Mass Spec - Fragmentation
... - Remember that for a ring system, at least 2 bonds must break for the ring to fragment. In addition, there are 10 general rules to keep in mind when predicting the most likely ions to be formed for a given ...
... - Remember that for a ring system, at least 2 bonds must break for the ring to fragment. In addition, there are 10 general rules to keep in mind when predicting the most likely ions to be formed for a given ...
Organic Chem Class #2
... 28. ALKANES: hydrocarbons with only single C-C bonding. Only contain carbon and hydrogen atoms. Chains of 1 to 10 labeled with prefixes in table P. All end in –ane. 29. AKLENES: hydrocarbons with only one double C=C bond. Only contain carbon and hydrogen atoms. Chains of 1 to 10 labeled with prefix ...
... 28. ALKANES: hydrocarbons with only single C-C bonding. Only contain carbon and hydrogen atoms. Chains of 1 to 10 labeled with prefixes in table P. All end in –ane. 29. AKLENES: hydrocarbons with only one double C=C bond. Only contain carbon and hydrogen atoms. Chains of 1 to 10 labeled with prefix ...
Two-coordinate group 14 element(ii) hydrides as
... this might be possible came with the kinetic stabilisation of group 14 element(II) hydride complexes, a small number of which (e.g. I–V, Scheme 1)8–11 have been reported since the turn of the millennium.12 Of these, the three-coordinate silicon(II) hydride, I, has been shown to hydrosilylate cyclope ...
... this might be possible came with the kinetic stabilisation of group 14 element(II) hydride complexes, a small number of which (e.g. I–V, Scheme 1)8–11 have been reported since the turn of the millennium.12 Of these, the three-coordinate silicon(II) hydride, I, has been shown to hydrosilylate cyclope ...
Reacciones redox
... contain polar metal–hydrogen bonds that place a partial negative charge on hydrogen. ...
... contain polar metal–hydrogen bonds that place a partial negative charge on hydrogen. ...
Naming organic compounds
... functional group is the parent molecule or simply the longest unbranched chain for alkanes. Remember that the longest chain can go round a bend. Indicate the position of the functional group with a number, numbering from the end nearest the functional group. Name the branches and indicate the number ...
... functional group is the parent molecule or simply the longest unbranched chain for alkanes. Remember that the longest chain can go round a bend. Indicate the position of the functional group with a number, numbering from the end nearest the functional group. Name the branches and indicate the number ...
Notetakers
... Although ethanol can be made from the fermentation of starch and sugars, much industrial ethanol is formed from the addition of steam to ethene. Hydrogenation The addition of hydrogen to unsaturated vegetable oils is used industrially to make margarine. Hydrogenation reduces the number of doub ...
... Although ethanol can be made from the fermentation of starch and sugars, much industrial ethanol is formed from the addition of steam to ethene. Hydrogenation The addition of hydrogen to unsaturated vegetable oils is used industrially to make margarine. Hydrogenation reduces the number of doub ...
Nomenclature of Organic Compounds
... Organic chemistry is the chemistry of carbon compounds. Carbon has the ability to bond with itself to form long chains and, as a result, millions of compounds from simple hydrocarbons to large biomolecules such as proteins, lipids, carbohydrates, and nucleic acids. Originally it was believed that th ...
... Organic chemistry is the chemistry of carbon compounds. Carbon has the ability to bond with itself to form long chains and, as a result, millions of compounds from simple hydrocarbons to large biomolecules such as proteins, lipids, carbohydrates, and nucleic acids. Originally it was believed that th ...
Sample Exercise 2.1 Illustrating the Size of an Atom
... the acid is given a hydro- prefix and an -ic ending: hydrocyanic acid. Only water solutions of HCN are referred to as hydrocyanic acid: The pure compound, which is a gas under normal conditions, is called hydrogen cyanide. Both hydrocyanic acid and hydrogen cyanide are extremely toxic. (b) Because i ...
... the acid is given a hydro- prefix and an -ic ending: hydrocyanic acid. Only water solutions of HCN are referred to as hydrocyanic acid: The pure compound, which is a gas under normal conditions, is called hydrogen cyanide. Both hydrocyanic acid and hydrogen cyanide are extremely toxic. (b) Because i ...
Ch 2 Sample Exercises PPT
... the acid is given a hydro- prefix and an -ic ending: hydrocyanic acid. Only water solutions of HCN are referred to as hydrocyanic acid: The pure compound, which is a gas under normal conditions, is called hydrogen cyanide. Both hydrocyanic acid and hydrogen cyanide are extremely toxic. (b) Because i ...
