Material
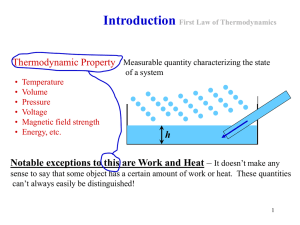
... defined by the thermodynamic state parameters. Thermodynamic state parameters are measurable macroscopic physical quantities of a system. Consider a gas in a cylinder. Measurable physical quantities are the pressure (P ), temperature (T ) and the volume (V ) of the gas. These physical quantities are ...
... defined by the thermodynamic state parameters. Thermodynamic state parameters are measurable macroscopic physical quantities of a system. Consider a gas in a cylinder. Measurable physical quantities are the pressure (P ), temperature (T ) and the volume (V ) of the gas. These physical quantities are ...
D12E12Safety1\4Curr\emet
... relationship between heat and mechanical energy or work, and the conversion of one form into the other FUNCTION: F1 – Marine Engineering at the operational level 7. COURSE OUTLINE: LEARNING OBJECTIVES/OUTCOMES: The students shall be able to . . . . . . 7.1 Thermodynamics Properties 7.1.1 describe th ...
... relationship between heat and mechanical energy or work, and the conversion of one form into the other FUNCTION: F1 – Marine Engineering at the operational level 7. COURSE OUTLINE: LEARNING OBJECTIVES/OUTCOMES: The students shall be able to . . . . . . 7.1 Thermodynamics Properties 7.1.1 describe th ...
transport processes and cross-coupling effects in non
... Multi-temperature approach is based on the assumption that some kinds of internal energy transitions proceed faster than others. For instance VV (vibration-vibration) transitions are much more probable than VT (vibration-translation) energy exchanges, which justifies such an assumption for the case ...
... Multi-temperature approach is based on the assumption that some kinds of internal energy transitions proceed faster than others. For instance VV (vibration-vibration) transitions are much more probable than VT (vibration-translation) energy exchanges, which justifies such an assumption for the case ...
ppt
... Where Q is the heat given to the system by the surroundings which are at a an infinitesimally higher temperature, T, than the system ...
... Where Q is the heat given to the system by the surroundings which are at a an infinitesimally higher temperature, T, than the system ...
Thermodynamics for Systems Biology
... moving (reversibly) from T1 to T2: the maximum work is the product of the entropy that moved and the temperature difference. To see this, consider a heat engine in which a working fluid picks up heat Q1 from system 1 at temperature T1 and deposits heat Q2 in system 2 at temperature T2. By the first ...
... moving (reversibly) from T1 to T2: the maximum work is the product of the entropy that moved and the temperature difference. To see this, consider a heat engine in which a working fluid picks up heat Q1 from system 1 at temperature T1 and deposits heat Q2 in system 2 at temperature T2. By the first ...
Thermodynamic Systems and State Functions
... define the state of the system and its eventual transformations, as conceptually depicted in Figure 3. ...
... define the state of the system and its eventual transformations, as conceptually depicted in Figure 3. ...
Chemical Thermodynamic
... substance is formed from its elements under given conditions of temperature and pressure. Amount of heat evolved or absorbed in a chemical equation which have completely reacted, is called heat of reaction. Q5. What do you understand by free energy and what is its physical significance? Ans5. It is ...
... substance is formed from its elements under given conditions of temperature and pressure. Amount of heat evolved or absorbed in a chemical equation which have completely reacted, is called heat of reaction. Q5. What do you understand by free energy and what is its physical significance? Ans5. It is ...
Example 1 First consider the case where there are no given
... The idea is that the function g should contain the same information as f . To get a feeling for this consider a function of one variable f (x) which is specified by the values over a set of points x. But we could also specify the function (up to some overall constant) by the values of the derivative ...
... The idea is that the function g should contain the same information as f . To get a feeling for this consider a function of one variable f (x) which is specified by the values over a set of points x. But we could also specify the function (up to some overall constant) by the values of the derivative ...
I Thermodynamics - Stanford University
... The field of thermodynamics began in the 19th Century as a means to enhance steam engine performance. It was soon determined that this study could be applied to a wider variety of systems. Today, thermodynamics is an important branch of physics relevant for not only engines but for material studies, ...
... The field of thermodynamics began in the 19th Century as a means to enhance steam engine performance. It was soon determined that this study could be applied to a wider variety of systems. Today, thermodynamics is an important branch of physics relevant for not only engines but for material studies, ...
Summary - Clarkson University
... "Thermodynamics is a funny subject. The first time you go through it, you don't understand it at all. The second time you go through it, you think you understand it, except for one or two small points. The third time you go through it, you know you don't understand it, but by then you are so used to ...
