Pre-test on THE UNIVERSE, GALAXIES, AND STARS
... hotter with time. b) The universe started out very dense and has become less dense with time. c) The universe is the same age as the Earth. ...
... hotter with time. b) The universe started out very dense and has become less dense with time. c) The universe is the same age as the Earth. ...
chapter23 - Empyrean Quest Publishers
... Expansion of universe has redshifted thermal radiation from that time to ~1000 times longer wavelength: microwaves ...
... Expansion of universe has redshifted thermal radiation from that time to ~1000 times longer wavelength: microwaves ...
Nineteenth lecture
... The nebulae gradually collapse and commonly start rotating, to form galaxies, like the Andromeda Galaxy, pictured here. (Note the other galaxies also in the picture!) ...
... The nebulae gradually collapse and commonly start rotating, to form galaxies, like the Andromeda Galaxy, pictured here. (Note the other galaxies also in the picture!) ...
ASTR100 Class 01 - University of Maryland Department of
... = total number of habitable planets in galaxy; = fraction of habitable planets with life; = fraction of life-bearing planets with civilization at some time; = fraction of civilizations around now. ...
... = total number of habitable planets in galaxy; = fraction of habitable planets with life; = fraction of life-bearing planets with civilization at some time; = fraction of civilizations around now. ...
The Merger of Two Disk Galaxies
... the material becomes part of the young Sun, but some debris forms a disk. Within this disk form the planets, moons, comets, asteroids, and meteoroids. Note that this process is repeated on a smaller scale in the ...
... the material becomes part of the young Sun, but some debris forms a disk. Within this disk form the planets, moons, comets, asteroids, and meteoroids. Note that this process is repeated on a smaller scale in the ...
CDFS Lecture
... Two nuclei of Deuterium fuse to form a Helium nucleus. Mass is lost and energy released, according to E = mc2 ...
... Two nuclei of Deuterium fuse to form a Helium nucleus. Mass is lost and energy released, according to E = mc2 ...
The Big Bang
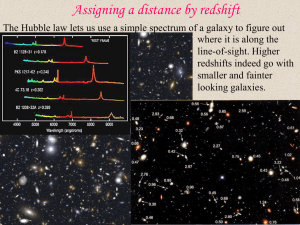
... away from the earth appears to be shifted toward the red end. • This is called the red shift. • The more the spectrum of light is shifted toward the blue or red end of the spectrum, the faster the star is moving toward or away from the earth. ...
... away from the earth appears to be shifted toward the red end. • This is called the red shift. • The more the spectrum of light is shifted toward the blue or red end of the spectrum, the faster the star is moving toward or away from the earth. ...
The Modern Origins Story: From the Big Bang to Habitable Planets
... Requires that most of Mass/Energy in universe is some weird “dark energy” we don’t understand ...
... Requires that most of Mass/Energy in universe is some weird “dark energy” we don’t understand ...
Where is the rest of the universe?
... Where is the rest of the Universe? If we can only “see” 4.9% of the universe, where is the other 95%? Dark matter Dark matter does not give off observable energy in any EM wavelength, but can be detected by watching the behavior of space objects. A few examples are: • The stars in the outer reaches ...
... Where is the rest of the Universe? If we can only “see” 4.9% of the universe, where is the other 95%? Dark matter Dark matter does not give off observable energy in any EM wavelength, but can be detected by watching the behavior of space objects. A few examples are: • The stars in the outer reaches ...
Light Years and Our Universe
... After the Big Bang the universe has continued to expand and as matter cooled more atoms developed as did galaxies and stars ...
... After the Big Bang the universe has continued to expand and as matter cooled more atoms developed as did galaxies and stars ...
Redshift takes us from 2-D to 3-D
... But then the past shouldn’t look different than the present (on average) 3) The Universe was hot and opaque in the distant past. This is proven by the thermal cosmic background radiation. Only if all space were opaque would all space be filled with thermal photons (and their current temperature is r ...
... But then the past shouldn’t look different than the present (on average) 3) The Universe was hot and opaque in the distant past. This is proven by the thermal cosmic background radiation. Only if all space were opaque would all space be filled with thermal photons (and their current temperature is r ...
Key Areas covered
... The Big Bang Theory took place around 13.8 billion years ago. The universe was originally very hot and very dense concentrated in a tiny point known as a singularity (smaller than an atom). It caused our universe to expand suddenly from the singularity bringing time and space into existence. Followi ...
... The Big Bang Theory took place around 13.8 billion years ago. The universe was originally very hot and very dense concentrated in a tiny point known as a singularity (smaller than an atom). It caused our universe to expand suddenly from the singularity bringing time and space into existence. Followi ...
Key Areas covered
... The Big Bang Theory took place around 13.8 billion years ago. The universe was originally very hot and very dense concentrated in a tiny point known as a singularity (smaller than an atom). It caused our universe to expand suddenly from the singularity bringing time and space into existence. Followi ...
