0.1 Minimum Principles and Thermodynamic Potentials
... The minimum principle for G then states that for all states at a fixed T and P , the equilibrium state is that for which G is a minimum. The proof is very similar to that for A: the second law states that ∆Q ≤ T ∆S or 0 ≥ T ∆S + ∆U + P ∆V , if P is held fixed. But dG = dU − T dS + P dV , so dG ≤ 0 i ...
... The minimum principle for G then states that for all states at a fixed T and P , the equilibrium state is that for which G is a minimum. The proof is very similar to that for A: the second law states that ∆Q ≤ T ∆S or 0 ≥ T ∆S + ∆U + P ∆V , if P is held fixed. But dG = dU − T dS + P dV , so dG ≤ 0 i ...
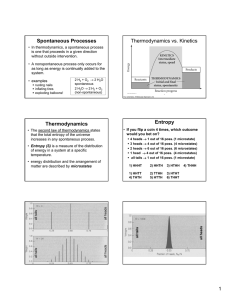
Spontaneous Processes Thermodynamics vs. Kinetics
... • This equation indicates that entropy increases as the number microstates increases. • This is entropy on the microscopic scale ...
... • This equation indicates that entropy increases as the number microstates increases. • This is entropy on the microscopic scale ...
CARNOT CYCLE i) substance starts at with temperature T2
... 1. There exists a STATE VARIABLE for any substance called the ENTROPY. 2. Entropy (S) may change by one of two ways; the substance may contact a thermal reservoir (heat source), or S may change due to “internal” changes in the substance. dse (externally-forced changes in S) dsi (internally-forced ...
... 1. There exists a STATE VARIABLE for any substance called the ENTROPY. 2. Entropy (S) may change by one of two ways; the substance may contact a thermal reservoir (heat source), or S may change due to “internal” changes in the substance. dse (externally-forced changes in S) dsi (internally-forced ...
Classical thermodynamics of particles in harmonic traps
... The form of the first law in Eq. 共4兲 runs counter to the intuition that we develop in studying ideal gases in rigid containers. It might seem more natural to express the term describing mechanical work as −b⌬A instead of A⌬b. The former would make the coefficient of the differential element an inten ...
... The form of the first law in Eq. 共4兲 runs counter to the intuition that we develop in studying ideal gases in rigid containers. It might seem more natural to express the term describing mechanical work as −b⌬A instead of A⌬b. The former would make the coefficient of the differential element an inten ...
06. Theoretic bases of bioenergetics
... system, which is described in terms of certain observable (measurable) properties such as temperature (Т), pressure (P), volume (V) etc. of the system. • If any of these properties of the system changes, the system is said to be in different state i.е. the state of the system changes. That is why th ...
... system, which is described in terms of certain observable (measurable) properties such as temperature (Т), pressure (P), volume (V) etc. of the system. • If any of these properties of the system changes, the system is said to be in different state i.е. the state of the system changes. That is why th ...
Thermodynamics: Lecture 2
... Equation of State As you can see, we may have too many state variables. One of the ways we can eliminate the redundant variables is through equation of state. Simply stated equation of state represents a relationship between state variables. For example, if our system is made up of ideal gas then w ...
... Equation of State As you can see, we may have too many state variables. One of the ways we can eliminate the redundant variables is through equation of state. Simply stated equation of state represents a relationship between state variables. For example, if our system is made up of ideal gas then w ...
Biological Thermodynamics
... Thermodynamics is fundamental to the development and applications of biophysical methods! ...
... Thermodynamics is fundamental to the development and applications of biophysical methods! ...
thermodynamics - La Salle High School
... where Stot is the total entropy of the isolated system ...
... where Stot is the total entropy of the isolated system ...
States of matter - Tennessee State University
... internal energy in common processes • adiabatic process - no heat is transferred U = W (dU = -dW) • isochoric process - constant volume process U = Q (dU = dQ) • cyclical process - the system returns to the initial state U = 0 • isothermal process - constant temperature U = Q - W (dU = dQ - ...
