green chemistry
... The Green Chemistry program supports the invention of more environmentally friendly chemical processes which reduce or even eliminate the generation of hazardous substances. ...
... The Green Chemistry program supports the invention of more environmentally friendly chemical processes which reduce or even eliminate the generation of hazardous substances. ...
File
... You can smell brownies baking in the oven and smoke from a campfire. You can see gas bubbles produced when you combine vinegar and baking soda. These are signs of chemical changes. Some chemical changes are easy to detect. Other chemical changes are less obvious. In a chemical reaction, two or more s ...
... You can smell brownies baking in the oven and smoke from a campfire. You can see gas bubbles produced when you combine vinegar and baking soda. These are signs of chemical changes. Some chemical changes are easy to detect. Other chemical changes are less obvious. In a chemical reaction, two or more s ...
gibbs free energy (g) - Clayton State University
... - Reaction is spontaneous in the reverse direction if ∆G is positive - Reaction is spontaneous in the forward direction if Q < Keq - Reaction is spontaneous in the reverse direction if Q > Keq - At equilibrium ∆G approaches zero and Q approaches Keq ...
... - Reaction is spontaneous in the reverse direction if ∆G is positive - Reaction is spontaneous in the forward direction if Q < Keq - Reaction is spontaneous in the reverse direction if Q > Keq - At equilibrium ∆G approaches zero and Q approaches Keq ...
Review of Thermodynamics - University of Alabama at Birmingham
... Mechanical Work: At constant pressure work can be defined as w = -PV where V = V2 – V1 ...
... Mechanical Work: At constant pressure work can be defined as w = -PV where V = V2 – V1 ...
1st mid unit test formative (pre-test)
... Is a substance that cannot be broken down into any simpler substance by chemical means. Iron, oxygen and neon are examples. ...
... Is a substance that cannot be broken down into any simpler substance by chemical means. Iron, oxygen and neon are examples. ...
1st mid unit test formative (pre-test)
... Is a substance that cannot be broken down into any simpler substance by chemical means. Iron, oxygen and neon are examples. ...
... Is a substance that cannot be broken down into any simpler substance by chemical means. Iron, oxygen and neon are examples. ...
Oxidation-Reduction Reactions
... Hess’s Law Hess’s Law: When reactants are converted to products, the change in enthalpy is the same whether the reaction takes place in one step or in a series of steps ...
... Hess’s Law Hess’s Law: When reactants are converted to products, the change in enthalpy is the same whether the reaction takes place in one step or in a series of steps ...
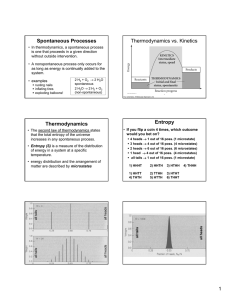
Spontaneous Processes Thermodynamics vs. Kinetics
... perfect crystal is zero at absolute zero. S is explicitly known (=0) at 0 K, S values at other temps can be calculated. ...
... perfect crystal is zero at absolute zero. S is explicitly known (=0) at 0 K, S values at other temps can be calculated. ...
Chap 2.1 Notes - Nature of Matter
... Chemical reaction – a process that changes one set of chemicals into another. All the Chemical reactions that occur in organisms are known as the organism’s metabolism. Ex) digestion, cellular respiration, photosynthesis, etc. Chemical reactions are summarized using chemical equations that include t ...
... Chemical reaction – a process that changes one set of chemicals into another. All the Chemical reactions that occur in organisms are known as the organism’s metabolism. Ex) digestion, cellular respiration, photosynthesis, etc. Chemical reactions are summarized using chemical equations that include t ...
chapter 5 thermochemistry
... Another common energy unit is the calorie (cal), which was originally defined as the quantity of energy necessary to increase the temperature of 1 g of water by 1°C: When we study thermodynamic properties, we define a specific amount of matter as the system. Everything outside the system is the surr ...
... Another common energy unit is the calorie (cal), which was originally defined as the quantity of energy necessary to increase the temperature of 1 g of water by 1°C: When we study thermodynamic properties, we define a specific amount of matter as the system. Everything outside the system is the surr ...
Chemical Reactions
... can only change forms So when we write equations… The number of each type of atom on the reactants side must be equal to the number of each type of atom on the products side ...
... can only change forms So when we write equations… The number of each type of atom on the reactants side must be equal to the number of each type of atom on the products side ...
107 - Bossier Parish Community College
... 13. recognize the interrelationship of the structure of matter and its chemical and physical properties. (B,C) 14. differentiate between intensive and extensive properties. (B,C) 15. determine if a change in matter is physical or chemical. (B,C) 16. recognize and differentiate the characteristics o ...
