Class notes
... For example one gram of H2O at 25oC is evaporated and condensed; the condensed gram of water at 25oC will have the same internal energy as it did previously. If only pV work is done and the pressure of the system is constant ...
... For example one gram of H2O at 25oC is evaporated and condensed; the condensed gram of water at 25oC will have the same internal energy as it did previously. If only pV work is done and the pressure of the system is constant ...
3 CO 2(g)
... the same Examples: change in state (phase change), breaking a pencil, tearing paper ...
... the same Examples: change in state (phase change), breaking a pencil, tearing paper ...
HERE
... 2) One difference between mixtures and pure substances is that A) mixtures can be physically separated. B) mixtures are made of one type of atom. C) pure substances have no chemical bonds. D) pure substances can be physically separated. 3) When two or more substances combine, but each keeps its own ...
... 2) One difference between mixtures and pure substances is that A) mixtures can be physically separated. B) mixtures are made of one type of atom. C) pure substances have no chemical bonds. D) pure substances can be physically separated. 3) When two or more substances combine, but each keeps its own ...
5. Potential Energy
... connecting r1 to r2 the work done can be found by breaking up the path into small steps and adding up the work done in each step. This is the integral ˆ r2 W = F · dl r1 ...
... connecting r1 to r2 the work done can be found by breaking up the path into small steps and adding up the work done in each step. This is the integral ˆ r2 W = F · dl r1 ...
P2-Equilibrium Activity
... Not all chemical reactions reach completion where the limiting reactant is consumed completely. In fact, most chemical reactions that occur in living systems never reach completion. Rather, they produce some amount of product then appear to stop reacting in the forward direction, never fully consumi ...
... Not all chemical reactions reach completion where the limiting reactant is consumed completely. In fact, most chemical reactions that occur in living systems never reach completion. Rather, they produce some amount of product then appear to stop reacting in the forward direction, never fully consumi ...
Unit 1: Matter and Energy HW Packet
... Part 16: Match the following types of energy with the correct description. 1. __________ Chemical a. energy of motion 2. __________ Electrical b. stored energy or energy due to position 3. __________ Electromagnetic c. energy stored in chemical bonds between atoms 4. __________ Kinetic d. energy tha ...
... Part 16: Match the following types of energy with the correct description. 1. __________ Chemical a. energy of motion 2. __________ Electrical b. stored energy or energy due to position 3. __________ Electromagnetic c. energy stored in chemical bonds between atoms 4. __________ Kinetic d. energy tha ...
Chapter Summary
... Answer to Essential Question 17.7: The capacitor plates, being oppositely charged, attract one another. Positive work is required to pull the plates farther apart. The energy associated with that process is the extra energy stored by the capacitor. ...
... Answer to Essential Question 17.7: The capacitor plates, being oppositely charged, attract one another. Positive work is required to pull the plates farther apart. The energy associated with that process is the extra energy stored by the capacitor. ...
Unit 5: Electrochemistry
... 3. More about standard reduction potential and Cell Potential Cell potential, also called electromotive force, or emf, is measured in volts and sometimes referred to as the cell voltage. For Eocell, the circle denotes that this is the cell potential at standard conditions. Standard conditions ...
... 3. More about standard reduction potential and Cell Potential Cell potential, also called electromotive force, or emf, is measured in volts and sometimes referred to as the cell voltage. For Eocell, the circle denotes that this is the cell potential at standard conditions. Standard conditions ...
B - Purdue Physics
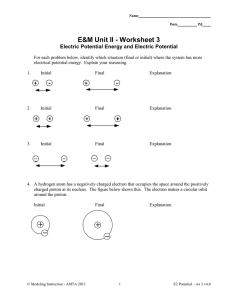
... charge density σ. Which of the following statements is (are) true? Select one of (a) – (e). 1. An electron would have a higher potential energy at point A than at point B 2. A proton would have a higher potential energy at point A than at point B 3. The electric potential is lower at A than at B 4. ...
... charge density σ. Which of the following statements is (are) true? Select one of (a) – (e). 1. An electron would have a higher potential energy at point A than at point B 2. A proton would have a higher potential energy at point A than at point B 3. The electric potential is lower at A than at B 4. ...