... "Thermodynamics is a funny subject. The first time you go through it, you don't understand it at all. The second time you go through it, you think you understand it, except for one or two small points. The third time you go through it, you know you don't understand it, but by then you are so used to ...
CHAPTER TWO The First Law and Other Basic Concepts
... contrast, mechanical work and heat are process quantities because their values depend on the specific transition (or path) between two equilibrium states. Path function: A thermodynamic quantity whose value depends on the path of the process through the equilibrium state space of a thermodynamic sys ...
... contrast, mechanical work and heat are process quantities because their values depend on the specific transition (or path) between two equilibrium states. Path function: A thermodynamic quantity whose value depends on the path of the process through the equilibrium state space of a thermodynamic sys ...
introduction
... is lower than its entropy when is released to open space. When in the balloon, the individual helium atoms are confined to the space within the balloon. When the gas is released the atoms rush out into a less ordered state. The Third law defines the zero of entropy for a system. ...
... is lower than its entropy when is released to open space. When in the balloon, the individual helium atoms are confined to the space within the balloon. When the gas is released the atoms rush out into a less ordered state. The Third law defines the zero of entropy for a system. ...
PY2P10: Thermodynamics Dr. Graham Cross www.tcd.ie/Physics/People/Graham.Cross
... • The temperature of a system is a physical property that determines whether or not that system will change when brought into thermal contact with other systems. • Ie. Any two systems in equilibrium with the same temperature will also have to be in thermal equilibrium with each other. ...
... • The temperature of a system is a physical property that determines whether or not that system will change when brought into thermal contact with other systems. • Ie. Any two systems in equilibrium with the same temperature will also have to be in thermal equilibrium with each other. ...
PS5, Thermo Thermodynamics Standards: 3. Energy cannot be
... a. Students know heat flow and work are two forms of energy transfer between systems. b. Students know that the work done by a heat engine that is working in a cycle is the difference between the heat flow into the engine at high temperature and the heat flow out at a lower temperature (first law of ...
... a. Students know heat flow and work are two forms of energy transfer between systems. b. Students know that the work done by a heat engine that is working in a cycle is the difference between the heat flow into the engine at high temperature and the heat flow out at a lower temperature (first law of ...
First law
... The entropy of an isolated system consisting of two regions of space, isolated from one another, each in thermodynamic equilibrium in itself, but not in equilibrium with each other, will, when the isolation that separates the two regions is broken, so that the two regions become able to exchange mat ...
... The entropy of an isolated system consisting of two regions of space, isolated from one another, each in thermodynamic equilibrium in itself, but not in equilibrium with each other, will, when the isolation that separates the two regions is broken, so that the two regions become able to exchange mat ...
about entropy in psoup
... symmetrical about the origin. What does equilibrium look like? A thermodynamic system in a state of equilibrium has a cloud of realvalued points, in the 3-D p-space, that is a hollow symmetrically formed sphere of radius ‘d’ centred at the origin, which can be derived from knowledge of the volume an ...
... symmetrical about the origin. What does equilibrium look like? A thermodynamic system in a state of equilibrium has a cloud of realvalued points, in the 3-D p-space, that is a hollow symmetrically formed sphere of radius ‘d’ centred at the origin, which can be derived from knowledge of the volume an ...
Tutorial 3 – Thermodynamics of Dielectric Relaxations in Complex
... microscopic polarizability and macroscopic permittivity. From the phenomenological point of view, it is necessary to know the kinetic of the Polarization. From molecular one it’s required the knowledge of the effective Electric field at which the dipole is subjected. 4 different ways are proposed to ...
... microscopic polarizability and macroscopic permittivity. From the phenomenological point of view, it is necessary to know the kinetic of the Polarization. From molecular one it’s required the knowledge of the effective Electric field at which the dipole is subjected. 4 different ways are proposed to ...
Lecture 4
... Let us define the entropy of the canonical ensemble with mean energy as being equal to the entropy of a
microcanonical ensemble with energy .
This corresponds to the thermodynamic situation because in
thermodynamics the entropy is fixed by the energy
independently of whether the system is iso ...
... Let us define the entropy of the canonical ensemble with mean energy
What is thermodynamics?
... Classical Thermodynamics (or what most people just call thermodynamics) is the theoretical framework via which we can understand and predict how materials will tend to change internally in response to forces of many types on a macroscopic level. ...
... Classical Thermodynamics (or what most people just call thermodynamics) is the theoretical framework via which we can understand and predict how materials will tend to change internally in response to forces of many types on a macroscopic level. ...