Synthesis of Aliphatic Nitro Compounds1i2 A simple new
... 1,2-Dinitroolefins (I) possess a n unsaturated system which is particularly vulnerable t o nucleophilic attack. I n this respect they are similar to nitroaryl halides, 0-chlorovinyl ketones, and alkoxymethylenemalonic esters. It is not k n o m whether these reactions are concerted or involve an unst ...
... 1,2-Dinitroolefins (I) possess a n unsaturated system which is particularly vulnerable t o nucleophilic attack. I n this respect they are similar to nitroaryl halides, 0-chlorovinyl ketones, and alkoxymethylenemalonic esters. It is not k n o m whether these reactions are concerted or involve an unst ...
Molecules with Nitrogen and Their Reactions
... Condensation reactions involve the joining of two small molecules to form one larger molecule with the loss of a small molecule (such as water). ...
... Condensation reactions involve the joining of two small molecules to form one larger molecule with the loss of a small molecule (such as water). ...
No Slide Title
... Lattice energy (U) (LE) of an ionic compound is the energy required to break apart the ions in their lattice arrangement into the ions in the gas phase. For example the energy to take NaCl from its lattice arrangement into the gas phase ions would be represented by NaCl(s) ---> Na+(g) + Cl-(g) ...
... Lattice energy (U) (LE) of an ionic compound is the energy required to break apart the ions in their lattice arrangement into the ions in the gas phase. For example the energy to take NaCl from its lattice arrangement into the gas phase ions would be represented by NaCl(s) ---> Na+(g) + Cl-(g) ...
Substituted Hydrocarbons and Their Reactions
... atom or group of atoms that always reacts in a certain way. The addition of a functional group to a hydrocarbon structure always produces a substance with physical and chemical properties that differ from those of the parent hydrocarbon. All the items—natural and synthetic—in Figure 1 contain functi ...
... atom or group of atoms that always reacts in a certain way. The addition of a functional group to a hydrocarbon structure always produces a substance with physical and chemical properties that differ from those of the parent hydrocarbon. All the items—natural and synthetic—in Figure 1 contain functi ...
Print out Reviews # 1 through # 17
... H2O (l) + energy H2O (g) 5. Is this reaction exothermic or endothermic? 6. Is the value of H for this reaction positive or negative? 7. Is the value of S for this reaction positive or negative? 8. This reaction is ( sometimes / always / never ) spontaneous. EOC REVIEW #16 1. If you start with 75 ...
... H2O (l) + energy H2O (g) 5. Is this reaction exothermic or endothermic? 6. Is the value of H for this reaction positive or negative? 7. Is the value of S for this reaction positive or negative? 8. This reaction is ( sometimes / always / never ) spontaneous. EOC REVIEW #16 1. If you start with 75 ...
EXPERIMENT 6: Reactions of Carbonyl Compounds: Qualitative
... cleavage that produce the haloform and the corresponding carboxylic acid. This is due to the weakened bond that only results when three halogens are attached to the carbon (making it a sufficient leaving group). Methyl secondary alcohols (-CHOHCH3) are also easily oxidized to their respective carbon ...
... cleavage that produce the haloform and the corresponding carboxylic acid. This is due to the weakened bond that only results when three halogens are attached to the carbon (making it a sufficient leaving group). Methyl secondary alcohols (-CHOHCH3) are also easily oxidized to their respective carbon ...
Organometallic Compounds: Alkyllithium Reagent
... not possible to prepare a Grignard reagent from an organic group that contains an acidic hydrogen (any hydrogen more acidic than the hydrogen atoms of an alkane or alkene). ...
... not possible to prepare a Grignard reagent from an organic group that contains an acidic hydrogen (any hydrogen more acidic than the hydrogen atoms of an alkane or alkene). ...
Handout 7
... In conclusion, all steps included in the conversion of an aldehyde or ketone to acetal or ketal via hemiacetal or hemiketal as intermediates, are reversible. Performing the reaction in large excess of an anhydrous alcohol and a small amount of an anhydrous acid will strongly favour the formation of ...
