File
... same molecular formula, but different structures, is called isomerism • Theses structures are called isomers ...
... same molecular formula, but different structures, is called isomerism • Theses structures are called isomers ...
Novel Strecker Degradation Products of Tyrosine and
... alcohols, acetals, acids, esters and other compounds. The importance of Strecker degradation for biological processes such as its role in aging process and age-related diseases has been established for a long time (DEGENHARDT et al. 1998). Tyrosine (Tyr) accompanies phenylalanine in the majority of ...
... alcohols, acetals, acids, esters and other compounds. The importance of Strecker degradation for biological processes such as its role in aging process and age-related diseases has been established for a long time (DEGENHARDT et al. 1998). Tyrosine (Tyr) accompanies phenylalanine in the majority of ...
Document
... C. The denomination of ”secondary amine” indicates the type of the carbon atom at which the functional group is bound D. Diethylamine and methylamine have a greater degree of basicity than ammonia E. Phenylamine has a greater degree of basicity than ammonia 28. The following statements regarding ami ...
... C. The denomination of ”secondary amine” indicates the type of the carbon atom at which the functional group is bound D. Diethylamine and methylamine have a greater degree of basicity than ammonia E. Phenylamine has a greater degree of basicity than ammonia 28. The following statements regarding ami ...
Compounds Containing a C=O (Carbonyl) Group
... Aldehydes and Ketones Naming Aldehydes, Naming Ketones, Physical Properties, Interesting Aldehydes and Ketones, Preparation of Aldehydes and Ketones, Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones (Addition of 1° Amines, Addition of 2° Amines, Addition of H2O—Hydration, Addition of Alcohols—Acetal Formation, A ...
... Aldehydes and Ketones Naming Aldehydes, Naming Ketones, Physical Properties, Interesting Aldehydes and Ketones, Preparation of Aldehydes and Ketones, Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones (Addition of 1° Amines, Addition of 2° Amines, Addition of H2O—Hydration, Addition of Alcohols—Acetal Formation, A ...
Stoichometry Notes (Unit 2)
... reactant side of the “à” must be equal to the total number of atoms of each element (and the sum of their respective masses) on the product side. Chemical equations frequently contain additional symbols to represent the physical state (phase) of the substance(s). These symbols include: (S) for solid ...
... reactant side of the “à” must be equal to the total number of atoms of each element (and the sum of their respective masses) on the product side. Chemical equations frequently contain additional symbols to represent the physical state (phase) of the substance(s). These symbols include: (S) for solid ...
314_lect_26_tosyl_SN..
... back to being trivalent (sp2). That mechanism is presented in just a bit as a problem for you to solve. The important result of this transformation is that a poor leaving group, the HO- of an alcohol, is made into a very good leaving group, a sulfonate group RSO3-. The reaction presented above is a ...
... back to being trivalent (sp2). That mechanism is presented in just a bit as a problem for you to solve. The important result of this transformation is that a poor leaving group, the HO- of an alcohol, is made into a very good leaving group, a sulfonate group RSO3-. The reaction presented above is a ...
Chapter 3 Molecules, Compounds, and Chemical Equations
... - hold atoms together to form compounds - are forces of attraction between atoms. - the bonding attraction comes from attractions between protons and electrons. i.) Ionic bonds - result when electrons have been transferred between atoms, resulting in oppositely charged ions that attract each other - ...
... - hold atoms together to form compounds - are forces of attraction between atoms. - the bonding attraction comes from attractions between protons and electrons. i.) Ionic bonds - result when electrons have been transferred between atoms, resulting in oppositely charged ions that attract each other - ...
Chapter 3 Molecules, Compounds, and Chemical Equations q
... - result when electrons have been transferred between atoms, resulting in oppositely charged ions that attract each other generally e a y formed o ed when e metal ea a atoms o s bo bonded ded to o - ge nonmetal atoms ii.) Covalent bonds – result when two atoms share some of their electrons. – genera ...
... - result when electrons have been transferred between atoms, resulting in oppositely charged ions that attract each other generally e a y formed o ed when e metal ea a atoms o s bo bonded ded to o - ge nonmetal atoms ii.) Covalent bonds – result when two atoms share some of their electrons. – genera ...
www.studyguide.pk
... Permission to reproduce items where third-party owned material protected by copyright is included has been sought and cleared where possible. Every reasonable effort has been made by the publisher (UCLES) to trace copyright holders, but if any items requiring clearance have unwittingly been included ...
