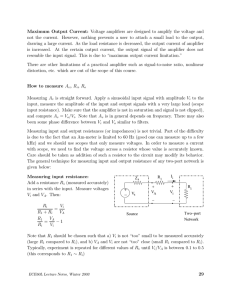
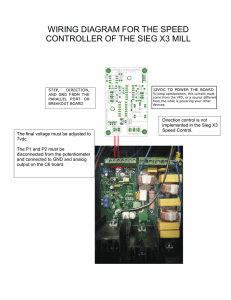
Review Topics for Exam #3
... due to a specific independent voltage or current source is directly proportional to the voltage or current level of that source. - principle of superposition: Any voltage or current in a circuit is a weighted sum of the contributions from the individual independent sources driving the circuit. State ...
... due to a specific independent voltage or current source is directly proportional to the voltage or current level of that source. - principle of superposition: Any voltage or current in a circuit is a weighted sum of the contributions from the individual independent sources driving the circuit. State ...
Video Transcript - Rose
... Next, we’ll find the voltage across each source. Finally, we’ll find the power associated with each source by multiplying the voltage across each source by the current through the source. Let’s begin by identifying all the nodes in the circuit. We have a total of three nodes. This tells us that we h ...
... Next, we’ll find the voltage across each source. Finally, we’ll find the power associated with each source by multiplying the voltage across each source by the current through the source. Let’s begin by identifying all the nodes in the circuit. We have a total of three nodes. This tells us that we h ...
File
... through it, but in which the current from the battery is as large as possible (without short circuiting the battery). ...
... through it, but in which the current from the battery is as large as possible (without short circuiting the battery). ...
Circuits and Circuit Diagrams
... • Total current equals the sum of currents in branches • As the number of branches is increased, overall resistance of the circuit is decreased – think about driving on a 4 lane highway – little resistance to the flow of traffic – now consider an accident that blocks three of the lanes…a reduction t ...
... • Total current equals the sum of currents in branches • As the number of branches is increased, overall resistance of the circuit is decreased – think about driving on a 4 lane highway – little resistance to the flow of traffic – now consider an accident that blocks three of the lanes…a reduction t ...
1. For the following circuit, assume the values of the resistor R is 1
... 1. For the following circuit, assume the values of the resistor R is 1 kQ, the value of the inductor L is 1 rnH, and the value of the capacitor C is 0.5 nF. The current source i,N(t)= 2xsin(lo6xt) mA and the initial voltage of the capacitor is -4 V, i.e., v,(O) = 4 v. (a). Please find the steady-sta ...
... 1. For the following circuit, assume the values of the resistor R is 1 kQ, the value of the inductor L is 1 rnH, and the value of the capacitor C is 0.5 nF. The current source i,N(t)= 2xsin(lo6xt) mA and the initial voltage of the capacitor is -4 V, i.e., v,(O) = 4 v. (a). Please find the steady-sta ...
Circuits #3 - Electro Tech Online
... The voltage in a circuit can be used to form a signal. For example, +5v could be used to represent the binary value ‘1’, while 0v could be used to represent the binary value ‘0’ ...
... The voltage in a circuit can be used to form a signal. For example, +5v could be used to represent the binary value ‘1’, while 0v could be used to represent the binary value ‘0’ ...
polytechnic of kota bharu
... by a single resistance in series with a single voltage source. It is especially useful for simplifying circuits with more than one power source to find the voltage drop across the load. EQUIPMENTS: ...
... by a single resistance in series with a single voltage source. It is especially useful for simplifying circuits with more than one power source to find the voltage drop across the load. EQUIPMENTS: ...
CIRCUITS WORKSHEET
... 8) Calculate the equivalent resistance of the circuit shown. 9) Determine the resistance of resistor R shown in the diagram. Questions 10 through 12 refer to the following: A 3.0-ohm resistor, an unknown resistor, R, and two ammeters, A1 and A2, are connected as shown below with a 12-volt source. Am ...
... 8) Calculate the equivalent resistance of the circuit shown. 9) Determine the resistance of resistor R shown in the diagram. Questions 10 through 12 refer to the following: A 3.0-ohm resistor, an unknown resistor, R, and two ammeters, A1 and A2, are connected as shown below with a 12-volt source. Am ...