... In conclusion, all steps included in the conversion of an aldehyde or ketone to acetal or ketal via hemiacetal or hemiketal as intermediates, are reversible. Performing the reaction in large excess of an anhydrous alcohol and a small amount of an anhydrous acid will strongly favour the formation of ...
Document
... • In order for ethers to undergo substitution or elimination reactions, their poor leaving group must first be converted into a good leaving group by reaction with strong acids such as HBr and HI. HBr and HI are strong acids that are also sources of good nucleophiles (Br¯ and I¯ respectively). • Whe ...
... • In order for ethers to undergo substitution or elimination reactions, their poor leaving group must first be converted into a good leaving group by reaction with strong acids such as HBr and HI. HBr and HI are strong acids that are also sources of good nucleophiles (Br¯ and I¯ respectively). • Whe ...
CHEMISTRY 101 Name Mock Final Exam Spring 2014 Signature Dr
... Ionization energies are generally endothermic. “Lower in energy” also means “more stable”. The ground state is the lowest energy state. In an exothermic chemical reaction, the products are more stable than the reactants. All of the above statements (a-d) are true. ...
... Ionization energies are generally endothermic. “Lower in energy” also means “more stable”. The ground state is the lowest energy state. In an exothermic chemical reaction, the products are more stable than the reactants. All of the above statements (a-d) are true. ...
ch15 by dr Dina
... Electrophilic aromatic substitution (SEAr) is an organic reaction in which an atom that is attached to an aromatic system (usually hydrogen) is replaced by an electrophile. For example, aromatic nitration, halogenation, sulfonation, acylation and Friedel–Crafts alkylation reactions ...
... Electrophilic aromatic substitution (SEAr) is an organic reaction in which an atom that is attached to an aromatic system (usually hydrogen) is replaced by an electrophile. For example, aromatic nitration, halogenation, sulfonation, acylation and Friedel–Crafts alkylation reactions ...
Carboxylic Acids Theory Sheet
... Carboxylic acids are compounds with the formula of that illustrated in Figure 1 and the general formula R-COOH where R is part of a larger organic molecule e.g.CH3, C2H5, C6H5. To name carboxylic acids you must look at the alkyl chain, take its prefix and add “oic acid” to it. CH3CH2COOH is PROPANOI ...
... Carboxylic acids are compounds with the formula of that illustrated in Figure 1 and the general formula R-COOH where R is part of a larger organic molecule e.g.CH3, C2H5, C6H5. To name carboxylic acids you must look at the alkyl chain, take its prefix and add “oic acid” to it. CH3CH2COOH is PROPANOI ...
Chapter 7: Chemical Formulas and Chemical Compounds
... For example, the ions Na+, Ca2+, and Clhave oxidation numbers of +1, +2, and -1, ...
... For example, the ions Na+, Ca2+, and Clhave oxidation numbers of +1, +2, and -1, ...
Document
... • Oxidation/Reduction Reactions: Review (Section 12.2) • Reduction of Carbonyls to Alcohols (Section 12.3) • Oxidation of Alcohols (Section 12.4) • Organometallic Compounds (Section 12.5) • Organolithium and Magnesium Compounds (Section 12.6) • Reactions of Organolithium/Magnesium Species (Section 1 ...
... • Oxidation/Reduction Reactions: Review (Section 12.2) • Reduction of Carbonyls to Alcohols (Section 12.3) • Oxidation of Alcohols (Section 12.4) • Organometallic Compounds (Section 12.5) • Organolithium and Magnesium Compounds (Section 12.6) • Reactions of Organolithium/Magnesium Species (Section 1 ...
aq - Wikispaces
... If there is NO decimal, the situation is ambiguous, and a bit of a JUDGEMENT CALL. If you trust the source to be precise, then you count all the zeros at the end. If you have reason to believe the person was estimating, then you don’t count the zeros at the end. ...
... If there is NO decimal, the situation is ambiguous, and a bit of a JUDGEMENT CALL. If you trust the source to be precise, then you count all the zeros at the end. If you have reason to believe the person was estimating, then you don’t count the zeros at the end. ...
