Practical 19 Characteristics of diodes
... are often used to prevent damage to a circuit should a reverse voltage be applied to it. They are also used in ‘rectifying’ AC supplies to the DC required by many electronic systems. ...
... are often used to prevent damage to a circuit should a reverse voltage be applied to it. They are also used in ‘rectifying’ AC supplies to the DC required by many electronic systems. ...
Soldering Basics
... • Voltage – Voltage is an electrical measure which describes the potential to do work. The higher the voltage the greater its risk to you and your health. Systems that use voltages below 50V are considered lowvoltage and are not governed by an as strict (some might say arcane) set of rules as high-v ...
... • Voltage – Voltage is an electrical measure which describes the potential to do work. The higher the voltage the greater its risk to you and your health. Systems that use voltages below 50V are considered lowvoltage and are not governed by an as strict (some might say arcane) set of rules as high-v ...
terminology guide
... Semiconductors are in between insulators and conductors. They are vital in electronics because they can be controlled to switch between behaving as a conductor and behaving as an insulator. Two important semiconductors are silicon, which is used in computer chips and germanium, which is used in fibr ...
... Semiconductors are in between insulators and conductors. They are vital in electronics because they can be controlled to switch between behaving as a conductor and behaving as an insulator. Two important semiconductors are silicon, which is used in computer chips and germanium, which is used in fibr ...
The FEE board requires 4 channels of DAC for the voltage regulator
... expected that a simple 2 or 3 transistor amplifier will give adequate performance at a lower power level than would be achieved with a design based on an op-amp. A common-base input stage will be used to handle the SiPM capacitance; an input transistor per SiPM might be considered. The response of a ...
... expected that a simple 2 or 3 transistor amplifier will give adequate performance at a lower power level than would be achieved with a design based on an op-amp. A common-base input stage will be used to handle the SiPM capacitance; an input transistor per SiPM might be considered. The response of a ...
02-Wattmeter
... Here, a pointer is attached to the movable coil and the deflection is propotional to the repulsive force generated from the currents moving through the two coils . ...
... Here, a pointer is attached to the movable coil and the deflection is propotional to the repulsive force generated from the currents moving through the two coils . ...
Series circuits - Eyemouth High School
... the other. A series circuit is similar. You get several components one after the other. • If you follow the circuit diagram from one side of the cell to the other, you should pass through all the different components, one after the other, without any branches. • In a series circuit, if a lamp breaks ...
... the other. A series circuit is similar. You get several components one after the other. • If you follow the circuit diagram from one side of the cell to the other, you should pass through all the different components, one after the other, without any branches. • In a series circuit, if a lamp breaks ...
Chapter 15
... Power supplies with pass transistors are linear and are not as efficient as switch-mode power supplies. PC = IC x VCE (The heat loss in a pass transistor can be significant.) Recall: Pulse width modulation (PWM) is one way to use a digital approach to an analog problem. ...
... Power supplies with pass transistors are linear and are not as efficient as switch-mode power supplies. PC = IC x VCE (The heat loss in a pass transistor can be significant.) Recall: Pulse width modulation (PWM) is one way to use a digital approach to an analog problem. ...
Electronic glossary
... determined by the semiconductor used. Since LEDs are diodes, they will only work when wired in the correct direction. The terminals can be identified in two ways: ...
... determined by the semiconductor used. Since LEDs are diodes, they will only work when wired in the correct direction. The terminals can be identified in two ways: ...
IV Characteristics
... You are going to investigate how electrical current through different components is affected by changing the voltage. The three components you are investigating are: ...
... You are going to investigate how electrical current through different components is affected by changing the voltage. The three components you are investigating are: ...
Here we`ll find the initial value of capacitor voltage - Rose
... Its current is the time rate of change of its voltage * its capacitance. Rewrite the equation to solve for what we want. This equation is true at t=0, so replace t with 0 in these cases. If we can find ic(0), we’ll know dvc(0) / dt. ic(0) needs to be defined according to passive sign convention. Not ...
... Its current is the time rate of change of its voltage * its capacitance. Rewrite the equation to solve for what we want. This equation is true at t=0, so replace t with 0 in these cases. If we can find ic(0), we’ll know dvc(0) / dt. ic(0) needs to be defined according to passive sign convention. Not ...
AC vs. DC
... Why do we have an AC current? Answer Electricity can be generated as either AC or DC, but AC allows us to change the Voltage Current ratio in order to save money (This cannot be done with DC). The full explanation... Electricity has to travel a long distance through wires to reach your home ...