... 13. recognize the interrelationship of the structure of matter and its chemical and physical properties. (B,C) 14. differentiate between intensive and extensive properties. (B,C) 15. determine if a change in matter is physical or chemical. (B,C) 16. recognize and differentiate the characteristics o ...
File
... (B) The quantity of solid minerals decreased. (C) The cloudiness in the last bottle of limewater was caused by the product of the reaction of the colorless gas and the limewater. (D) The bubbles of gas rising from the mineral remained colorless throughout the experiment. (E) There was a 4oC rise in ...
... (B) The quantity of solid minerals decreased. (C) The cloudiness in the last bottle of limewater was caused by the product of the reaction of the colorless gas and the limewater. (D) The bubbles of gas rising from the mineral remained colorless throughout the experiment. (E) There was a 4oC rise in ...
spontaneous processes
... irreversible process: getting back what you started with requires more than just an “undo” -- we can restore the original system, but the surroundings will have changed ...
... irreversible process: getting back what you started with requires more than just an “undo” -- we can restore the original system, but the surroundings will have changed ...
General Chemistry First Semester Review General
... - solid: This could refer to a multitude of different substances: metals, flakes, crystals, and precipitates; use (s) - gas: Use (g), these are usually diatomic molecules such as O2, H2, Cl2, etc. - read given information carefully. Water vapor is noted with a (g) because it is a gas, not a liquid. ...
... - solid: This could refer to a multitude of different substances: metals, flakes, crystals, and precipitates; use (s) - gas: Use (g), these are usually diatomic molecules such as O2, H2, Cl2, etc. - read given information carefully. Water vapor is noted with a (g) because it is a gas, not a liquid. ...
+ 2 HCL(aq) CaCl2(aq) + H2O(l) + CO2(g)
... Subscript: A number that represents how many atoms of an element are in a compound. Compound: A substance made of the combined atoms of two or more elements. Chemical Formula: States what elements a compound contains and the exact number of atoms of these elements. Oxidation Number: positive or nega ...
... Subscript: A number that represents how many atoms of an element are in a compound. Compound: A substance made of the combined atoms of two or more elements. Chemical Formula: States what elements a compound contains and the exact number of atoms of these elements. Oxidation Number: positive or nega ...
Snc2d Chapter 5 Practice Test
... 12. BALANCING CHEMICAL REACTIONS/ IDENTIFYING REACTION TYPES balance the following chemical reactions with the lowest possible numbers. write the name of the type or reaction beside each of the reactions. ...
... 12. BALANCING CHEMICAL REACTIONS/ IDENTIFYING REACTION TYPES balance the following chemical reactions with the lowest possible numbers. write the name of the type or reaction beside each of the reactions. ...
chemistry syllabus
... Equilibrium in physical and chemical processes Equilibrium in physical and chemical processes, dynamic equilibrium, law of chemical equilibrium and equilibrium constant, homogeneous equilibrium, heterogenous equilibrium, application of equilibrium constants, Relationship between reaction quotient Q, ...
... Equilibrium in physical and chemical processes Equilibrium in physical and chemical processes, dynamic equilibrium, law of chemical equilibrium and equilibrium constant, homogeneous equilibrium, heterogenous equilibrium, application of equilibrium constants, Relationship between reaction quotient Q, ...
Laws of Thermodynamics
... The absolute temperature and the metrical entropy The first law enables one to define an empirical temperature and the second law allows one to define an empirical entropy. What this means is that the laws allow us to order states with parameters t and s. Consider two states of a system labeled 1 an ...
... The absolute temperature and the metrical entropy The first law enables one to define an empirical temperature and the second law allows one to define an empirical entropy. What this means is that the laws allow us to order states with parameters t and s. Consider two states of a system labeled 1 an ...
entropy - Helios
... DS>0 This is also the second law of thermodynamics Entropy always increases ...
... DS>0 This is also the second law of thermodynamics Entropy always increases ...
Chemical thermodynamics

Chemical thermodynamics is the study of the interrelation of heat and work with chemical reactions or with physical changes of state within the confines of the laws of thermodynamics. Chemical thermodynamics involves not only laboratory measurements of various thermodynamic properties, but also the application of mathematical methods to the study of chemical questions and the spontaneity of processes.The structure of chemical thermodynamics is based on the first two laws of thermodynamics. Starting from the first and second laws of thermodynamics, four equations called the ""fundamental equations of Gibbs"" can be derived. From these four, a multitude of equations, relating the thermodynamic properties of the thermodynamic system can be derived using relatively simple mathematics. This outlines the mathematical framework of chemical thermodynamics.