... The Big Bang Theory took place around 13.8 billion years ago. The universe was originally very hot and very dense concentrated in a tiny point known as a singularity (smaller than an atom). It caused our universe to expand suddenly from the singularity bringing time and space into existence. Followi ...
Astro 10: Introductory Astronomy
... Then galaxies and the supermassive black holes at their heart ...
... Then galaxies and the supermassive black holes at their heart ...
Document
... • Hubble: Universe is expanding • “Run movie backward” – at beginning • all matter within small region (single point) • very, very hot ...
... • Hubble: Universe is expanding • “Run movie backward” – at beginning • all matter within small region (single point) • very, very hot ...
Our Place in the Cosmos
... that some nebulae lie outside our Galaxy and that these objects are receding from us at a speed proportional to their distance, the Hubble expansion ...
... that some nebulae lie outside our Galaxy and that these objects are receding from us at a speed proportional to their distance, the Hubble expansion ...
Milky Way Galaxy
... • Theory that the universe began as a point and has been expanding ever since – Thought to have begun as an infinitesimally small, hot, and dense “singularity”. – About 14 (13.7) billion years ago ...
... • Theory that the universe began as a point and has been expanding ever since – Thought to have begun as an infinitesimally small, hot, and dense “singularity”. – About 14 (13.7) billion years ago ...
Our Picture of The Universe
... In 1609, Death blow to the old theory came as Galileo started observing the night sky with a telescope, he found that there are several moon that orbit around the ...
... In 1609, Death blow to the old theory came as Galileo started observing the night sky with a telescope, he found that there are several moon that orbit around the ...
Origins of the Universe - Fraser Heights Chess Club
... • Universe was actually expanding more slowly than it is today. So the expansion of the Universe has not been slowing due to gravity, as everyone thought, it has been accelerating. No one expected this, no one knew how to explain it. But something was causing it. ...
... • Universe was actually expanding more slowly than it is today. So the expansion of the Universe has not been slowing due to gravity, as everyone thought, it has been accelerating. No one expected this, no one knew how to explain it. But something was causing it. ...
DO NOT WRITE ON THIS PAPER Standard 1 Objective 1 Study
... 1. Light from stars support the Big Bang Theory because it shows that most objects in space are moving away from one another. 2. The spectrum of hydrogen on a distant star is red shifted. 3. Stars farthest from Earth with the greatest speed have the greatest red shift. 4. Scientists accept the Big B ...
... 1. Light from stars support the Big Bang Theory because it shows that most objects in space are moving away from one another. 2. The spectrum of hydrogen on a distant star is red shifted. 3. Stars farthest from Earth with the greatest speed have the greatest red shift. 4. Scientists accept the Big B ...
Galaxies and the Universe
... • Speed of Light is Independent of Source • Michelson and Morley, 1887 - Speed of Light Independent of Observer • “One of the Most Unexpected Results in the History of Science” - Isaac Asimov • Conclusion: Speed of Light is the Same for All Observers • Implication: Space and Time Must Change to Keep ...
... • Speed of Light is Independent of Source • Michelson and Morley, 1887 - Speed of Light Independent of Observer • “One of the Most Unexpected Results in the History of Science” - Isaac Asimov • Conclusion: Speed of Light is the Same for All Observers • Implication: Space and Time Must Change to Keep ...
Big Bang

The Big Bang theory is the prevailing cosmological model for the universe from the earliest known periods through its subsequent large-scale evolution. The model accounts for the fact that the universe expanded from a very high density and high temperature state, and offers a comprehensive explanation for a broad range of observed phenomena, including the abundance of light elements, the cosmic microwave background, large scale structure, and Hubble's Law. If the known laws of physics are extrapolated beyond where they are valid, there is a singularity. Modern measurements place this moment at approximately 13.8 billion years ago, which is thus considered the age of the universe. After the initial expansion, the universe cooled sufficiently to allow the formation of subatomic particles, and later simple atoms. Giant clouds of these primordial elements later coalesced through gravity to form stars and galaxies.Since Georges Lemaître first noted, in 1927, that an expanding universe might be traced back in time to an originating single point, scientists have built on his idea of cosmic expansion. While the scientific community was once divided between supporters of two different expanding universe theories, the Big Bang and the Steady State theory, accumulated empirical evidence provides strong support for the former. In 1929, from analysis of galactic redshifts, Edwin Hubble concluded that galaxies are drifting apart, important observational evidence consistent with the hypothesis of an expanding universe. In 1965, the cosmic microwave background radiation was discovered, which was crucial evidence in favor of the Big Bang model, since that theory predicted the existence of background radiation throughout the universe before it was discovered. More recently, measurements of the redshifts of supernovae indicate that the expansion of the universe is accelerating, an observation attributed to dark energy's existence. The known physical laws of nature can be used to calculate the characteristics of the universe in detail back in time to an initial state of extreme density and temperature.