Classification of colorectal cancer based on correlation of clinical
... growth advantage. Invoking other components of the Wnt signalling pathway such as AXIN240 or TCF441 in the initiation of sporadic MSI-H neoplasia does not provide a surrogate directly equivalent to APC inactivation, since these genes are mutated at a relatively late stage (after the acquisition of M ...
... growth advantage. Invoking other components of the Wnt signalling pathway such as AXIN240 or TCF441 in the initiation of sporadic MSI-H neoplasia does not provide a surrogate directly equivalent to APC inactivation, since these genes are mutated at a relatively late stage (after the acquisition of M ...
draft nhmrc guidelines and discussion paper on xenotransplantation
... demonstrate that the dividing line between individual values and ecological values is no longer distinct. The Discussion Paper suggests it is acceptable to use animals for xenotransplantation so long as protocols are humane to animals and respect the essential characteristics and welfare of their sp ...
... demonstrate that the dividing line between individual values and ecological values is no longer distinct. The Discussion Paper suggests it is acceptable to use animals for xenotransplantation so long as protocols are humane to animals and respect the essential characteristics and welfare of their sp ...
Gene Section MLL (myeloid/lymphoid or
... t(X;11)(q13;q23)/ANLL, T-ALL --> MLL/AFX1 t(X;11)(q22;q23)/ANLL --> MLL/Septin2 t(1;11)(p32;q23)/ALL --> MLL/AF1p t(1;11)(q21;q23)/ANLL --> MLL/AF1q t(2;11)(q11;q23)/MDS --> MLL/LAF4 t(3;11)(p21;q23)/t-ANLL --> MLL/AF3p21 t(3;11)(q25;q23)/t-ANLL --> MLL/GMPS ins(5;11)(q31;q13q23)/ALL --> MLL/AF5q31 ...
... t(X;11)(q13;q23)/ANLL, T-ALL --> MLL/AFX1 t(X;11)(q22;q23)/ANLL --> MLL/Septin2 t(1;11)(p32;q23)/ALL --> MLL/AF1p t(1;11)(q21;q23)/ANLL --> MLL/AF1q t(2;11)(q11;q23)/MDS --> MLL/LAF4 t(3;11)(p21;q23)/t-ANLL --> MLL/AF3p21 t(3;11)(q25;q23)/t-ANLL --> MLL/GMPS ins(5;11)(q31;q13q23)/ALL --> MLL/AF5q31 ...
Chapter 03 Lecture Outline 3.1 Mendel`s Study of Pea Plants
... Copyright ©The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display Copyright © 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction or distribution without the prior written consent of McGraw-Hill Education. ...
... Copyright ©The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display Copyright © 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction or distribution without the prior written consent of McGraw-Hill Education. ...
UCSD_PevznerMolecula.. - Purdue University :: Computer Science
... • Phenotype: the physical expressed traits of an organism • Nucleic acid: Biological molecules(RNA and DNA) that allow organisms to reproduce; ...
... • Phenotype: the physical expressed traits of an organism • Nucleic acid: Biological molecules(RNA and DNA) that allow organisms to reproduce; ...
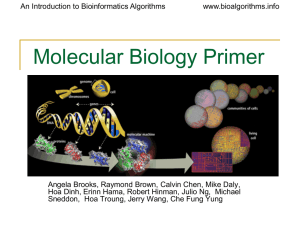
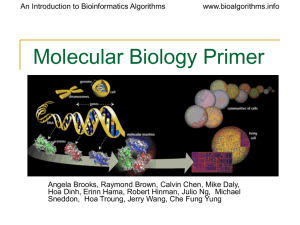
Primer on Molecular Biology
... • Phenotype: the physical expressed traits of an organism • Nucleic acid: Biological molecules(RNA and DNA) that allow organisms to reproduce; ...
... • Phenotype: the physical expressed traits of an organism • Nucleic acid: Biological molecules(RNA and DNA) that allow organisms to reproduce; ...
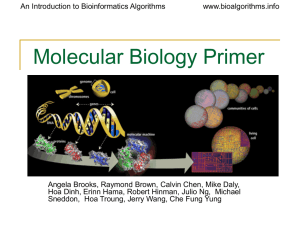
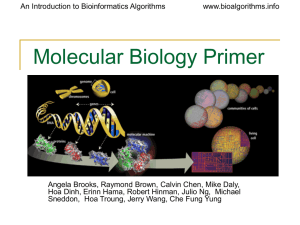
Primer on Molecular Biology
... • Phenotype: the physical expressed traits of an organism • Nucleic acid: Biological molecules(RNA and DNA) that allow organisms to reproduce; ...