... the acid is given a hydro- prefix and an -ic ending: hydrocyanic acid. Only water solutions of HCN are referred to as hydrocyanic acid: The pure compound, which is a gas under normal conditions, is called hydrogen cyanide. Both hydrocyanic acid and hydrogen cyanide are extremely toxic. (b) Because i ...
Chapter 17 Aldehydes and Ketones
... • As with any other equilibrium, we can drive it in either direction by using Le Chatelier's principle. • To drive it to the right, we either use a large excess of alcohol or remove water from the equilibrium mixture ...
... • As with any other equilibrium, we can drive it in either direction by using Le Chatelier's principle. • To drive it to the right, we either use a large excess of alcohol or remove water from the equilibrium mixture ...
Nuggets of Knowledge for Chapter 14 – Ethers
... extractions. Because of its flammability, it is also used as a starter fluid for gasoline and diesel engines. It was the first compound used as a general anesthetic, but has now been replaced by safer compounds like halothane. o Another common ether is methyl tert-butyl ether, usually called MTBE. I ...
... extractions. Because of its flammability, it is also used as a starter fluid for gasoline and diesel engines. It was the first compound used as a general anesthetic, but has now been replaced by safer compounds like halothane. o Another common ether is methyl tert-butyl ether, usually called MTBE. I ...
alcohols and oxidation products
... Deduce the empirical formula of methyl 2-hydroxy benzoate and draw the full structural formula, including any multiple bonds that may be present. The computer-generated representation shown does not distinguish between single and multiple bonds. ...
... Deduce the empirical formula of methyl 2-hydroxy benzoate and draw the full structural formula, including any multiple bonds that may be present. The computer-generated representation shown does not distinguish between single and multiple bonds. ...
Chapter 7
... Organic Compounds • Organic compounds are named using a different set of rules. • The simplest group is the hydrocarbons. These compounds are composed solely of the elements carbon and hydrogen. • Carbon atoms can link to each other in chains and in rings. ...
... Organic Compounds • Organic compounds are named using a different set of rules. • The simplest group is the hydrocarbons. These compounds are composed solely of the elements carbon and hydrogen. • Carbon atoms can link to each other in chains and in rings. ...
Chapter 14 Selenium reagents
... base, giving alkyl bromides: the overall reaction is ROH RBr with retention of configuration. • Aryl alkyl selenides are preparable either (as above) from electrophilic selenium reagents and carbon ncleophiles or from nucleophilic selenium reagents, e.g. ArSe-Na+, and carbon electrophiles. On oxidat ...
... base, giving alkyl bromides: the overall reaction is ROH RBr with retention of configuration. • Aryl alkyl selenides are preparable either (as above) from electrophilic selenium reagents and carbon ncleophiles or from nucleophilic selenium reagents, e.g. ArSe-Na+, and carbon electrophiles. On oxidat ...
Kekulé structure of benzene
... There are many different types of isomers, including those in which the molecules have different functional groups. Different functional groups different classes, different reactivities. E.g. C2H6O describes both an alcohol and ether ...
... There are many different types of isomers, including those in which the molecules have different functional groups. Different functional groups different classes, different reactivities. E.g. C2H6O describes both an alcohol and ether ...
Naming the Carboxylic Acids
... The carboxy group is polar and forms hydrogen-bonded dimers. The carboxy function is strongly polar and forms hydrogen bonds to other polarized molecules such as water, alcohols and other carboxylic acids. Carboxylic acids up to butanoic acid are completely soluble in water. As neat liquids, and ev ...
... The carboxy group is polar and forms hydrogen-bonded dimers. The carboxy function is strongly polar and forms hydrogen bonds to other polarized molecules such as water, alcohols and other carboxylic acids. Carboxylic acids up to butanoic acid are completely soluble in water. As neat liquids, and ev ...
Chapter 4 Student Notes
... The other product, H2O, is a common weak electrolyte. A typical example of a neutralization reaction is the reaction between an acid and a metal hydroxide: o Mg(OH)2 (milk of magnesia) is a suspension. o As HCl is added, the magnesium hydroxide dissolves, and a clear solution containing Mg 2+ and Cl ...
... The other product, H2O, is a common weak electrolyte. A typical example of a neutralization reaction is the reaction between an acid and a metal hydroxide: o Mg(OH)2 (milk of magnesia) is a suspension. o As HCl is added, the magnesium hydroxide dissolves, and a clear solution containing Mg 2+ and Cl ...
