thermodynamic states
... Thus, the process proceeds to state with lower G, and the equilibrium state occurs at min Gibbs free energy, ...
... Thus, the process proceeds to state with lower G, and the equilibrium state occurs at min Gibbs free energy, ...
States of Matter
... Classify changes of state in terms of endothermic and exothermic processes Classify mixtures as being homogenous or heterogeneous Distinguish among elements, atoms, compounds, and mixtures Distinguish between a chemical and physical change. Demonstrate the conservation of energy in calculations usin ...
... Classify changes of state in terms of endothermic and exothermic processes Classify mixtures as being homogenous or heterogeneous Distinguish among elements, atoms, compounds, and mixtures Distinguish between a chemical and physical change. Demonstrate the conservation of energy in calculations usin ...
Chemistry
... http://www.dailymotion.com/video/xlp2y1_billnye-chemical-reactions_tech#.URez2lrjk3I ...
... http://www.dailymotion.com/video/xlp2y1_billnye-chemical-reactions_tech#.URez2lrjk3I ...
Physical or Chemical Properties
... With a physical change no new substance is created and the original matter can be recovered. Physical change does not change the composition of the matter. The original matter is still present. The substance may seem different, but the way the atoms are linked up are the same. ...
... With a physical change no new substance is created and the original matter can be recovered. Physical change does not change the composition of the matter. The original matter is still present. The substance may seem different, but the way the atoms are linked up are the same. ...
Balancing a Chemical Equation
... Chemical reactions occur when bonds (between the electrons of atoms) are formed or broken Chemical reactions involve ...
... Chemical reactions occur when bonds (between the electrons of atoms) are formed or broken Chemical reactions involve ...
Balancing a Chemical Equation
... Chemical reactions occur when bonds (between the electrons of atoms) are formed or broken Chemical reactions involve ...
... Chemical reactions occur when bonds (between the electrons of atoms) are formed or broken Chemical reactions involve ...
Process
... The difference between the electrode potentials of the two half cell is known as electromotive force (EMF) of the cell or cell potential or cell voltage. The EMF of the cell depends on the nature of the reactants, concentration of the solution in the two half cells, and ...
... The difference between the electrode potentials of the two half cell is known as electromotive force (EMF) of the cell or cell potential or cell voltage. The EMF of the cell depends on the nature of the reactants, concentration of the solution in the two half cells, and ...
balancing eqns teacher
... Chemical reactions occur when bonds (between the electrons of atoms) are formed or broken Chemical reactions involve ...
... Chemical reactions occur when bonds (between the electrons of atoms) are formed or broken Chemical reactions involve ...
Holt Chemistry – Guided Notes, Chapter 1
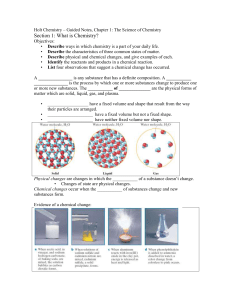
... • Describe the characteristics of three common states of matter. • Describe physical and chemical changes, and give examples of each. • Identify the reactants and products in a chemical reaction. • List four observations that suggest a chemical change has occurred. A _______________ is any substance ...
... • Describe the characteristics of three common states of matter. • Describe physical and chemical changes, and give examples of each. • Identify the reactants and products in a chemical reaction. • List four observations that suggest a chemical change has occurred. A _______________ is any substance ...
Chemical Equations
... Steps involved in writing a 'balanced' equation for a chemical reaction: 1. Write the chemical formula for each of the named substances. Don’t forget that the diatomic elements always have a subscript of two if not combined with another element. 2. Write the skeleton equation using formulas of react ...
... Steps involved in writing a 'balanced' equation for a chemical reaction: 1. Write the chemical formula for each of the named substances. Don’t forget that the diatomic elements always have a subscript of two if not combined with another element. 2. Write the skeleton equation using formulas of react ...
