Capacitor Self
... 2. With the current meter in series with the entire circuit, set the supply voltage so that the current meter reads exactly 6 ma. Measure the source voltage and record. ...
... 2. With the current meter in series with the entire circuit, set the supply voltage so that the current meter reads exactly 6 ma. Measure the source voltage and record. ...
pptx
... d) How much power is dissipated by the resistor? e) How much power is delivered (or absorbed) by the batteries? ...
... d) How much power is dissipated by the resistor? e) How much power is delivered (or absorbed) by the batteries? ...
Practice Exam 1 - UIC Department of Physics
... follow a circular arc of radius R, what is the radius of the arc followed by the lighter? A) 4R B) 3R C) 2 R D) R/ 2 E) R/2 Answer: D ...
... follow a circular arc of radius R, what is the radius of the arc followed by the lighter? A) 4R B) 3R C) 2 R D) R/ 2 E) R/2 Answer: D ...
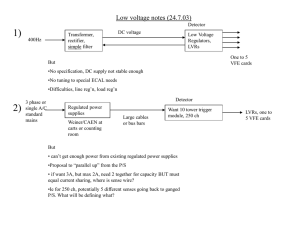
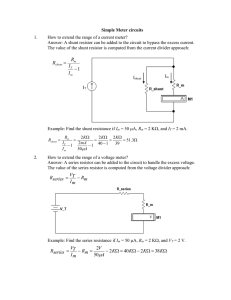
How to Create a Precision Current Source Using
... point at the high end of the current range can cause the transistor to saturate, which will result in a reduced maximum current. Conversely, if the op amp uses VCC and GND as its rails, then current settings at the low end of the current range can cause insufficient voltage to overcome the transisto ...
... point at the high end of the current range can cause the transistor to saturate, which will result in a reduced maximum current. Conversely, if the op amp uses VCC and GND as its rails, then current settings at the low end of the current range can cause insufficient voltage to overcome the transisto ...
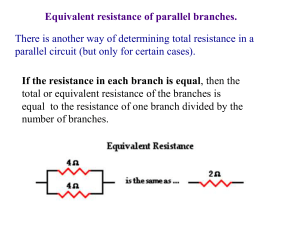
There is another way of determining total resistance in a parallel circuit
... If the resistance in each branch is equal, then the total or equivalent resistance of the branches is equal to the resistance of one branch divided by the number of branches. ...
... If the resistance in each branch is equal, then the total or equivalent resistance of the branches is equal to the resistance of one branch divided by the number of branches. ...
Video Transcript - Rose
... For the ideal op amp circuit, the input current should be zero. So the current through R1 should flow through the capacitor. The voltage at the non-inverting node is V positive, which should be the current multiplied by the impedance. So this expression should represent the current. [math equation] ...
... For the ideal op amp circuit, the input current should be zero. So the current through R1 should flow through the capacitor. The voltage at the non-inverting node is V positive, which should be the current multiplied by the impedance. So this expression should represent the current. [math equation] ...
GRAPHING RESISTANCE Goal • Find the relationship between
... 5. Not all resistors follow this law, Look at the following graph. There is only a certain range of data that this nichrome wire is considered an ohmic resistor. What is this range of data in current? ...
... 5. Not all resistors follow this law, Look at the following graph. There is only a certain range of data that this nichrome wire is considered an ohmic resistor. What is this range of data in current? ...
Worksheet for Exploration 31.5
... Worksheet for Exploration 31.5: RL Circuits and Phasors Assume an ideal power supply. The graph shows the voltage as a function of time across the source (red), the resistor (blue), and the inductor (green) (voltage is given in volts and time is given in seconds). Restart. To analyze the currents an ...
... Worksheet for Exploration 31.5: RL Circuits and Phasors Assume an ideal power supply. The graph shows the voltage as a function of time across the source (red), the resistor (blue), and the inductor (green) (voltage is given in volts and time is given in seconds). Restart. To analyze the currents an ...
LEP 5.3.04 Band gap of germanium
... Problems 1. The current and voltage are to be measured across a germanium test-piece as a function of temperature. ...
... Problems 1. The current and voltage are to be measured across a germanium test-piece as a function of temperature. ...
Water Flow
... with it because size of the Water Pipe is reduced at that spot (if You get what I mean), hence with Resistance (Resistor) you can reduce Current by creating a Voltage drop at a certain spot in a circuit. ...
... with it because size of the Water Pipe is reduced at that spot (if You get what I mean), hence with Resistance (Resistor) you can reduce Current by creating a Voltage drop at a certain spot in a circuit. ...
Measurement CKT
... capacitor. You may need to switch the positions between the two components if the AC voltmeter does not have a floating ground. C ...
... capacitor. You may need to switch the positions between the two components if the AC voltmeter does not have a floating ground. C ...
Electric Current
... It has a current (I), requires a difference in energy to keep moving (V) and can be slowed down by objects in its path (R). ...
... It has a current (I), requires a difference in energy to keep moving (V) and can be slowed down by objects in its path (R). ...
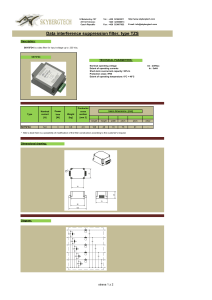
TZS - Skybergtech
... TECHNICAL PARAMETERS: Nominal operating voltage Extent of operating currents Short-term overcurrent capacity: 50% In Protection class: IP00 Extent of operating temperature: 0°C + 40°C ...
... TECHNICAL PARAMETERS: Nominal operating voltage Extent of operating currents Short-term overcurrent capacity: 50% In Protection class: IP00 Extent of operating temperature: 0°C + 40°C ...
Series and Parallel Circuits
... toll booths in series increases resistance and slows the current flow. Adding toll booths in parallel lowers resistance and increases the current flow. ...
... toll booths in series increases resistance and slows the current flow. Adding toll booths in parallel lowers resistance and increases the current flow. ...
Current source
A current source is an electronic circuit that delivers or absorbs an electric current which is independent of the voltage across it.A current source is the dual of a voltage source. The term constant-current 'sink' is sometimes used for sources fed from a negative voltage supply. Figure 1 shows the schematic symbol for an ideal current source, driving a resistor load. There are two types - an independent current source (or sink) delivers a constant current. A dependent current source delivers a current which is proportional to some other voltage or current in the circuit.