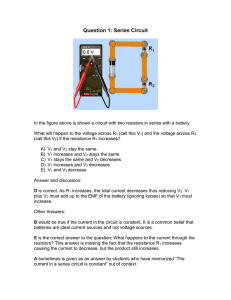
Basic Electricity
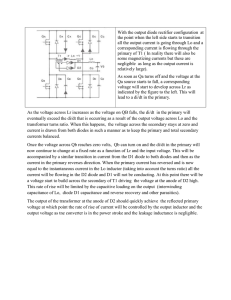
... This was a 33 W resistor connected to a 20 V supply. The current would be 20 V ÷ 33 W = 0.61 A The power would be 0.61 × 20 V = 12 watts. Plenty enough to fry a 1 watt resistor. It is important that we ensure that any current limiting resistors can dissipate the power through them. The above situati ...
... This was a 33 W resistor connected to a 20 V supply. The current would be 20 V ÷ 33 W = 0.61 A The power would be 0.61 × 20 V = 12 watts. Plenty enough to fry a 1 watt resistor. It is important that we ensure that any current limiting resistors can dissipate the power through them. The above situati ...
Ohm*s Law
... To calculate resistance, R: put your finger over R, this leaves you with V over I, so the equation is R = V/I ...
... To calculate resistance, R: put your finger over R, this leaves you with V over I, so the equation is R = V/I ...
Engineering Review – Electric Circuits I
... This can be applied to a node to determine the current in a leg of the other legs are know, by summing the currents in and out of the node. ...
... This can be applied to a node to determine the current in a leg of the other legs are know, by summing the currents in and out of the node. ...
Science Lesson Plan
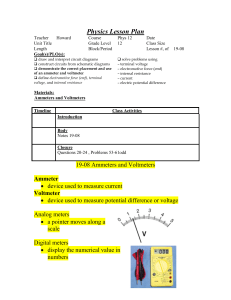
... The analog meters have a galvanometer inside them for which the amount of current passing through the device determines how much the needle deflects. In the ammeter there is a parallel circuit so only a fraction of the current passes through the galvanometer and the rest goes through the shunt resi ...
... The analog meters have a galvanometer inside them for which the amount of current passing through the device determines how much the needle deflects. In the ammeter there is a parallel circuit so only a fraction of the current passes through the galvanometer and the rest goes through the shunt resi ...
Chapter 36 Summary – Magnetism
... Static electricity is when (charges, circuits) accumulate on the (inside, surface) of an object which gains or loses (electrons, branches) which move more easily on a (conductor, insulator) than they do on a (conductor, insulator). A negatively charged object has (fewer, more) electrons than a neutr ...
... Static electricity is when (charges, circuits) accumulate on the (inside, surface) of an object which gains or loses (electrons, branches) which move more easily on a (conductor, insulator) than they do on a (conductor, insulator). A negatively charged object has (fewer, more) electrons than a neutr ...
I I-i1 i1 i2 I-i2 i1
... But after the reflection, the assembly of these 5 resistors looks exactly the same as before. Hence they are the same circuit. We see that the direction of the current through the middle resistor (I3) is flipped, so the only way to ensure that both circuit are equivalent is for I3=0 We could have a ...
... But after the reflection, the assembly of these 5 resistors looks exactly the same as before. Hence they are the same circuit. We see that the direction of the current through the middle resistor (I3) is flipped, so the only way to ensure that both circuit are equivalent is for I3=0 We could have a ...
Microelectronics… - Oakland University
... water wave motion to create electricity • Electrical energy is conditioned and stored for later use ...
... water wave motion to create electricity • Electrical energy is conditioned and stored for later use ...
Block ______ minutes spent on DH:______ Last name First name
... Freshman Physics Honors with Dr. Leopold DH42 – Voltage, Resistance and Ohm’s Law (Goes with day 62. Self-grade out of 23.) 1. The source in an electric circuit performs two functions. What are they? ...
... Freshman Physics Honors with Dr. Leopold DH42 – Voltage, Resistance and Ohm’s Law (Goes with day 62. Self-grade out of 23.) 1. The source in an electric circuit performs two functions. What are they? ...
1 - Pui Chor Wong
... • Conductor: a material which offers little resistance to current flow, e.g. silver, copper, iron, etc… • Insulator: a material which offers high resistance to current flow, e.g. wood, paper, plastic, etc... ...
... • Conductor: a material which offers little resistance to current flow, e.g. silver, copper, iron, etc… • Insulator: a material which offers high resistance to current flow, e.g. wood, paper, plastic, etc... ...
2.9 Understanding electricity
... wants to measure the voltage and find out if there is a break in the circuit. • How could she do this? ...
... wants to measure the voltage and find out if there is a break in the circuit. • How could she do this? ...
Homework 1 - the GMU ECE Department
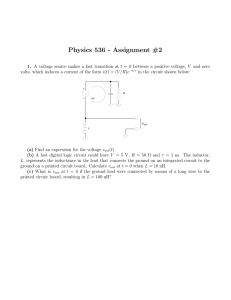
... 2. For a given product, the test specification for a given input device is a maximum leakage of 3.0mA when 2.5V. This is tested by forcing a given voltage and measuring the resultant current. The tester to be used has the following accuracy: forcing voltage +/-(0.1% +4mV+0.6mV/10mA), measured curren ...
... 2. For a given product, the test specification for a given input device is a maximum leakage of 3.0mA when 2.5V. This is tested by forcing a given voltage and measuring the resultant current. The tester to be used has the following accuracy: forcing voltage +/-(0.1% +4mV+0.6mV/10mA), measured curren ...
sot-23 bipolar transistors transistor(npn)
... Rectron Inc reserves the right to make changes without notice to any product specification herein, to make corrections, modifications, enhancements or other changes. Rectron Inc or anyone on its behalf assumes no responsibility or liability for any errors or inaccuracies. Data sheet specifications a ...
... Rectron Inc reserves the right to make changes without notice to any product specification herein, to make corrections, modifications, enhancements or other changes. Rectron Inc or anyone on its behalf assumes no responsibility or liability for any errors or inaccuracies. Data sheet specifications a ...
Current source
A current source is an electronic circuit that delivers or absorbs an electric current which is independent of the voltage across it.A current source is the dual of a voltage source. The term constant-current 'sink' is sometimes used for sources fed from a negative voltage supply. Figure 1 shows the schematic symbol for an ideal current source, driving a resistor load. There are two types - an independent current source (or sink) delivers a constant current. A dependent current source delivers a current which is proportional to some other voltage or current in the circuit.