... Permission to reproduce items where third-party owned material protected by copyright is included has been sought and cleared where possible. Every reasonable effort has been made by the publisher (UCLES) to trace copyright holders, but if any items requiring clearance have unwittingly been included ...
Chem 101 Test #1 review questions. Please don`t look at the
... We need to know also the millimoles of O: mg O = total – (mmol C+mmol H)= 156.0(60.95+13.41)=81.64mg O mmol O = 81.64 mgx (1molO/16.0g)= 5.125 mmol O So, our formula becomes: C5.080H13.41O5.125 . Or, dividing by the smallest number, it becomes CH2O. 2) One mole of copper metal can react completely w ...
... We need to know also the millimoles of O: mg O = total – (mmol C+mmol H)= 156.0(60.95+13.41)=81.64mg O mmol O = 81.64 mgx (1molO/16.0g)= 5.125 mmol O So, our formula becomes: C5.080H13.41O5.125 . Or, dividing by the smallest number, it becomes CH2O. 2) One mole of copper metal can react completely w ...
All chemical equations must be balanced, that is, they must have the
... coefficient of 2 in front of your hydrocarbon and proceed from there) There are times, however, that hydrocarbons do not combust completely; this is called incomplete combustion and the products are slightly different. You would always be told if the reaction was compete or incomplete, if nothing is ...
... coefficient of 2 in front of your hydrocarbon and proceed from there) There are times, however, that hydrocarbons do not combust completely; this is called incomplete combustion and the products are slightly different. You would always be told if the reaction was compete or incomplete, if nothing is ...
Lecture 14
... 1. Write the correct symbols and formulas for all of the reactants and products. 2. Count the number of each type of atom on BOTH sides of the equation. 3. Insert coefficients until there are the equal numbers of each kind of atom on both sides of the equation. ...
... 1. Write the correct symbols and formulas for all of the reactants and products. 2. Count the number of each type of atom on BOTH sides of the equation. 3. Insert coefficients until there are the equal numbers of each kind of atom on both sides of the equation. ...
Chapter 1 Chemical Bonding and Chemical Structure
... 1) Monobromination of toluene gives 3 products. Draw the entire mechanism for the formation of one product and draw the other two. ...
... 1) Monobromination of toluene gives 3 products. Draw the entire mechanism for the formation of one product and draw the other two. ...
Chapter 2 Elements and Compounds 2.1 The Structure of the Atom
... Atoms of each element can be distinguished by the number of protons in the nucleus. The atomic number (Z) of an element is equal to the number of protons in the nucleus. For example, a carbon atom has six protons in its nucleus, and therefore carbon has an atomic number of six (Z = 6). Each element ...
... Atoms of each element can be distinguished by the number of protons in the nucleus. The atomic number (Z) of an element is equal to the number of protons in the nucleus. For example, a carbon atom has six protons in its nucleus, and therefore carbon has an atomic number of six (Z = 6). Each element ...
Carbonyl The carbonyl function, C=O, exists in a number of organic
... The stereochemistry of Wittig reactions is very interesting, and the detailed mechanisms involved are somewhat cloudy. As shown below the reagents add in a fast step to form an eclipsed betaine (or goes directly to the oxaphosphetane). The oxaphosphetane breaks down by syn elimination to give the tr ...
... The stereochemistry of Wittig reactions is very interesting, and the detailed mechanisms involved are somewhat cloudy. As shown below the reagents add in a fast step to form an eclipsed betaine (or goes directly to the oxaphosphetane). The oxaphosphetane breaks down by syn elimination to give the tr ...
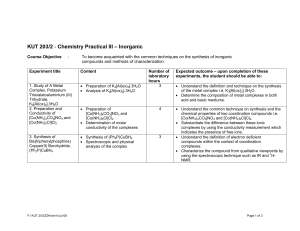
KUT 203/2 - Chemistry Practical III (Inorganic Chemistry)
... • Understand the correlation between the colors of transition metal or metal ion with its oxidation state i.e. VO2+ (yellow), VO2+ (blue) etc. • Determine the composition of a metal complex of which the metal exists in various oxidation states by using the titration technique. • Synthesize several c ...
... • Understand the correlation between the colors of transition metal or metal ion with its oxidation state i.e. VO2+ (yellow), VO2+ (blue) etc. • Determine the composition of a metal complex of which the metal exists in various oxidation states by using the titration technique. • Synthesize several c ...