Chemistry 11 - Sardis Secondary
... - calculating the amount of excess reactant - calculating the amount of product formed in a reaction using the limiting reactant C. Percent Yield (text pgs. 365-373) - calculating the efficiency of a chemical reaction from percent yield ...
... - calculating the amount of excess reactant - calculating the amount of product formed in a reaction using the limiting reactant C. Percent Yield (text pgs. 365-373) - calculating the efficiency of a chemical reaction from percent yield ...
Topic 16 IB Chemistry Definitions
... Created during a bimolecular process. Not a chemical substance which can be isolated, but consists of reacting particles in which bonds are in the process of being broken and formed. Can break down to form either the products or back to the original reactants. ...
... Created during a bimolecular process. Not a chemical substance which can be isolated, but consists of reacting particles in which bonds are in the process of being broken and formed. Can break down to form either the products or back to the original reactants. ...
Chemical Reactions and Equations
... in one substance on each side of the equation, make sure that each side of the equation has an equal # of that element. Proceed with all elements. Remember that changing the # of one element may alter elements that have already been ...
... in one substance on each side of the equation, make sure that each side of the equation has an equal # of that element. Proceed with all elements. Remember that changing the # of one element may alter elements that have already been ...
thermochermistry ap - Mater Academy Lakes High School
... An irreversible process is a process in which more than just doing the opposite thing makes the system reverse o For example, if you cook chicken, o A spontaneous process is irreversible o An isothermal process is a process with a constant temperature; it is typically used when dealing with the pr ...
... An irreversible process is a process in which more than just doing the opposite thing makes the system reverse o For example, if you cook chicken, o A spontaneous process is irreversible o An isothermal process is a process with a constant temperature; it is typically used when dealing with the pr ...
Section 1: Temperature and Heat Temperature A measure of the
... Energy=specific heat x mass x temp. change Q=mc∆T Adding energy: Raises its temp or state of matter but not both at the same time ...
... Energy=specific heat x mass x temp. change Q=mc∆T Adding energy: Raises its temp or state of matter but not both at the same time ...
Matter and Change
... Law of Conservation of Energy • Law of Conservation of Energy: in all physical and chemical changes, energy is neither created or destroyed • Energy: the capacity to do work or produce heat ...
... Law of Conservation of Energy • Law of Conservation of Energy: in all physical and chemical changes, energy is neither created or destroyed • Energy: the capacity to do work or produce heat ...
Study Guide - Flagler Schools
... Understand the relationship between current, voltage, and resistance. Know what gravity is and how it relates to acceleration, the distance between two objects, and mass of the two objects. Understand free body diagrams Be able to decipher a phase change diagram. Be able to decipher a Poten ...
... Understand the relationship between current, voltage, and resistance. Know what gravity is and how it relates to acceleration, the distance between two objects, and mass of the two objects. Understand free body diagrams Be able to decipher a phase change diagram. Be able to decipher a Poten ...
Lecture 4
... member of the canonical ensemble, may have its energy in the specified range. Clearly, the product of the relevant single-state probability and the number of energy states lying in the specified range will give this. Denoting the latter by g(E)dE, where g(E) stands for the density of states of the s ...
... member of the canonical ensemble, may have its energy in the specified range. Clearly, the product of the relevant single-state probability and the number of energy states lying in the specified range will give this. Denoting the latter by g(E)dE, where g(E) stands for the density of states of the s ...
Chemical thermodynamics

Chemical thermodynamics is the study of the interrelation of heat and work with chemical reactions or with physical changes of state within the confines of the laws of thermodynamics. Chemical thermodynamics involves not only laboratory measurements of various thermodynamic properties, but also the application of mathematical methods to the study of chemical questions and the spontaneity of processes.The structure of chemical thermodynamics is based on the first two laws of thermodynamics. Starting from the first and second laws of thermodynamics, four equations called the ""fundamental equations of Gibbs"" can be derived. From these four, a multitude of equations, relating the thermodynamic properties of the thermodynamic system can be derived using relatively simple mathematics. This outlines the mathematical framework of chemical thermodynamics.