... • Phenotype: the physical expressed traits of an organism • Nucleic acid: Biological molecules(RNA and DNA) that allow organisms to reproduce; ...
and GvpD-mediated transcription regulation of the p
... to study the formation of the preinitiation complex and the action of various transcription regulators (Hochheimer et al., 1999; Bell et al., 1999a; Brinkman et al., 2000; Enoru-Eta et al., 2000; Leonard et al., 2001; Ouhammouch et al., 2003). However, an in vitro transcription system is not availab ...
... to study the formation of the preinitiation complex and the action of various transcription regulators (Hochheimer et al., 1999; Bell et al., 1999a; Brinkman et al., 2000; Enoru-Eta et al., 2000; Leonard et al., 2001; Ouhammouch et al., 2003). However, an in vitro transcription system is not availab ...
DNA
... • Phenotype: the physical expressed traits of an organism • Nucleic acid: Biological molecules(RNA and DNA) that allow organisms to reproduce; ...
... • Phenotype: the physical expressed traits of an organism • Nucleic acid: Biological molecules(RNA and DNA) that allow organisms to reproduce; ...
Exp 1 Single Gene Inheritance
... governs wing shape in Drosophila melanogaster fruit flies. The gene is found on the second chromosome of our flies and normally results in the fly having a wild flat wing shape. However, a mutant allele has been found which causes the wing to become twisted and useless. This wing shape is called ves ...
... governs wing shape in Drosophila melanogaster fruit flies. The gene is found on the second chromosome of our flies and normally results in the fly having a wild flat wing shape. However, a mutant allele has been found which causes the wing to become twisted and useless. This wing shape is called ves ...
Clinical Features, and Nucleotide Changes in Three Families with
... muscle palsy was based on the presence of hypertropia (upward deviation of the eye) on the affected paralyzed side, which became greatest in the gaze toward the nasal field of the involved eye. The additional diagnostic feature was a positive Bielschowsky head tilt test, showing an upward deviation of ...
... muscle palsy was based on the presence of hypertropia (upward deviation of the eye) on the affected paralyzed side, which became greatest in the gaze toward the nasal field of the involved eye. The additional diagnostic feature was a positive Bielschowsky head tilt test, showing an upward deviation of ...
出國報告電子檔規格
... and aneuploidy are the hallmarks of neoplasia (19). Amplification is one of the mechanisms that leads to an increase in activity of oncogenes and development of drug resistance (20, 21), while allelic deletion results in inactivation of tumor suppressors. Identification and characterization of genes ...
... and aneuploidy are the hallmarks of neoplasia (19). Amplification is one of the mechanisms that leads to an increase in activity of oncogenes and development of drug resistance (20, 21), while allelic deletion results in inactivation of tumor suppressors. Identification and characterization of genes ...
MOLECULAR BIOLOGY OF FRUIT MATURATION AND
... A clarification of the common genetic regulatory elements that are shared among climacteric and non-climacteric species is central to a full understanding of fruit ripening. Such primary regulators of fruit maturation might be shared by, or at least related to, those that regulate maturation of dehi ...
... A clarification of the common genetic regulatory elements that are shared among climacteric and non-climacteric species is central to a full understanding of fruit ripening. Such primary regulators of fruit maturation might be shared by, or at least related to, those that regulate maturation of dehi ...
Identity-by-descent filtering of exome sequence data for disease
... However, existing tools for linkage analysis require pedigree data over at least two generations and are not optimized for the relatively high error rates of variant calls in NGS data. In this work, we describe a procedure for efficiently filtering exome sequencing data obtained from two or more aff ...
... However, existing tools for linkage analysis require pedigree data over at least two generations and are not optimized for the relatively high error rates of variant calls in NGS data. In this work, we describe a procedure for efficiently filtering exome sequencing data obtained from two or more aff ...
Supplemental Results Spatial dispersion often indicates
... significance: 13.5Å; P = 0.014, Mann–Whitney U test). These findings support previous conclusions that both gain- and loss-of-function variants are more clustered than neutral variants. The smaller clusters formed by dominant variants additionally support the hypothesis that gainof-function mutation ...
... significance: 13.5Å; P = 0.014, Mann–Whitney U test). These findings support previous conclusions that both gain- and loss-of-function variants are more clustered than neutral variants. The smaller clusters formed by dominant variants additionally support the hypothesis that gainof-function mutation ...
Anterior boundaries of Hox gene expression in mesoderm
... mesoderm, was the first indication that a murine homeobox gene may encode positional information along the rostralcaudal axis [9]. Transcripts of the Hox 1.5 gene are expressed in mesoderm and ectoderm of 7- to 9-day p.c. embryos, but are spatially restricted to the ectoderm-derived neural tube, mye ...
... mesoderm, was the first indication that a murine homeobox gene may encode positional information along the rostralcaudal axis [9]. Transcripts of the Hox 1.5 gene are expressed in mesoderm and ectoderm of 7- to 9-day p.c. embryos, but are spatially restricted to the ectoderm-derived neural tube, mye ...
