Internal Resistance and Resistivity in DC Circuits
... Internal Resistance All components in a circuit off some type of resistance regardless of how large or small it is. Batteries especially have what is called an internal resistance, r. Within the schematic it will be represented as a resistor symbol next to a battery symbol and between 2 points that ...
... Internal Resistance All components in a circuit off some type of resistance regardless of how large or small it is. Batteries especially have what is called an internal resistance, r. Within the schematic it will be represented as a resistor symbol next to a battery symbol and between 2 points that ...
Internal Resistance and Resistivity in DC Circuits
... Internal Resistance All components in a circuit off some type of resistance regardless of how large or small it is. Batteries especially have what is called an internal resistance, r. Within the schematic it will be represented as a resistor symbol next to a battery symbol and between 2 points that ...
... Internal Resistance All components in a circuit off some type of resistance regardless of how large or small it is. Batteries especially have what is called an internal resistance, r. Within the schematic it will be represented as a resistor symbol next to a battery symbol and between 2 points that ...
Chapter 18
... A 10-V-emf battery is connected in series with a 2-μF capacitor, a 2-Ω resistor, an ammeter and a switch. A voltmeter is connected in parallel across the capacitor. At the instant the switch is closed, what are the current and capacitor voltage readings, respectively? (RC Circuit) ...
... A 10-V-emf battery is connected in series with a 2-μF capacitor, a 2-Ω resistor, an ammeter and a switch. A voltmeter is connected in parallel across the capacitor. At the instant the switch is closed, what are the current and capacitor voltage readings, respectively? (RC Circuit) ...
Final Review CIRCUITS:
... 13. What happens to the light intensity of each bulb in a series circuit when more bulbs are added to the circuit? ...
... 13. What happens to the light intensity of each bulb in a series circuit when more bulbs are added to the circuit? ...
Slide 1 - MrSimonPorter
... Vary the voltage and current using a variable resistor (rheostat). Plot a graph of resistance against current ...
... Vary the voltage and current using a variable resistor (rheostat). Plot a graph of resistance against current ...
ETEE1123 Homework 4 - Personal Web Pages
... How much resistance is required to limit the current to 1.5 mA if the potential drop across the resistor is 6 V? ...
... How much resistance is required to limit the current to 1.5 mA if the potential drop across the resistor is 6 V? ...
2) In the circuit in Fig. 1, using modified nodal analysis
... (Problems 2 and 3: Copyright © L.R.Linares 2009) ...
... (Problems 2 and 3: Copyright © L.R.Linares 2009) ...
Exercise 4
... Exercise 4: Kirchoff’s Current and Voltage Laws Kirchoff’s Current Law is a statement of the conservation of current. For the picture on the right, it implies that i1=i2+i3. In other words, the sum of the currents at any node must be zero. As you know, you can add electrical load to a circuit in two ...
... Exercise 4: Kirchoff’s Current and Voltage Laws Kirchoff’s Current Law is a statement of the conservation of current. For the picture on the right, it implies that i1=i2+i3. In other words, the sum of the currents at any node must be zero. As you know, you can add electrical load to a circuit in two ...
Electric Power Distribution
... The Power Distribution Process 1. A generator at a power station produces AC electricity at V = 25,000 volts, flowing at 8,000 A. 2. A step-up transformer raises V 16x to 400,000 volts (decreases current by 16x to 500 A) ...
... The Power Distribution Process 1. A generator at a power station produces AC electricity at V = 25,000 volts, flowing at 8,000 A. 2. A step-up transformer raises V 16x to 400,000 volts (decreases current by 16x to 500 A) ...
Chapter 20 Summary
... If devices are in series, the current is the same everywhere in the circuit Equivalent resistance is sum of individual resistors (Rs>Rn) You can still find power delivered to the resistors. In general, total power delivered is equal to power delivered to equivalent resistance ...
... If devices are in series, the current is the same everywhere in the circuit Equivalent resistance is sum of individual resistors (Rs>Rn) You can still find power delivered to the resistors. In general, total power delivered is equal to power delivered to equivalent resistance ...
Downlaod File
... charge flows from one end to the other. 2- what is Ohm’s Law? States that the current in a circuit varies in direct proportion to the potential difference, or voltage, and inversely with the resistance. 3- what is Electric Power? Rate at which electric energy is converted into another form. 4- What ...
... charge flows from one end to the other. 2- what is Ohm’s Law? States that the current in a circuit varies in direct proportion to the potential difference, or voltage, and inversely with the resistance. 3- what is Electric Power? Rate at which electric energy is converted into another form. 4- What ...
