Free energy and Equilibrium
... such cases, in the initial state, only the reactants are present but as the reaction proceeds, the concentration of reactants decreases and that of products increases. Finally a stage is reached when no further change in concentration of the reactants and products is observed and a state of chemical ...
... such cases, in the initial state, only the reactants are present but as the reaction proceeds, the concentration of reactants decreases and that of products increases. Finally a stage is reached when no further change in concentration of the reactants and products is observed and a state of chemical ...
17.5 Electric Potential due to Point Charges
... The force F2 must have the same magnitude as F1. This is due to the fact that the form of Coulomb’s Law is totally symmetric with respect to the two charges involved. The ...
... The force F2 must have the same magnitude as F1. This is due to the fact that the form of Coulomb’s Law is totally symmetric with respect to the two charges involved. The ...
electrical potential
... For things like batteries, we specify the potential difference between the contacts (poles) on the batery. So a "D-cell" has a rating of 1.5 volts which means that every 1C of charge (electrons) that moves from the negative side of the cell to the positive side will do 1.5 Joules work. 1. Potential ...
... For things like batteries, we specify the potential difference between the contacts (poles) on the batery. So a "D-cell" has a rating of 1.5 volts which means that every 1C of charge (electrons) that moves from the negative side of the cell to the positive side will do 1.5 Joules work. 1. Potential ...
How many significant figures are there in each of these
... - Dalton's theory sets LIMITS on what can be done with chemistry. For example: Chemistry can't convert lead (an element) into gold (another element). Sorry, alchemists! You can't have a compound form in a chemical reaction that contains an element that was not in your starting materials. You can onl ...
... - Dalton's theory sets LIMITS on what can be done with chemistry. For example: Chemistry can't convert lead (an element) into gold (another element). Sorry, alchemists! You can't have a compound form in a chemical reaction that contains an element that was not in your starting materials. You can onl ...
Thermochemistry
... Hess’s law of Heat summation: For a chemical equation that can be written as the sum of two or more steps, the enthalpy change for the overall reaction equals the sum of the enthalpy changes for the individual steps ‘Faulty water heater’ example: Find ΔHrxn for the following: ...
... Hess’s law of Heat summation: For a chemical equation that can be written as the sum of two or more steps, the enthalpy change for the overall reaction equals the sum of the enthalpy changes for the individual steps ‘Faulty water heater’ example: Find ΔHrxn for the following: ...
chemical reaction
... elements is represented in an equation by its molecular formula. Other elements in the elemental state are usually represented simply by their atomic symbols. For Example carbon is represented as C. The symbols are not given any subscripts because the elements do not form definite molecular structur ...
... elements is represented in an equation by its molecular formula. Other elements in the elemental state are usually represented simply by their atomic symbols. For Example carbon is represented as C. The symbols are not given any subscripts because the elements do not form definite molecular structur ...
Physical and Chemical Properties worksheet
... 3. To observe a chemical property, a chemical change must occur (new substances produced). To see if a piece of paper has the chemical property of combustability (will burn in oxygen), you must actually try to burn it, producing carbon (ash), water vapor, carbon dioxide – the material is no longer p ...
... 3. To observe a chemical property, a chemical change must occur (new substances produced). To see if a piece of paper has the chemical property of combustability (will burn in oxygen), you must actually try to burn it, producing carbon (ash), water vapor, carbon dioxide – the material is no longer p ...
Ue and Voltage
... If r, the distance between the two charges, increases the force decreases If r, the distance between the two charges, decreases the force increases Because r appears as 1/r2 the dependence on r is ...
... If r, the distance between the two charges, increases the force decreases If r, the distance between the two charges, decreases the force increases Because r appears as 1/r2 the dependence on r is ...
r - Personal.psu.edu
... Negative charge moves in opposite direction to electric field Positive charge moves in the same direction as an electric field ...
... Negative charge moves in opposite direction to electric field Positive charge moves in the same direction as an electric field ...
Glossary
... Dynamics − the branch of mechanics dealing with the motion of physical systems. Equilibrium − stable, at minimum energy with no apparent motion. Equipartition theorem − consequence of the kinetic molecular theory that molecules have average kinetic energy proportional to the number of different type ...
... Dynamics − the branch of mechanics dealing with the motion of physical systems. Equilibrium − stable, at minimum energy with no apparent motion. Equipartition theorem − consequence of the kinetic molecular theory that molecules have average kinetic energy proportional to the number of different type ...
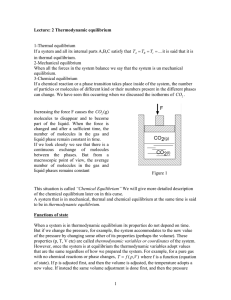
1 Lecture: 2 Thermodynamic equilibrium 1
... A system that is in mechanical, thermal and chemical equilibrium at the same time is said to be in thermodynamic equilibrium. Functions of state When a system is in thermodynamic equilibrium its properties do not depend on time. But if we change the pressure, for example, the system accommodates to ...
... A system that is in mechanical, thermal and chemical equilibrium at the same time is said to be in thermodynamic equilibrium. Functions of state When a system is in thermodynamic equilibrium its properties do not depend on time. But if we change the pressure, for example, the system accommodates to ...
MS. Structure and Properties of Matter Associated Units: • Chemical
... Describe temperature in terms of proportions and differentiate temperature and heat. Measure and interpret the heat and temperature relationship. Plan an investigation to determine the relationships among the energy transferred, the type of matter, the mass, and the change in the average kinetic e ...
... Describe temperature in terms of proportions and differentiate temperature and heat. Measure and interpret the heat and temperature relationship. Plan an investigation to determine the relationships among the energy transferred, the type of matter, the mass, and the change in the average kinetic e ...