NQO1 Pro187Ser polymorphism confers to the susceptibility of
... complex process and its exact mechanism has not yet been fully elucidated. Genetic variation, life style, and environmental factors are widely considered to be the most essential factors in carcinogenesis [3]. Therefore, screening feasible nucleotide and protein markers is of provital significance. ...
... complex process and its exact mechanism has not yet been fully elucidated. Genetic variation, life style, and environmental factors are widely considered to be the most essential factors in carcinogenesis [3]. Therefore, screening feasible nucleotide and protein markers is of provital significance. ...
Two-Component System of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis
... induced by DevRS, that are accompanied by growth arrest and a dormant drug-tolerant phenotype under in vitro and ex vivo conditions[15,16]. For example, It could up-regulate the expression of a 16 KDa α-crystallin homolog protein (Acr, HspX) [17], which is a small heat shock protein with a chaperoni ...
... induced by DevRS, that are accompanied by growth arrest and a dormant drug-tolerant phenotype under in vitro and ex vivo conditions[15,16]. For example, It could up-regulate the expression of a 16 KDa α-crystallin homolog protein (Acr, HspX) [17], which is a small heat shock protein with a chaperoni ...
cis-Regulatory Elements and trans-Acting Factors
... negative regulatory element could bind a specific nuclear protein, present in the submandibular gland, resulting in the inhibition of Reni expression in this tissue.4 Second, the high expression of submandibular Ren2 could be due to the nonfunctionality of the negative regulatory element.4 Recently, ...
... negative regulatory element could bind a specific nuclear protein, present in the submandibular gland, resulting in the inhibition of Reni expression in this tissue.4 Second, the high expression of submandibular Ren2 could be due to the nonfunctionality of the negative regulatory element.4 Recently, ...
DnaJ-related protein essential for placentation - Development
... showed no abnormal phenotypes in other trophoblast cell types or in the embryo proper. This study indicates a previously unsuspected role for chaperone proteins in placental development and represents the first genetic analysis of DnaJ-related protein function in higher eukaryotes. Based on a survey ...
... showed no abnormal phenotypes in other trophoblast cell types or in the embryo proper. This study indicates a previously unsuspected role for chaperone proteins in placental development and represents the first genetic analysis of DnaJ-related protein function in higher eukaryotes. Based on a survey ...
Clamp loader structure predicts the architecture of DNA polymerase
... Current Biology 2001, 11:R935–R946 ...
... Current Biology 2001, 11:R935–R946 ...
Are sperm-binding proteins among two closely related frog species
... binding and therefore, regulate the population of human and animals (Rankin and Dean et al, 2000). On a larger scale, infertility between individuals from separate populations would be the formation of new species (a group of organisms capable of interbreeding and producing fertile offspring) since ...
... binding and therefore, regulate the population of human and animals (Rankin and Dean et al, 2000). On a larger scale, infertility between individuals from separate populations would be the formation of new species (a group of organisms capable of interbreeding and producing fertile offspring) since ...
HEREDITARY ECTODERMAL DYSPLASIA
... In the first case, the proband was the only child of her parents. No similar case of ectodermal dysplasia has been identified among the relatives, which suggests that the propositus was probably a fresh mutation or due to translocation of genes while in the second case it was inherited from her moth ...
... In the first case, the proband was the only child of her parents. No similar case of ectodermal dysplasia has been identified among the relatives, which suggests that the propositus was probably a fresh mutation or due to translocation of genes while in the second case it was inherited from her moth ...
Expression of p53 Target Genes in the Early Phase of Long
... activation of p53 have? The control of the transcriptional activity of p53 is considered crucial for determining which p53 response is activated [5]. In this paper, we describe the expression of p53-related genes in the rat hippocampal CA1 area in the early phase of long-term potentiation (30 min af ...
... activation of p53 have? The control of the transcriptional activity of p53 is considered crucial for determining which p53 response is activated [5]. In this paper, we describe the expression of p53-related genes in the rat hippocampal CA1 area in the early phase of long-term potentiation (30 min af ...
Set - people.vcu.edu
... Anab7120:all0687 hupL [NiFe] uptake hydrogenase large subunit, C terminus Anab7120:all0687 hupL [NiFe] uptake hydrogenase large subunit, N terminus Anab7120:all0688 hupS [NiFe] uptake hydrogenase small subunit Anab7120:alr0692 ...
... Anab7120:all0687 hupL [NiFe] uptake hydrogenase large subunit, C terminus Anab7120:all0687 hupL [NiFe] uptake hydrogenase large subunit, N terminus Anab7120:all0688 hupS [NiFe] uptake hydrogenase small subunit Anab7120:alr0692 ...