Series_RLC_Circuit
... The students vary the frequency of the input from the signal generator while observing the globe. At resonance the globe will be brightest. They then vary the inductance for a fixed input frequency and again look for resonance. The Physics The globe acts as a resistor, dissipating energy as heat and ...
... The students vary the frequency of the input from the signal generator while observing the globe. At resonance the globe will be brightest. They then vary the inductance for a fixed input frequency and again look for resonance. The Physics The globe acts as a resistor, dissipating energy as heat and ...
ch4_L1_i
... Loop: a closed path going from one circuit node back to itself without passing through any intermediate node more than once Kirchhoff’s first (or current) law: at a circuit node, the current flowing into the node equals the current flowing out (charge is conserved) Kirchhoff’s second (or voltage) la ...
... Loop: a closed path going from one circuit node back to itself without passing through any intermediate node more than once Kirchhoff’s first (or current) law: at a circuit node, the current flowing into the node equals the current flowing out (charge is conserved) Kirchhoff’s second (or voltage) la ...
Electricity - Gulf Islands Secondary School
... The voltage drop over each load sums to the voltage across the battery The current through each path sums to the current supplied by the battery In a series circuit, the voltage drop across each device can differ, but the current through each device is the same In a parallel circuit, the voltage dro ...
... The voltage drop over each load sums to the voltage across the battery The current through each path sums to the current supplied by the battery In a series circuit, the voltage drop across each device can differ, but the current through each device is the same In a parallel circuit, the voltage dro ...
solns
... 19) By inspection, what is the current ic? ic = -.1 A 20) What is the Thevenin Voltage of the Circuit shown: (no current flows thru 25 Ohm resistors) Vth = V4A = 60 + 4*(20+20) = 220V ...
... 19) By inspection, what is the current ic? ic = -.1 A 20) What is the Thevenin Voltage of the Circuit shown: (no current flows thru 25 Ohm resistors) Vth = V4A = 60 + 4*(20+20) = 220V ...
electronics
... Introduction/Purpose: This experiment extends the application of Ohm’s Law to two or more components connected in simple series and parallel circuits. Analysis of our measurements should enable us to derive relationships between total resistance - RT, total current - IT, and the individual voltage d ...
... Introduction/Purpose: This experiment extends the application of Ohm’s Law to two or more components connected in simple series and parallel circuits. Analysis of our measurements should enable us to derive relationships between total resistance - RT, total current - IT, and the individual voltage d ...
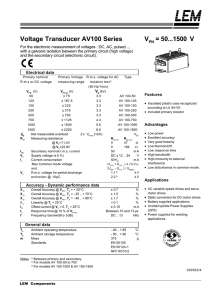
AV100-750 - Europower Components Ltd
... Terminal + : Supply voltage +12 .. 24 V Terminal M : Measure Terminal - : Supply voltage - 12 .. 24V ...
... Terminal + : Supply voltage +12 .. 24 V Terminal M : Measure Terminal - : Supply voltage - 12 .. 24V ...
Test Procedure for the NCP1351LEDEVB Driver Evaluation Board
... 3. A variable electronic load or rheostat capable of up to a 2 amp load at 40 volts. If an electronic load is used it is preferable to have it operate in a constant resistance load mode. 4. Oscilloscope with probe to monitor output ripple on the demo converter. ...
... 3. A variable electronic load or rheostat capable of up to a 2 amp load at 40 volts. If an electronic load is used it is preferable to have it operate in a constant resistance load mode. 4. Oscilloscope with probe to monitor output ripple on the demo converter. ...
Exam2_review
... Answer: Box your answer. Does this answer make sense (order of magnitude?), have UNITS!!!!? , include all parts (vector or directions, etc.)? This step is to make sure your answer is complete and reasonable. Here are a few problems like the ones that you may see on the exam. 1. Suppose you have a DC ...
... Answer: Box your answer. Does this answer make sense (order of magnitude?), have UNITS!!!!? , include all parts (vector or directions, etc.)? This step is to make sure your answer is complete and reasonable. Here are a few problems like the ones that you may see on the exam. 1. Suppose you have a DC ...
Current source
A current source is an electronic circuit that delivers or absorbs an electric current which is independent of the voltage across it.A current source is the dual of a voltage source. The term constant-current 'sink' is sometimes used for sources fed from a negative voltage supply. Figure 1 shows the schematic symbol for an ideal current source, driving a resistor load. There are two types - an independent current source (or sink) delivers a constant current. A dependent current source delivers a current which is proportional to some other voltage or current in the circuit.