... synthesis of small–molecule libraries with several degrees of structural diversities [1-10] , Creation of new products in a single step via one-pot multicomponent coupling reactions (MCRs) technique has considered as a highly economic method among the multi-component reactions especially if we use m ...
Unit 4 - INTEC Chemistry Blog
... Optical Isomerism Where molecules(chiral molecules) have mirror-image isomers that are not superimposable on the original compound. Sole criterion for chirality is existence of non-superimposable mirror images • Commonest origin of chirality is a carbon atom having 4 diff groups attached to it(the c ...
... Optical Isomerism Where molecules(chiral molecules) have mirror-image isomers that are not superimposable on the original compound. Sole criterion for chirality is existence of non-superimposable mirror images • Commonest origin of chirality is a carbon atom having 4 diff groups attached to it(the c ...
Chapter 17 Allylic and Benzylic Reactivity
... substituents outweigh their resonance effects. Consequently, compound (3) reacts more slowly. The nitro group exerts no resonance effect in the carbocation intermediates derived from compounds (1) and (4); the question is then whether its polar effect is stronger from the meta or para position. As i ...
... substituents outweigh their resonance effects. Consequently, compound (3) reacts more slowly. The nitro group exerts no resonance effect in the carbocation intermediates derived from compounds (1) and (4); the question is then whether its polar effect is stronger from the meta or para position. As i ...
Organic Chemistry
... Formula: each carbon is written separately followed by atoms bonded to it. ...
... Formula: each carbon is written separately followed by atoms bonded to it. ...
Degradation pattern of illicit drugs in soil
... clandestine laboratories from commonly available chemicals (Sasaki and Makino 2006). Methamphetamine manufacture is typically located throughout East and South-East Asia, North America and Oceania due to easy availability of precursors and high demand (UNODC 2008a). In Australia, the ATS market is s ...
... clandestine laboratories from commonly available chemicals (Sasaki and Makino 2006). Methamphetamine manufacture is typically located throughout East and South-East Asia, North America and Oceania due to easy availability of precursors and high demand (UNODC 2008a). In Australia, the ATS market is s ...
Role of Water as a Solvent
... Step 2) From the changes in oxidation numbers, identify the oxidized and reduced species. Step 3) Compute the number of electrons lost in the oxidation and gained in the reduction from the oxidation number changes. Draw tie-lines between these atoms to show electron changes. Step 4) Multiply one or ...
... Step 2) From the changes in oxidation numbers, identify the oxidized and reduced species. Step 3) Compute the number of electrons lost in the oxidation and gained in the reduction from the oxidation number changes. Draw tie-lines between these atoms to show electron changes. Step 4) Multiply one or ...
FahadH. Ahmad (Contact: +92 323 509 4443)
... carbon atoms because the intermolecular forces are much stronger. Carboxylic acids are weak acids, so they can donate a hydrogen ion(H+) in acidbase reactions: This means that they will react with carbonates to produce a salt, water and carbon dioxide: They will also react with reactive metals to pr ...
... carbon atoms because the intermolecular forces are much stronger. Carboxylic acids are weak acids, so they can donate a hydrogen ion(H+) in acidbase reactions: This means that they will react with carbonates to produce a salt, water and carbon dioxide: They will also react with reactive metals to pr ...
Document
... Nitro benzene is electron withdrawing group by both inductive effect and resonance effect. Hence it deactivates the benzene ring and it is meta directing group. ...
... Nitro benzene is electron withdrawing group by both inductive effect and resonance effect. Hence it deactivates the benzene ring and it is meta directing group. ...
Organosulfur compounds

Organosulfur compounds are organic compounds that contain sulfur. They are often associated with foul odors, but many of the sweetest compounds known are organosulfur derivatives, e.g., saccharin. Nature abounds with organosulfur compounds—sulfur is essential for life. Of the 20 common amino acids, two (cysteine and methionine) are organosulfur compounds, and the antibiotics penicillin (pictured below) and sulfa drugs both contain sulfur. While sulfur-containing antibiotics save many lives, sulfur mustard is a deadly chemical warfare agent. Fossil fuels, coal, petroleum, and natural gas, which are derived from ancient organisms, necessarily contain organosulfur compounds, the removal of which is a major focus of oil refineries.Sulfur shares the chalcogen group with oxygen, selenium and tellurium, and it is expected that organosulfur compounds have similarities with carbon–oxygen, carbon–selenium and carbon–tellurium compounds, which is true to some extent.A classical chemical test for the detection of sulfur compounds is the Carius halogen method.