Test Procedure for the NCP1013ADAP Evaluation Board
... above 12V. Beware of the resistor that gets hot during the measurement (P = 6W). 5. Now decrease the input voltage down to 90VAC and check that bullet 3 is also ok. 6. Disconnect the resistor. Now connect the amp-meter (5A DC range) between pins +Vout et Ground. You actually create a short which sha ...
... above 12V. Beware of the resistor that gets hot during the measurement (P = 6W). 5. Now decrease the input voltage down to 90VAC and check that bullet 3 is also ok. 6. Disconnect the resistor. Now connect the amp-meter (5A DC range) between pins +Vout et Ground. You actually create a short which sha ...
(1) You are given the circuit of Figure 1 with the indicated source
... (4) You are given the AC circuit shown in Figure 4. (a) Use nodal analysis to find the node voltages V1 and Vz as indicated in the circuit diagram. Express V1 and Vz in polar form. (b) Prepare a phasor diagram showing V1 and V2. Which voltage is leading? Explain. L ...
... (4) You are given the AC circuit shown in Figure 4. (a) Use nodal analysis to find the node voltages V1 and Vz as indicated in the circuit diagram. Express V1 and Vz in polar form. (b) Prepare a phasor diagram showing V1 and V2. Which voltage is leading? Explain. L ...
Shocking Stuff - Kotara High School
... Consider the circuit you have drawn in Qu. 7. If one light globe was to go out in the circuit, what would be the effect on the other globe? ...
... Consider the circuit you have drawn in Qu. 7. If one light globe was to go out in the circuit, what would be the effect on the other globe? ...
Resisting the Movement of Charge
... component in the circuit Parallel circuits - have several current paths - the total current is divided, with some of the moving charges traveling through each branch, or part of the circuit. - If one path is broken there is still another path for current to come through - Example: your home- lamps, ...
... component in the circuit Parallel circuits - have several current paths - the total current is divided, with some of the moving charges traveling through each branch, or part of the circuit. - If one path is broken there is still another path for current to come through - Example: your home- lamps, ...
Circuits - Instructor Outline - University of Michigan SharePoint Portal
... ***Note: the students may short out the battery causing heat and discomfort. This isn’t hazardous; you can warn them at your discretion. The students build a basic flashlight with three ingredients (a battery, a bulb, and an aluminum strip). They see how a complete circuit works. The students then b ...
... ***Note: the students may short out the battery causing heat and discomfort. This isn’t hazardous; you can warn them at your discretion. The students build a basic flashlight with three ingredients (a battery, a bulb, and an aluminum strip). They see how a complete circuit works. The students then b ...
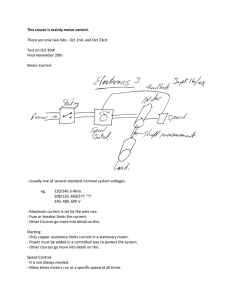
This course is mainly motor control. There are only two labs. Oct 2nd
... ‐ Only copper resistance limits current in a stationary motor. ‐ Power must be added in a controlled way to protect the system. ‐ Other courses go more into detail on this. ...
... ‐ Only copper resistance limits current in a stationary motor. ‐ Power must be added in a controlled way to protect the system. ‐ Other courses go more into detail on this. ...
LS 14500
... of storage at +20°C) ● Stainless steel container ● Hermetic glass-to-metal sealing ● Non flammable electrolyte ● Compliant with IEC 86-4 safety standard and EN 50020 intrinsic safety ● Underwriters Laboratories (UL) Component Recognition (File Number MH 12609) ● Non restricted for transport ...
... of storage at +20°C) ● Stainless steel container ● Hermetic glass-to-metal sealing ● Non flammable electrolyte ● Compliant with IEC 86-4 safety standard and EN 50020 intrinsic safety ● Underwriters Laboratories (UL) Component Recognition (File Number MH 12609) ● Non restricted for transport ...
Current source
A current source is an electronic circuit that delivers or absorbs an electric current which is independent of the voltage across it.A current source is the dual of a voltage source. The term constant-current 'sink' is sometimes used for sources fed from a negative voltage supply. Figure 1 shows the schematic symbol for an ideal current source, driving a resistor load. There are two types - an independent current source (or sink) delivers a constant current. A dependent current source delivers a current which is proportional to some other voltage or current in the circuit.