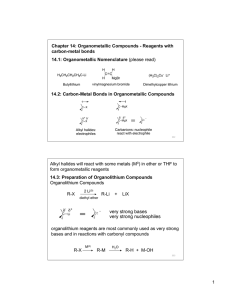
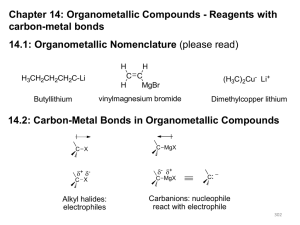
Lecture1
... Using metals, you can make complicated organic structures that would be hard to make otherwise. This is because, compared to "standard organic chemistry", metals display new and unusual reaction types. ...
... Using metals, you can make complicated organic structures that would be hard to make otherwise. This is because, compared to "standard organic chemistry", metals display new and unusual reaction types. ...
Final Review 2006
... a. negatively charged group of atoms held together by covalent bonds. b. positively charged group of atoms held together by covalent bonds. c. neutral group of atoms held together by covalent bonds. d. neutral group of atoms held together by ionic bonds. ____ 76. What principle states that atoms ten ...
... a. negatively charged group of atoms held together by covalent bonds. b. positively charged group of atoms held together by covalent bonds. c. neutral group of atoms held together by covalent bonds. d. neutral group of atoms held together by ionic bonds. ____ 76. What principle states that atoms ten ...
Chapter 4- Carbon and the Molecular Diversity of
... who had studied with Berzelius, attempted to make an "inorganic" salt, ammonium cyanate, by mixing solutions of ammonium ions (NH4 +)and cyanate ions (CNO - ). Wohler was astonished to find that instead he had made urea, an organic compound present in the urine of animals. Wohler challenged the vita ...
... who had studied with Berzelius, attempted to make an "inorganic" salt, ammonium cyanate, by mixing solutions of ammonium ions (NH4 +)and cyanate ions (CNO - ). Wohler was astonished to find that instead he had made urea, an organic compound present in the urine of animals. Wohler challenged the vita ...
Reporting Category 3: Bonding and Chemical Reactions
... How to construct electron dot formulas: Different kinds of bonds often form between different atoms. A simple way to show how electrons are transferred or shared during bond formation is with an electron dot formula. Learning how to draw and interpret these diagrams is an important skill. An electro ...
... How to construct electron dot formulas: Different kinds of bonds often form between different atoms. A simple way to show how electrons are transferred or shared during bond formation is with an electron dot formula. Learning how to draw and interpret these diagrams is an important skill. An electro ...
Molecular Orbitals - Calderglen High School
... This is not always the case. When there is a large difference between the electronegativities of the two elements involved in the bond, the bonding molecular orbital will be asymmetrical. Water molecules contain highly electronegative oxygen atoms. Because oxygen has a greater attraction for the bon ...
... This is not always the case. When there is a large difference between the electronegativities of the two elements involved in the bond, the bonding molecular orbital will be asymmetrical. Water molecules contain highly electronegative oxygen atoms. Because oxygen has a greater attraction for the bon ...
Long-Range Coupling
... Aromatics: Long-Range Coupling H’s on aromatic rings may couple with non-neighboring protons due to long-range coupling. You will see this in lab! Why? Nuclei “communicate” via bonding electrons - p electrons that are in resonance will allow non-neighboring H’s to “communicate” and couple/split. Thi ...
... Aromatics: Long-Range Coupling H’s on aromatic rings may couple with non-neighboring protons due to long-range coupling. You will see this in lab! Why? Nuclei “communicate” via bonding electrons - p electrons that are in resonance will allow non-neighboring H’s to “communicate” and couple/split. Thi ...
Organosulfur compounds

Organosulfur compounds are organic compounds that contain sulfur. They are often associated with foul odors, but many of the sweetest compounds known are organosulfur derivatives, e.g., saccharin. Nature abounds with organosulfur compounds—sulfur is essential for life. Of the 20 common amino acids, two (cysteine and methionine) are organosulfur compounds, and the antibiotics penicillin (pictured below) and sulfa drugs both contain sulfur. While sulfur-containing antibiotics save many lives, sulfur mustard is a deadly chemical warfare agent. Fossil fuels, coal, petroleum, and natural gas, which are derived from ancient organisms, necessarily contain organosulfur compounds, the removal of which is a major focus of oil refineries.Sulfur shares the chalcogen group with oxygen, selenium and tellurium, and it is expected that organosulfur compounds have similarities with carbon–oxygen, carbon–selenium and carbon–tellurium compounds, which is true to some extent.A classical chemical test for the detection of sulfur compounds is the Carius halogen method.