... internal energy in common processes • adiabatic process - no heat is transferred U = W (dU = -dW) • isochoric process - constant volume process U = Q (dU = dQ) • cyclical process - the system returns to the initial state U = 0 • isothermal process - constant temperature U = Q - W (dU = dQ - ...
Fluids – Lecture 11 Notes
... pressure po are still usable, but their definitions and relevant equations will be different from the low speed versions. Some flow solution techniques used in incompressible flow problems will no longer be applicable to compressible flows. In particular, the technique of superposition will no longer be ...
... pressure po are still usable, but their definitions and relevant equations will be different from the low speed versions. Some flow solution techniques used in incompressible flow problems will no longer be applicable to compressible flows. In particular, the technique of superposition will no longer be ...
Lacture №1. Chemical thermodynamics. The first law of
... Work (W) is said to be performed if the point of application of force is displaced in the direction of the force. It is equal to the distance through which the force acts. There are two main types of work electrical and mechanical. Electrical work is important ...
... Work (W) is said to be performed if the point of application of force is displaced in the direction of the force. It is equal to the distance through which the force acts. There are two main types of work electrical and mechanical. Electrical work is important ...
Lecture August 28
... All reversible processes are quasi-static but a quasi-static process is not necessarily reversible e.g. a slow leak in a tire is quasi-static but not reversible A reversible process is an idealization ➣ friction is always present Irreversible process ☛ involves a finite change in a property in a giv ...
... All reversible processes are quasi-static but a quasi-static process is not necessarily reversible e.g. a slow leak in a tire is quasi-static but not reversible A reversible process is an idealization ➣ friction is always present Irreversible process ☛ involves a finite change in a property in a giv ...
Heat and Thermodynamics
... as the energy required to create a system in the absence of changes in temperature or volume. But if the process changes the volume, as in a chemical reaction which produces a gaseous product, then work must be done to produce the change in volume. For a constant pressure process the work you must d ...
... as the energy required to create a system in the absence of changes in temperature or volume. But if the process changes the volume, as in a chemical reaction which produces a gaseous product, then work must be done to produce the change in volume. For a constant pressure process the work you must d ...
Lecture Section 10
... First Law of Thermodynamics (conservation of energy) • Change in internal energy = heat flowing in + work done on • dU = dQ + dR = TdS + dR • For thermally insulated body, dQ = TdS = 0 ...
... First Law of Thermodynamics (conservation of energy) • Change in internal energy = heat flowing in + work done on • dU = dQ + dR = TdS + dR • For thermally insulated body, dQ = TdS = 0 ...
notes02 - Colorado State University College of Engineering
... polytropic exponent was measured to be 1.175. Based on the temperatures and pressures at the inlet and exit, the specific internal energy, u, at each state is known to be 234.9 kJ/kg to 267.5 kJ/kg, respectively. Also, based on the pressure, temperature and volume at state 1, it is known that each c ...
... polytropic exponent was measured to be 1.175. Based on the temperatures and pressures at the inlet and exit, the specific internal energy, u, at each state is known to be 234.9 kJ/kg to 267.5 kJ/kg, respectively. Also, based on the pressure, temperature and volume at state 1, it is known that each c ...
1st Set of Notes - Idaho State University
... The number of degrees of freedom necessary to specify the thermodynamic state of a system is: ...............................F = C - P + 2 where C is the number of independent components P is the number of phases present As an example: Consider Argon (an ideal gas) in a vessel. How many intensive va ...
... The number of degrees of freedom necessary to specify the thermodynamic state of a system is: ...............................F = C - P + 2 where C is the number of independent components P is the number of phases present As an example: Consider Argon (an ideal gas) in a vessel. How many intensive va ...
Course Home - Haldia Institute of Technology
... ME201.5 Ability to design and develop solutions for practical engineering problems related to different cycles, refrigeration systems and system components. ME201.6 Ability to apply the knowledge of thermodynamics and fluid mechanics for coming semester subjects (eg. Food Process Engineering etc.), ...
... ME201.5 Ability to design and develop solutions for practical engineering problems related to different cycles, refrigeration systems and system components. ME201.6 Ability to apply the knowledge of thermodynamics and fluid mechanics for coming semester subjects (eg. Food Process Engineering etc.), ...