... Why do we have an AC current? Answer Electricity can be generated as either AC or DC, but AC allows us to change the Voltage Current ratio in order to save money (This cannot be done with DC). The full explanation... Electricity has to travel a long distance through wires to reach your home ...
Electricity Unit Test Review
... 14. Electricity always takes the easiest path to the ground. Why is the earth a good ground despite soil and rock not being a good conductor? 15. What are the three criteria that determine whether charge will jump between objects? 16. Explain using a diagram how lightning forms. 17. Define Coulomb, ...
... 14. Electricity always takes the easiest path to the ground. Why is the earth a good ground despite soil and rock not being a good conductor? 15. What are the three criteria that determine whether charge will jump between objects? 16. Explain using a diagram how lightning forms. 17. Define Coulomb, ...
Table of Electrical Symbols - I blogs dell`ISIS Leonardo da Vinci
... Photo-resistor - change resistance with light intensity change ...
... Photo-resistor - change resistance with light intensity change ...
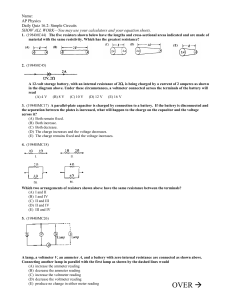
Quiz 16.2–AP–Simple Circuits w- multi battery loop
... 1. (1984MC44) The five resistors shown below have the lengths and cross-sectional areas indicated and are made of material with the same resistivity. Which has the greatest resistance? ...
... 1. (1984MC44) The five resistors shown below have the lengths and cross-sectional areas indicated and are made of material with the same resistivity. Which has the greatest resistance? ...
Lab: " Ohm`s Law "
... B. Choose three resistors. R1 = _________ Ω R2 = __________ Ω R3 = __________ Ω. Connect one of the resistors to the power supply. Turn on the voltmeter and adjust it to read DCV 20. Connect it in parallel (across) the resistor. Turn on the ammeter and adjust it to read 10 A. Place it in series with ...
... B. Choose three resistors. R1 = _________ Ω R2 = __________ Ω R3 = __________ Ω. Connect one of the resistors to the power supply. Turn on the voltmeter and adjust it to read DCV 20. Connect it in parallel (across) the resistor. Turn on the ammeter and adjust it to read 10 A. Place it in series with ...
Spectrum Management Systems
... 2) Frequency: 50/60 Hz. 3) Line Current: 16A Maximum 4) Load Capacity: 11.04 KVA 5) Power Cord: 10' (3m), #12AWG(3.3mm )/5C 6) Connector: IEC309-16A 7) Indicators: Power-on, LED 8) Transient Voltage Suppression (TVS) 9) Integral EMI Filter B. Output Characteristics: 1) Voltage: 230 VAC 2) Current: 1 ...
... 2) Frequency: 50/60 Hz. 3) Line Current: 16A Maximum 4) Load Capacity: 11.04 KVA 5) Power Cord: 10' (3m), #12AWG(3.3mm )/5C 6) Connector: IEC309-16A 7) Indicators: Power-on, LED 8) Transient Voltage Suppression (TVS) 9) Integral EMI Filter B. Output Characteristics: 1) Voltage: 230 VAC 2) Current: 1 ...
REVIEW SHEET – ELECTRIC CIRCUITS
... conventional current, drift velocity, conduction electrons, voltage drop, potential difference, Ohmic device, non-Ohmic device, power, charge, energy, schematic, variable resistor, series circuit, parallel circuit, fuse, circuit breaker, ground, short circuit, open circuit, equivalent resistance, ju ...
... conventional current, drift velocity, conduction electrons, voltage drop, potential difference, Ohmic device, non-Ohmic device, power, charge, energy, schematic, variable resistor, series circuit, parallel circuit, fuse, circuit breaker, ground, short circuit, open circuit, equivalent resistance, ju ...
Current source
A current source is an electronic circuit that delivers or absorbs an electric current which is independent of the voltage across it.A current source is the dual of a voltage source. The term constant-current 'sink' is sometimes used for sources fed from a negative voltage supply. Figure 1 shows the schematic symbol for an ideal current source, driving a resistor load. There are two types - an independent current source (or sink) delivers a constant current. A dependent current source delivers a current which is proportional to some other voltage or current in the circuit.