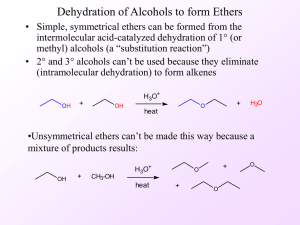
12.1 Alcohols: Structure and Physical Properties
... • Some alcohol dehydration reactions produce a mixture of products • Zaitsev’s rule states that in an elimination reaction the alkene with the greatest number of alkyl groups on the double bonded carbon is the major product of the reaction ...
... • Some alcohol dehydration reactions produce a mixture of products • Zaitsev’s rule states that in an elimination reaction the alkene with the greatest number of alkyl groups on the double bonded carbon is the major product of the reaction ...
Chemistry - Onslow College
... From their previous studies in science, students should have an understanding of Writing formula of ionic substances and simple covalent compounds Writing word equations and balanced chemical equations for inorganic reactions By the end of this topic students will be able to 1. use solubility ru ...
... From their previous studies in science, students should have an understanding of Writing formula of ionic substances and simple covalent compounds Writing word equations and balanced chemical equations for inorganic reactions By the end of this topic students will be able to 1. use solubility ru ...
102 Lecture Ch14b
... • Oxidation can also be defined as a loss of bonds to hydrogen • This is because H is less electronegative than all other nonmetals (besides P which is the same), so adds electron density to any element with which it forms a covalent bond • Thiols can be oxidized to disulfides using I2 (or Br2) • In ...
... • Oxidation can also be defined as a loss of bonds to hydrogen • This is because H is less electronegative than all other nonmetals (besides P which is the same), so adds electron density to any element with which it forms a covalent bond • Thiols can be oxidized to disulfides using I2 (or Br2) • In ...
Sodium is an abundant metallic element with atomic number as 11
... -Sodium hardly reacts with carbon, but it does react with halogens. It also reacts with various metallic halides to form the metal and sodium chloride. -Sodium doesn’t react with paraffinic hydrocarbons, but it forms addition compounds with naphthalene and other aromatic polycyclic compounds and wit ...
... -Sodium hardly reacts with carbon, but it does react with halogens. It also reacts with various metallic halides to form the metal and sodium chloride. -Sodium doesn’t react with paraffinic hydrocarbons, but it forms addition compounds with naphthalene and other aromatic polycyclic compounds and wit ...
Abstract OXIDATIVE TRANSFORMATIONS AND CYCLIZATIONS
... enantioselectivity. Section II. One-pot synthesis of 2-Substituted Quinazolines and Oxazines via Oxidative Dehydrogenation using NaOCl Quinazolines are important class of compounds frequently found in alkaloids and in many bioactive compounds. Quinazoline ring structure is an essential component in ...
... enantioselectivity. Section II. One-pot synthesis of 2-Substituted Quinazolines and Oxazines via Oxidative Dehydrogenation using NaOCl Quinazolines are important class of compounds frequently found in alkaloids and in many bioactive compounds. Quinazoline ring structure is an essential component in ...
Organosulfur compounds

Organosulfur compounds are organic compounds that contain sulfur. They are often associated with foul odors, but many of the sweetest compounds known are organosulfur derivatives, e.g., saccharin. Nature abounds with organosulfur compounds—sulfur is essential for life. Of the 20 common amino acids, two (cysteine and methionine) are organosulfur compounds, and the antibiotics penicillin (pictured below) and sulfa drugs both contain sulfur. While sulfur-containing antibiotics save many lives, sulfur mustard is a deadly chemical warfare agent. Fossil fuels, coal, petroleum, and natural gas, which are derived from ancient organisms, necessarily contain organosulfur compounds, the removal of which is a major focus of oil refineries.Sulfur shares the chalcogen group with oxygen, selenium and tellurium, and it is expected that organosulfur compounds have similarities with carbon–oxygen, carbon–selenium and carbon–tellurium compounds, which is true to some extent.A classical chemical test for the detection of sulfur compounds is the Carius halogen method.